Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: This clinical study aimed to investigate the relationship between affected joints and the quality of life (QOL) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Japan.
Methods: We analyzed data from 15,553 RA patients registered in the NinJa database in 2020 to investigate the relationship between affected joints and the quality of life (QOL). QOL was assessed using the EuroQol 5-Dimensions (EQ-5D) questionnaire. Patients for whom EQ-5D data were acquired were included in this study. The affected joints, based on a 68-joint count, were categorized into four regions: upper/large, upper/small, lower/large, and lower/small. The presence or absence of swelling or tenderness in the joints within each region was evaluated as a binary variable. We performed multivariable regression analysis with EQ-5D scores as the dependent variable. The independent variables included demographic factors (age, sex), disease duration, pain visual analogue scale (pain VAS), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, positivity of rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA), scores from the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS-A and HADS-D), modified health assessment questionnaire (mHAQ), Steinbrocker’s stage, and the presence/absence of swelling or tenderness in the affected joints within each region.
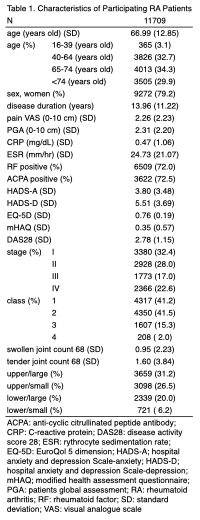
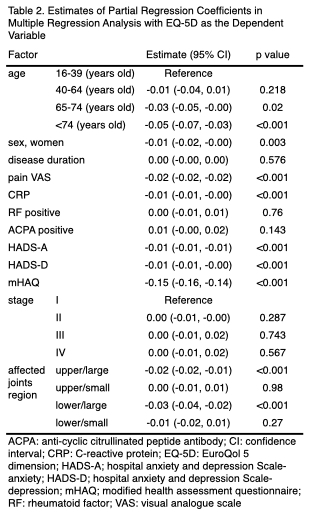
Results: The study included 11,709 RA patients, with a mean age of 67.0 years (SD = 12.9), and 79.2% were women. The mean disease duration was 14.0 years (SD = 11.2). (Table 1) After adjusting for covariates, the activity of upper/large joints region (β = -0.02, 95% CI: -0.02 to -0.01, p < 0.01), lower/large (β = -0.03, 95% CI: -0.04 to -0.02, p < 0.01), 65 to 74 years old (β = -0.03, 95% CI: -0.05 to -0.00, p = 0.02), 75 years old or older (β = -0.05, 95% CI: -0.07 to -0.03, p < 0.01), women sex (β = -0.01, 95% CI: -0.02 to -0.00, p < 0.01), pain VAS (β = -0.02, 95% CI: -0.02 to -0.02), CRP (β = -0.01, 95% CI: -0.01 to -0.00, p < 0.01), HADS-A (β = -0.01, 95% CI: -0.01 to -0.01, p < 0.01), HADS-D (β = -0.01, 95% CI: -0.01 to -0.00, p < 0.01), and mHAQ (β = -0.15, 95% CI: -0.16 to -0.14, p < 0.01) were found to be significantly associated with lower EQ-5D scores, indicating worse QOL. (Table 2)
Conclusion: In this study, we found significant associations between various factors and QOL of RA patients in Japan. Specifically, among the demographic factors, being aged 65 or older and female, along with higher scores on pain VAS, elevated CRP levels, increased scores on HADS-A and HADS-D, and higher mHAQ scores were all associated with decreased EQ-5D scores, indicating lower QOL. Furthermore, we observed that the presence of swelling or tenderness in the affected joints within both the upper and lower extremities, particularly in the large joints, was significantly associated with lower EQ-5D scores. By considering these factors and the specific joint distribution, healthcare professionals can tailor interventions and treatment strategies to improve the QOL of RA patients, focusing on mitigating pain, reducing inflammation, and addressing functional limitations associated with affected joints.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tokunaga K, Nishino T, Oshikawa H, Matsui T, Tohma S. Relationship Between Quality of Life and the Region of the Affected Joints in Japanese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-sectional Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-quality-of-life-and-the-region-of-the-affected-joints-in-japanese-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-quality-of-life-and-the-region-of-the-affected-joints-in-japanese-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study/