Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic immune-mediated fibroinflammatory disease that can affect nearly every organ system. Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is among the most common manifestations of IgG4-RD, but data are limited on its disease characteristics in the broader context of systemic IgG4-RD. In addition, the prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) and endocrine pancreatic insufficiency (diabetes mellitus [DM]) in IgG4-related AIP is not well established. We aimed to evaluate disease features and burden of damage due to AIP in a large cohort of patients with IgG4-RD.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study using our large single-center IgG4-RD cohort. Subjects were included if they met ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD and were excluded if there were missing data or if AIP presence was unclear. Demographics and overall disease characteristics were compared between subjects with and without AIP using Chi-square and unpaired T tests for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. For subjects with AIP, we extracted details regarding clinical presentation, laboratory results, and imaging findings representing both active disease and pancreatic damage. For subjects without known EPI and no documented fecal elastase measurements, letters were sent encouraging them to have these performed.
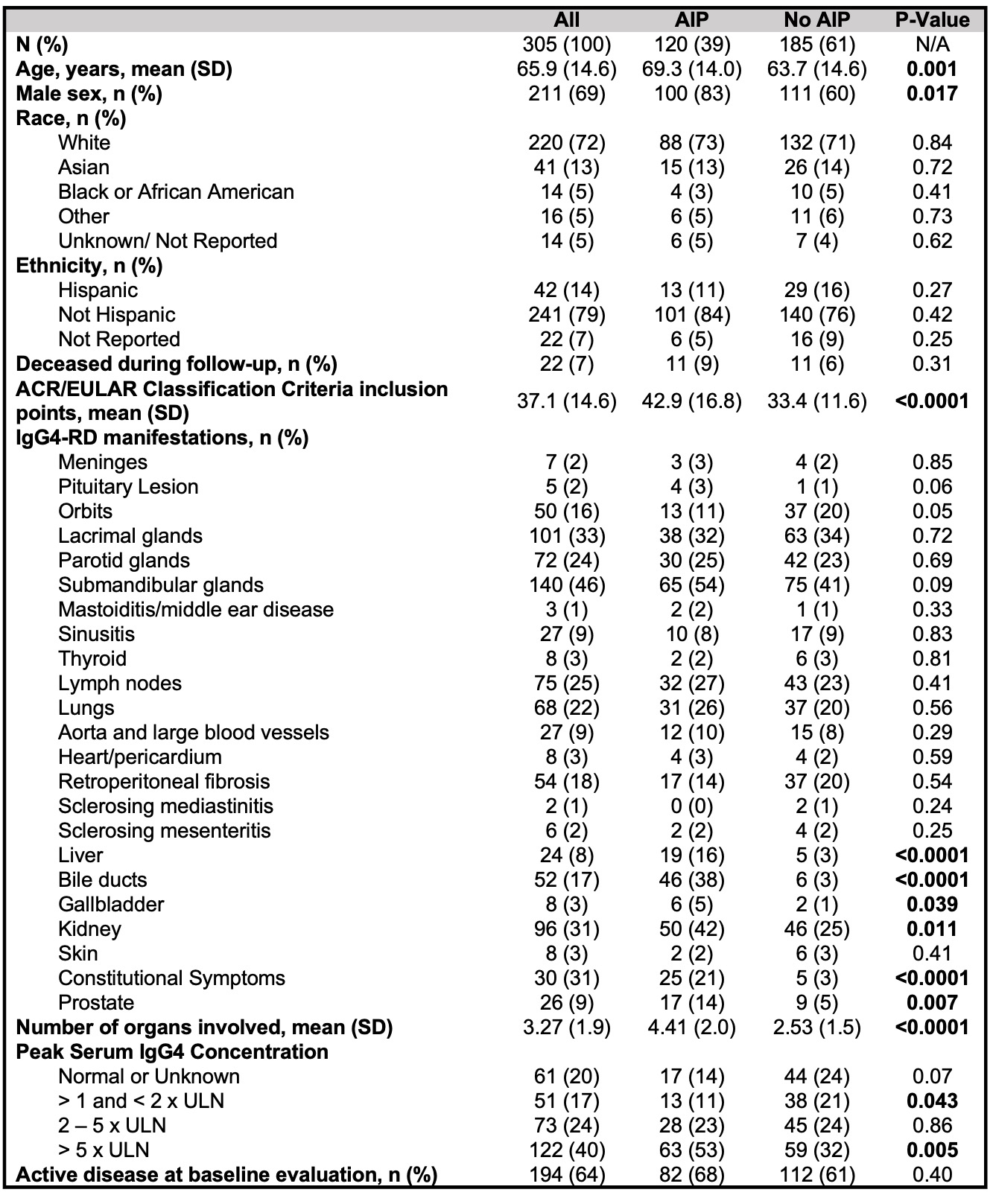
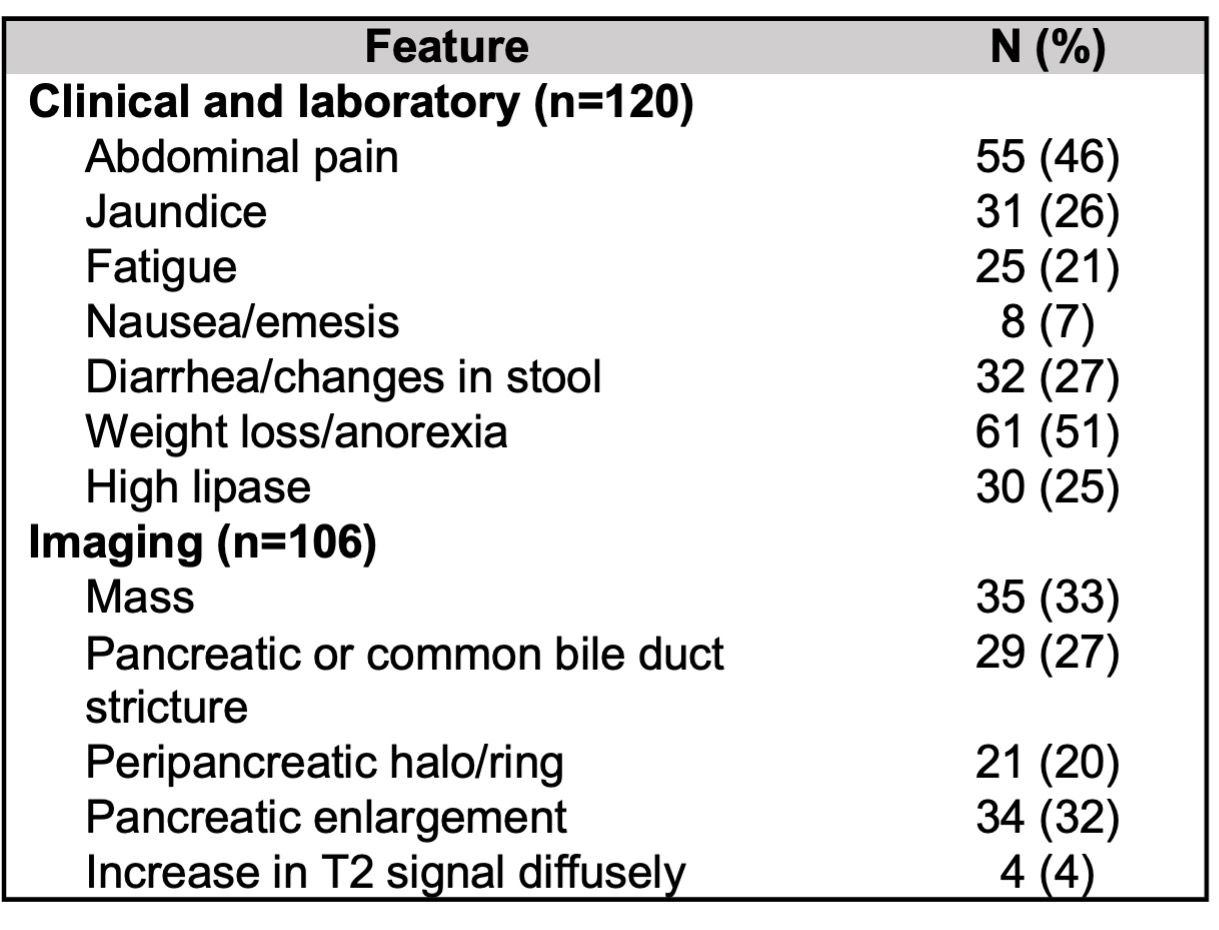
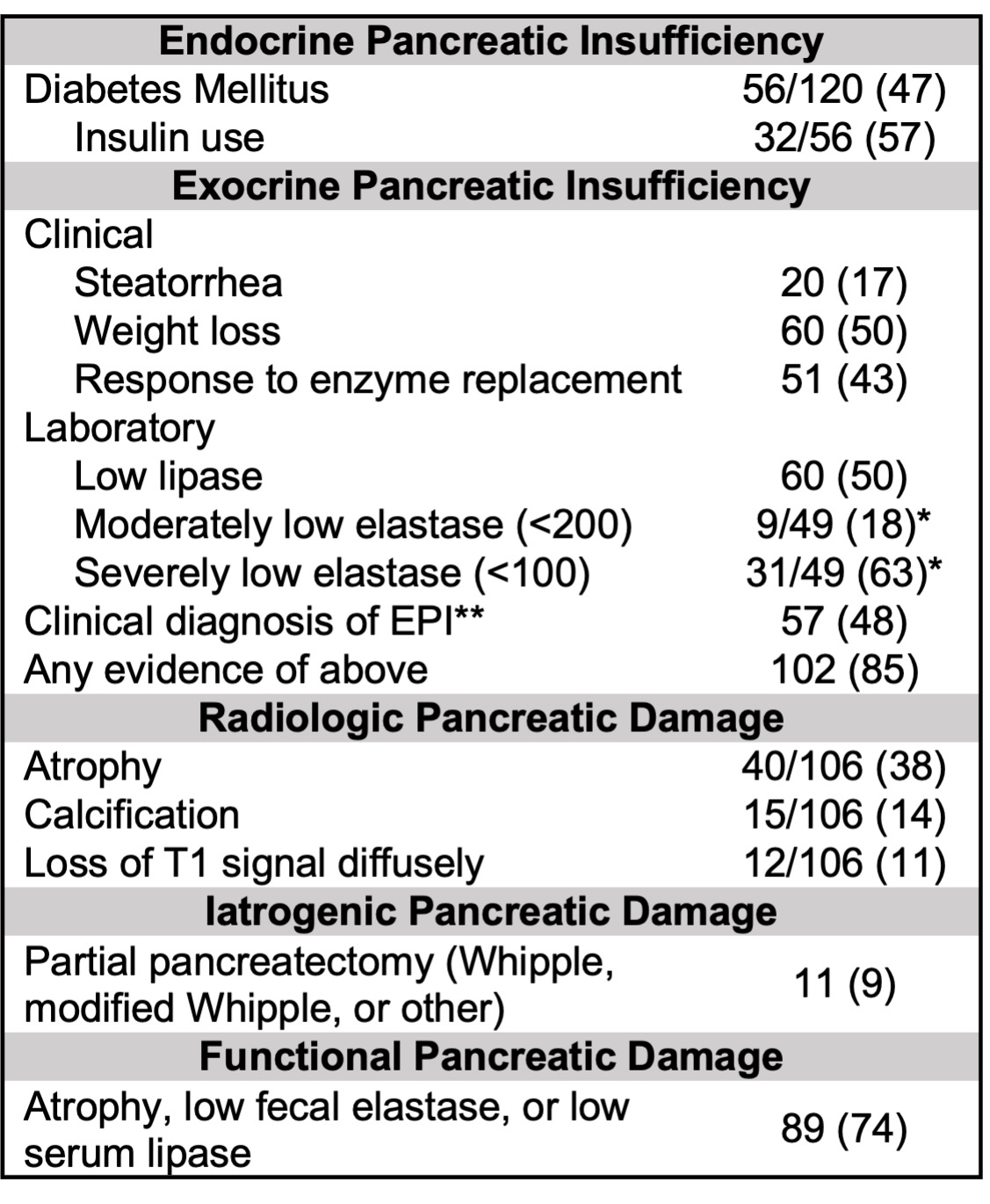
Results: Of 305 eligible subjects, 120 (39%) had pancreatic involvement. Demographics and disease features in patients with and without AIP are shown in Table 1. Subjects with AIP were significantly older and more commonly male than those without AIP. Subjects with AIP had significantly more organs involved and higher ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria inclusion points, and they were significantly more likely to have had highly-elevated serum IgG4 concentrations ( > 5 x upper limit of normal) than subjects without AIP. Among subjects with AIP, the most common symptoms of active AIP were weight loss or anorexia (51%), abdominal pain (46%), diarrhea or changes in stool (27%), and jaundice (26%); 25% had lipase elevations, and 33% had mass-forming AIP (Table 2). Damage due to AIP is summarized in Table 3. 47% had DM, 57% of which required insulin. Clinical EPI as defined using stringent criteria was present in 48%, while 85% had any evidence of EPI. Of 49 elastase measurements obtained, 40 (82%) were low. Functional pancreatic damage was present in 74%, defined as low serum lipase, low fecal elastase, or pancreatic atrophy. Eleven (9%) patients had partial pancreatectomies in their diagnostic workups.
Conclusion: Patients with IgG4-RD with AIP are more commonly male and have more extensive and severe disease than those without AIP. Classic acute pancreatitis, manifesting as abdominal pain and high lipase, occurs in a minority of patients with IgG4-related AIP. Features concerning for malignancy, including weight loss, painless jaundice, and pancreatic masses, are common, and many patients have Whipple procedures as a result. Endocrine and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency are highly prevalent. The burden of clinical and functional pancreatic damage in IgG4-RD is striking and emphasizes the need for early recognition of the disease and prompt initiation of treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz G, Harvey L, Hernandez-Barco Y, Fernandes A, McMahon G, Jha I, Wallace Z, Perugino C, Stone J. Disease Characteristics and Pancreatic Damage in IgG4-Related Disease with Pancreatic Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-characteristics-and-pancreatic-damage-in-igg4-related-disease-with-pancreatic-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-characteristics-and-pancreatic-damage-in-igg4-related-disease-with-pancreatic-involvement/