Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with a higher prevalence of insulin resistance (IR). Dysregulation of adipokines driven by low-level systemic inflammation plays a central role in the development of IR. Adiponectin (Adp) is an adipokine exerting anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing activity. However suppression of Adp secretion by IL-6 was shown in previous studies, data on associations of Adp with serum lipid profiles and disease activity in patients with RA treated with biologic DMARDs are controversial. Here we present the changes in serum Adp levels in patients with active RA during treatment with IL-6 inhibitor olokizumab (OKZ).
Methods: Data were extracted from 3 double-blind RCTs (NCT02760368; NCT02760407; NCT02760433). Patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous (SC) injections of OKZ 64 mg every 2 weeks (q2w), OKZ 64 mg once every 4 weeks (q4w), or placebo for 24 weeks, all on background of МТX.
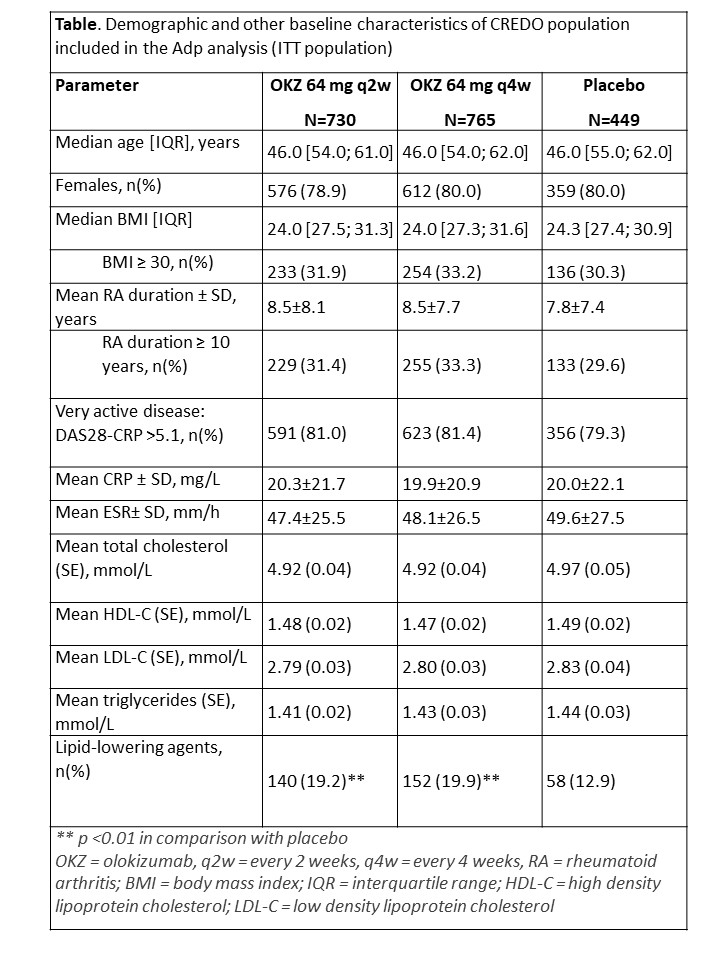
Demographics were assessed at baseline. Body weight and height were assessed at baseline, week 4, 8, 12, 18, and 24. Clinical and laboratory data were collected at baseline, week 4, 12, and 24. Associations with changes in Adp were evaluated by partial correlations adjusted for gender, age, BMI, and lipid-modifying therapy for lipid profiles or for gender, age; BMI; Adp; changes in BMI and cholesterol for disease activity.
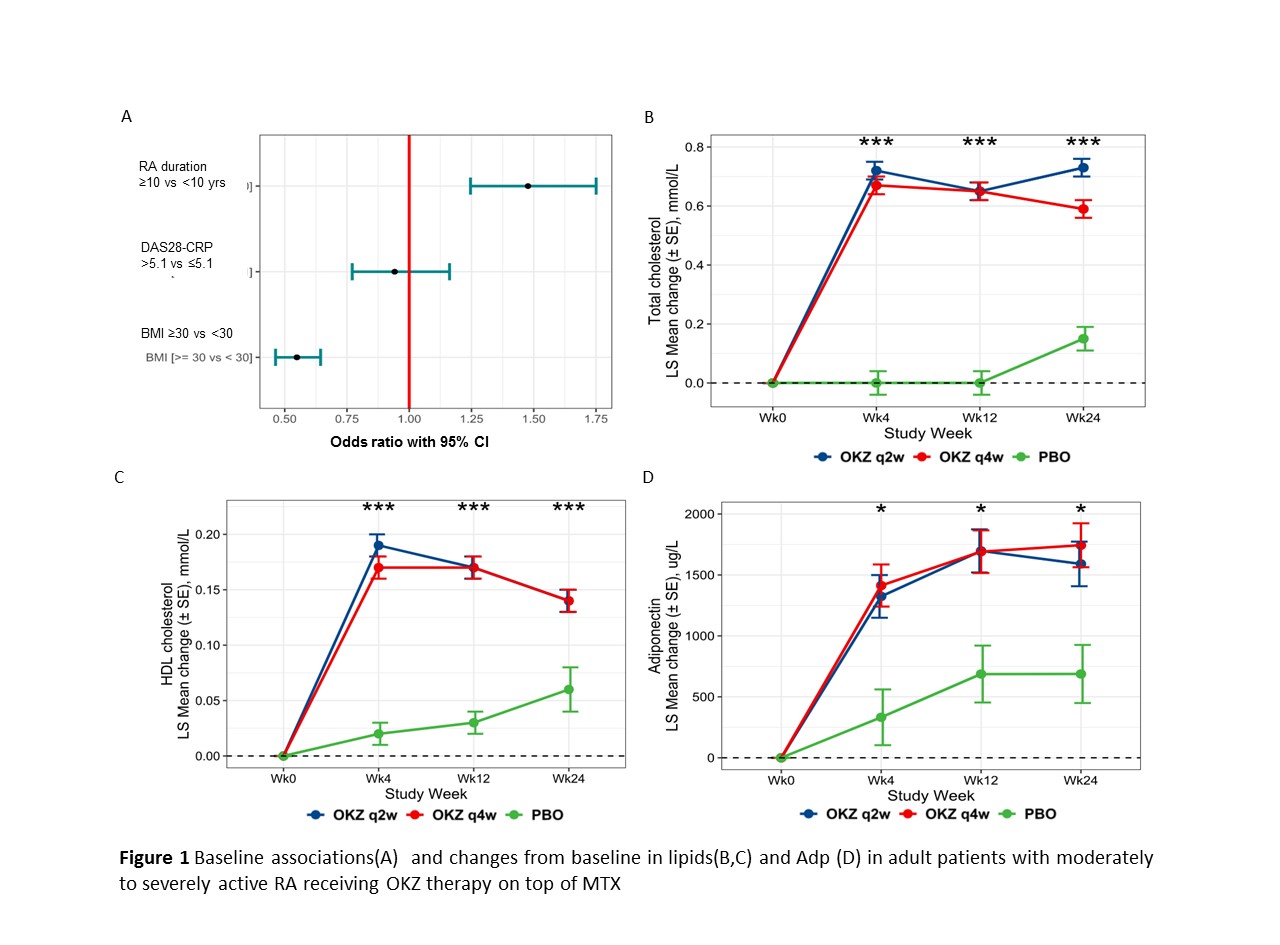
Results: Serum Adp measurements were available for 1944 pts (730/765/499 pts in OKZ q2w, OKZ q4w, and placebo groups). Baseline characteristics were equally distributed across treatment groups. In total 18% of patients received lipid modifying agents, with the percentage slightly higher in OKZ groups compared to placebo. Pre-dose Adp levels were positively associated with longer disease duration, and inversely associated with BMI at baseline, however no association was observed with disease activity (Figure 1A).
Significantly elevated levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL- and LDL-cholesterol were observed at all post-dose timepoints (figure 1B, 1C). After 24 weeks of treatment, Adp increased significantly by 1590.46 (182.90) ug/L, 1743.61 (180.14) ug/L, and 687.58 (238.33) in OKZ q2w, OKZ q4w, and placebo groups. Significant difference with placebo was observed in OKZ q4w group only (difference (SE) 1056.03 (299.37) µg/L, p = 0.02).
