Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Abnormal cytokine regulation is the fundamental pathology of immune-mediated diseases (IMDs). Clinical transcriptome data has a potential to monitor real-time cytokine pathway activities of each IMD patient and guide treatment choices. However, multiple confounders including immunosuppressive therapies and experimental batch effects obscures the biologically relevant signals underlying clinical transcriptome data. The aim of this study is i) to establish an analytical strategy to accurately quantify cytokine pathway activities excluding the confounder effects and ii) elucidate the similarity and dissimilarity across 10 immune-related diseases by applying our strategy to the clinical transcriptome database.
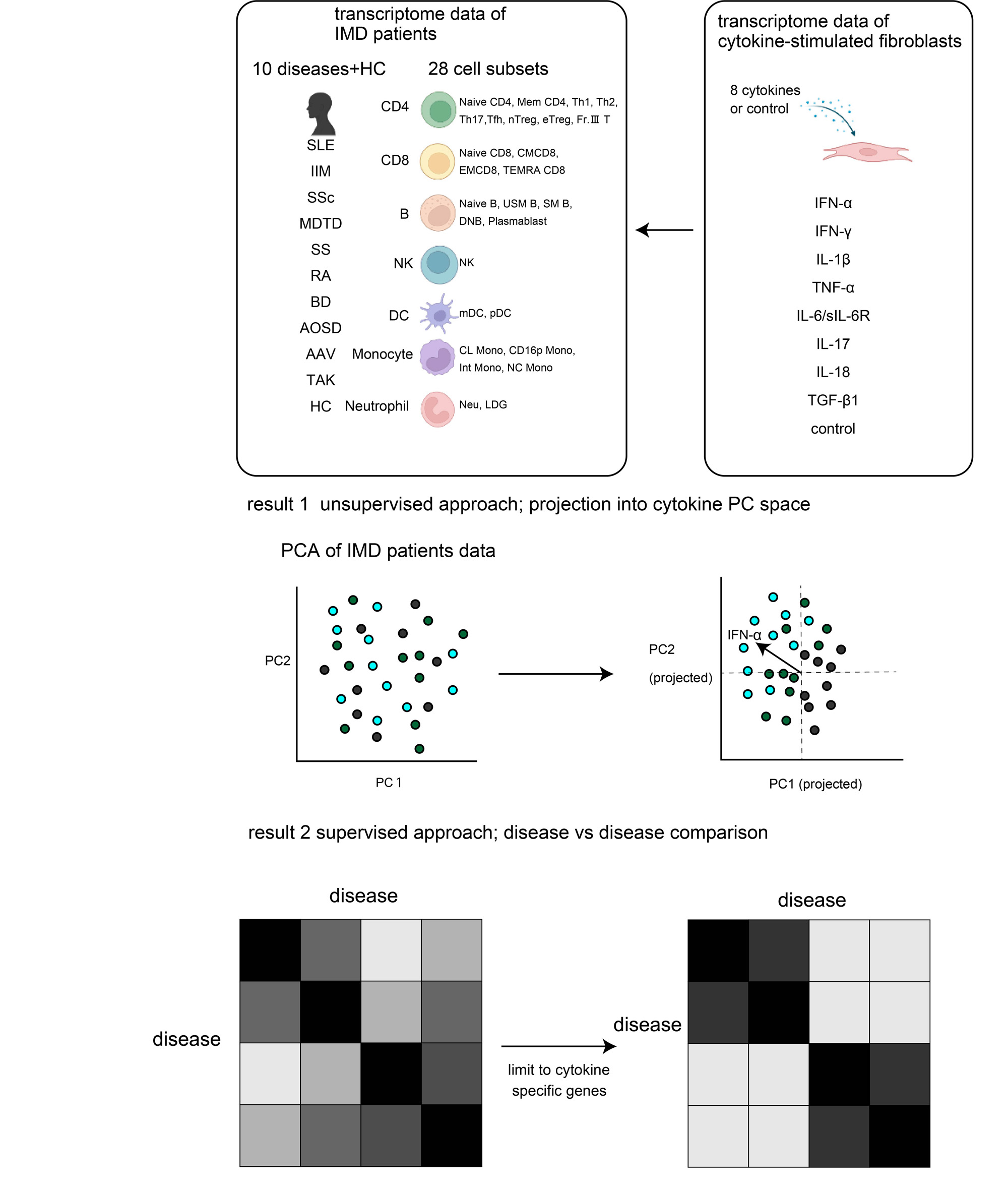
Methods: We utilized the ImmuNexUT database, the largest open-access database of clinical transcriptome data with 28 FACS-sorted immune cell subsets obtained from 10 IMDs: SLE, idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM), SSc, MCTD, SS, RA, Behcet’s disease (BD), adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD), ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), and Takayasu arteritis (TAK) (Figure 1). Using the combination of supervised and unsupervised approaches, we learned the cytokine-induced transcriptome alterations from a large-scale in-vitro cultured fibroblast experiments stimulated by eight cytokines: IFN-α, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6/sIL-6R, IL-17, IL-18 and TGF-β1 (n=506 samples in total). We then transferred the knowledge to the clinical transcriptome data. To mitigate the different statistical power due to unbalanced sample sizes across 10 IMDs, we applied the multivariate adaptive shrinkage approach.
Results: We first took an unsupervised approach and conducted the principal component analysis (PCA) of the cytokine-stimulated fibroblast datasets to learn the transcriptome axes reflecting multiple cytokine signatures. We then projected clinical transcriptome data onto the PC space and confirmed that IMDs were separated by cytokine signatures, with a pronounced shift in SLE. We next took a supervised approach