Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Complete peripheral B cell depletion has been considered as a relevant indicator of short-term response to rituximab (RTX) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The purpose of our study was to determine whether sustained complete B cell (BC) depletion is associated with a better clinical response in RA patients long-term treated with RTX.
Methods: Retrospective routine care study conducted in the Rheumatology department of Cochin hospital. We included consecutive patients fulfilling the ACR/EULAR 2010 classification criteria for RA hospitalized in 2021 for a new RTX infusion. All recruited patients had received at least 3 prior RTX infusions and had disease activity assessment (DAS28 and DAS28-CRP) and CD19 counts (Aquios, Beckman Coulter) available during each of the 4 last infusion visits. The primary endpoint was the evaluation of the disease activity (mean DAS28 and DAS28-CRP) calculated the day of the last 4 infusion visits, according to the persistence of complete BC depletion (mean CD19 counts of the last 4 visits < 18/mL) or incomplete BC depletion (mean CD19 counts of the last 4 visits ≥18/mL). Secondary endpoints were the frequency of end-of-dose effect and patient self-reported RA flares at each infusion visit, the course of pain/fatigue VAS, CRP and gammaglobulin levels
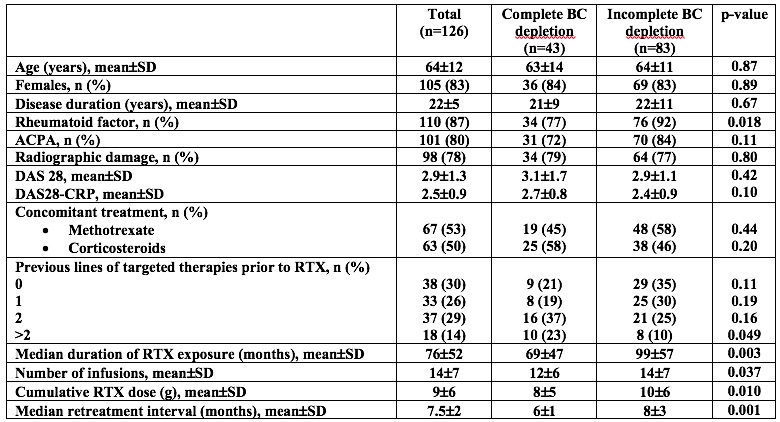
Results: We included 126 patients with a mean age of 64±12 years and a mean disease duration of 22± 5 years. Only 43 patients (34%) had maintained complete BC depletion during the last 4 infusions (mean CD19 counts 13±4/mL) (Figure 1A-B). Patients with incomplete BC depletion (n=83, mean CD19 counts: 77±73/mL, p< 0.001) did not differ from those who maintained complete BC depletion in terms of age, gender, disease duration, structural damages and concomitant treatment. Patients with incomplete BC depletion had received RTX for a longer period (99±57 months vs. 69±47 months, p=0.003), with significantly higher number of infusions (14±7 vs. 12±6 infusions, p=0.037) and increased cumulative dose (10±6 g vs. 8±5 g, p=0.10) compared to patients with sustained complete BC depletion. On the other hand, their interval between 2 infusions was significantly longer (8±3 months vs. 6±1 months, p< 0.001). The course of DAS28 and DAS28-CRP during the last 4 infusions was not different between the 2 groups (Figures 1C-D). The mean DAS28 and DAS28-CRP calculated at the time of last 4 infusion visits did not differ between patients with incomplete or sustained complete BC depletion (DAS28: 2.71±1.06 vs. 3.01±1.10, p=0.33 and DAS28-CRP: 2.53±0.88 vs. 2.88±0.84, p=0.095). Secondary outcomes were similar between the 2 groups (Figures 1E-H).
Conclusion: While it is associated with a better response to RTX at the start of treatment, the persistence of complete BC depletion is not associated with better efficacy of RTX in RA patients receiving this treatment over the long term. There is a limited benefit of monitoring CD19 in RA patients long term treated with RTX and having achieved low disease activity/remission. During the COVID-19 pandemic, this data is all the more important as the humoral anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response is preferentially obtained in patients with incomplete BC depletion.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghossan R, AL TABAA O, Combier A, STEELANDT A, THOMAS M, Fogel O, MICELI C, Molto A, Avouac J. Should Complete B-cell Depletion Be Maintained in Patients Treated Long-term with Rituximab for Rheumatoid Arthritis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/should-complete-b-cell-depletion-be-maintained-in-patients-treated-long-term-with-rituximab-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/should-complete-b-cell-depletion-be-maintained-in-patients-treated-long-term-with-rituximab-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/