Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is a predictor of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. In patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, AIP is correlated with increased cardiovascular risk measured by Framingham’s risk score. The correlation between AIP and calculated cardiovascular risk has not been studied in PsA-patients. To evaluate the correlation between AIP and six cardiovascular risk scores in patients with PsA.
Methods: Cross-sectional study that included PsA-patients aged 40 to 75 years who fulfilled the 2006 Classification Criteria for PsA. Patients with previous cardiovascular disease were excluded. AIP was defined by log (TG/HDL-C) mg/dL, and levels ≥0.21 were considered as high AIP. Cardiovascular disease risk was evaluated using 6 algorithms: ACC/AHA 2013, FRS-Lipids, FRS-BMI, RRS, QRISK3, and SCORE2. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was performed to evaluate the distribution of variables. The correlation between the AIP and cardiovascular risk algorithms was assessed by Spearman’s correlation coefficient. A value of p≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
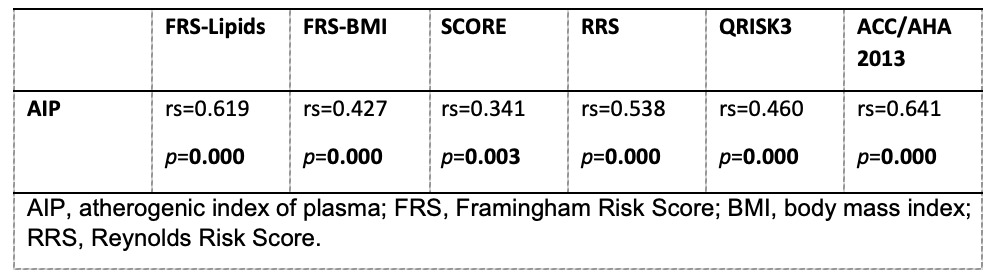
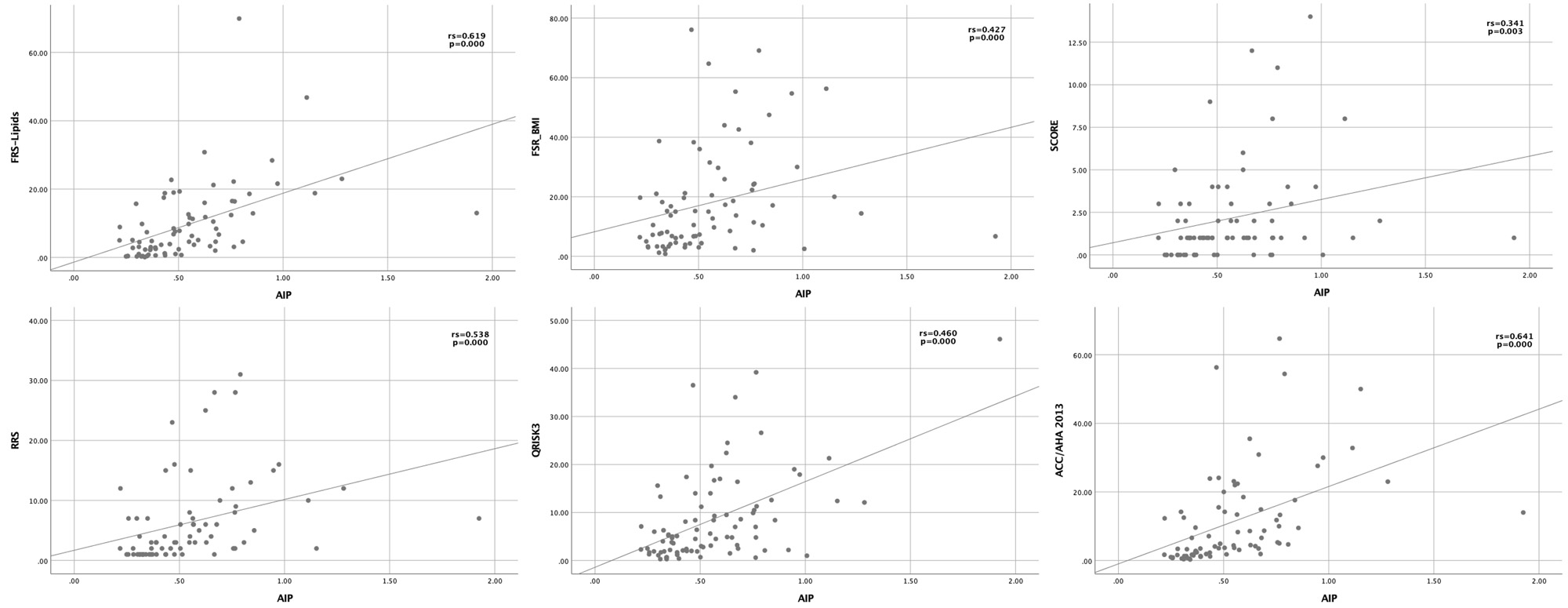
Results: A total of 94 patients with PsA were included, mostly women (n=52, 55.3%), the mean age was 53 ± 11.2, the disease duration of PsA was 5.0 (2.0-10.0) years, and the median AIP of all patients included was 0.49 (0.35-0.67). The median of each algorithm was: FRS-BMI 15.0 (6.7-27.8), FRS-Lipids 7.4 (3.0-16.4), SCORE 1.0 (1.0-3.0), QRISK3 5.6 (2.4-12.5), RRS 3 (2.0-7.5) and ACC/AHA 2013 5.3 (2.1-14.5). The most prevalent cardiovascular risk factor was dyslipidemia (n= 41, 43.6%). All cardiovascular risk algorithms presented a high positive correlation between AIP levels and cardiovascular risk. The calculator with the highest correlation was ACC/AHA 2013 (rs=0.641, p=0.000). (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Conclusion: In patients with PsA, higher values of AIP are associated with increased cardiovascular risk irrespective of the algorithm used. High AIP values could identify patients who would benefit from a non-invasive evaluation for subclinical atherosclerosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez-Gonzalez V, Colunga I, Galarza-Delgado D, Azpiri-López J, Arvizu-Rivera R, Cardenas-De la Garza J, Beltran V, Arias Peralta A. Higher Values of Atherogenic Index of Plasma Are Correlated with Increased Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-values-of-atherogenic-index-of-plasma-are-correlated-with-increased-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-values-of-atherogenic-index-of-plasma-are-correlated-with-increased-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/