and detected the IMD- and cytokine-related transcriptome signatures from both datasets. By jointly analyzing both signatures simultaneously, we successfully characterized the transcriptome similarity and dissimilarity across 10 immune-related diseases from a viewpoint of cytokine-related signatures. The cytokine signatures grouped IMDs into two clusters: the autoimmune diseases (MCTD, SLE, IIM, SSc, RA and SS) and autoinflammatory diseases (BD, AAV, and TAK).
Conclusion: Our new analytical strategy successfully detected cytokine-related transcriptome characteristics of 10 IMDs, which would be a foundation to elucidate the IMD pathology.
We analyzed transcriptome data of 10 immune-related diseases using the knowledge obtained from transcriptome data of cytokine stimulated fibroblasts. We utilized both unsupervised and supervised approaches.
Disclosures: H. Takahashi: None; H. Hatano: None; M. Nakano: None; H. Tsuchiya: None; M. Ota: Chugai, 12, MO belonged to the Social Cooperation Program, Department of functional genomics and immunological diseases, supported by Chugai Pharmaceu; T. Okamura: Chugai Pharmaceutical., 12, belong to the Social Cooperation Program, Department of Functional Genomics and Immunological Diseases, supported by Chugai Pharmaceutical.; K. Fujio: AbbVie/Abbott, 6, Asahi Kasei, 5, 6, Astellas, 6, AstraZeneca, 6, Ayumi, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, 6, Chugai Pharmaceutical., 5, 6, Daiichi-Sankyo, 6, Eisai, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, Janssen, 6, Novartis, 6, Ono, 6, Pfizer, 6, Sanofi, 6, Tanabe Mitsubishi, 5, 6, Tsumura, 5; K. Ishigaki: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Takahashi H, Hatano H, Nakano M, Tsuchiya H, Ota M, Okamura T, Fujio K, Ishigaki K. Cytokine-induced Transcriptome Modification Elucidates the Similarity and Dissimilarity Across 10 Immune-related Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-induced-transcriptome-modification-elucidates-the-similarity-and-dissimilarity-across-10-immune-related-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-induced-transcriptome-modification-elucidates-the-similarity-and-dissimilarity-across-10-immune-related-diseases/