Adp changes were positively correlated with changes in total and HDL-cholesterol (r=0.134 and r=0.281, p< 0.001), a very weak however significant correlation was seen with changes in LDL-cholesterol (r=0.067, p=0.018) and probability to reach low disease activity (DAS28-CRP < 3.2) at week 24 (r=0.061, p=0.001), but not with post-baseline changes in triglycerides or BMI. Adp levels were inversely correlated with DAS28-ESR and ESR at week 24 (r=-0.061, p=0.048, r=-0.082, p=0.004).
Conclusion: Significant elevation of serum Adp was observed after 24 weeks of OKZ treatment in patients with RA. Adp changes positively correlated with elevations of total and HDL-cholesterol, independently of post-treatment changes in BMI. Increased Adp may have protective insulin-sensitizing effects and may contribute to decreasing the risk of CV complications in RA patients.
OKZ = olokizumab, q2w = every 2 weeks, q4w = every 4 weeks, PBO = placebo; RA = rheumatoid arthritis; BMI = body mass index; IQR = interquartile range; MTX = methotrexate; LS Mean = least square mean; SE = standard error
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zonova E, Abbate A, Feist E, Yakushin S, Lemak M, Egorova A, Bukhanova D, Grishin S, Kuzkina S, Samsonov M, NASONOV E. Elevated Serum Adiponectin Levels During Olokizumab Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Correlate with High-density Lipoprotein Lipid Profile Independently of Body Mass Index: Results from the Double-blind, Randomized Controlled Phase III Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-serum-adiponectin-levels-during-olokizumab-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-correlate-with-high-density-lipoprotein-lipid-profile-independently-of-body-mass-index-results-from/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-serum-adiponectin-levels-during-olokizumab-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-correlate-with-high-density-lipoprotein-lipid-profile-independently-of-body-mass-index-results-from/