Session Information
Date: Friday, March 31, 2023
Title: Poster Breakout 5 - Autoinflammatory/Vasculitis: STAT3, NLRP3, KD and MIS-C
Session Type: Breakout Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-5:00PM
Background/Purpose: Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a hyperinflammatory illness associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and has overlapping features with Kawasaki Disease (KD). The objective was to describe fulfillment of complete and incomplete KD criteria among patients with MIS-C, and to compare features at admission and clinical outcomes among patients with MIS-C who did or did not meet KD criteria.
Methods: Single pediatric hospital retrospective chart review of all patients who met U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) MIS-C criteria and received treatment between April 2020 to February 2021.
Results: 79 patients with MIS-C were identified. 55/79 patients (70%) met criteria for KD at admission (n=26) or later in the hospitalization (n=29). Of those, 28/55 (51%) met criteria for complete KD and 27/55 (49%) for incomplete KD. Patients meeting KD criteria at admission presented later (mean day 7 vs. 5, P< 0.001) and were more likely to have rash, mucous membrane changes, conjunctivitis, extremity changes, and hypoalbuminemia at admission compared to those who did not (P=0.01, 0.005, < 0.001, 0.008, and < 0.001, respectively). There were no differences in coronary artery lesions (CAL), left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, respiratory failure, or needs for intensive care, vasoactive medications, or second- or third-line MIS-C therapy. Patients who did not meet KD criteria at admission but did later in the hospitalization were more likely to have rash, hypoalbuminemia, and elevated alanine transaminase at admission (P=0.05, 0.007, and < 0.001, respectively), respiratory failure (P=0.02) and had greater need for intensive care, vasoactive medications, and second- and third-line therapy than patients never meeting KD criteria (P< 0.001, < 0.001, 0.001, and 0.005, respectively). There were no differences in CAL or LV dysfunction.
Conclusion: Most patients with MIS-C met criteria for KD by time of hospital discharge. Fulfillment of KD criteria at admission was not associated with changes in MIS-C patient outcomes, though fulfillment of KD criteria later during hospitalization was associated with greater need for intensive care, vasoactive medications, and second- and third-line MIS-C therapy. KD criteria fulfillment in patients with MIS-C at any timepoint was not associated with increased risk of CAL or LV dysfunction. Further investigation is needed to understand how pathophysiology of MIS-C compares to KD and if presence of KD features can help predict outcomes in MIS-C.
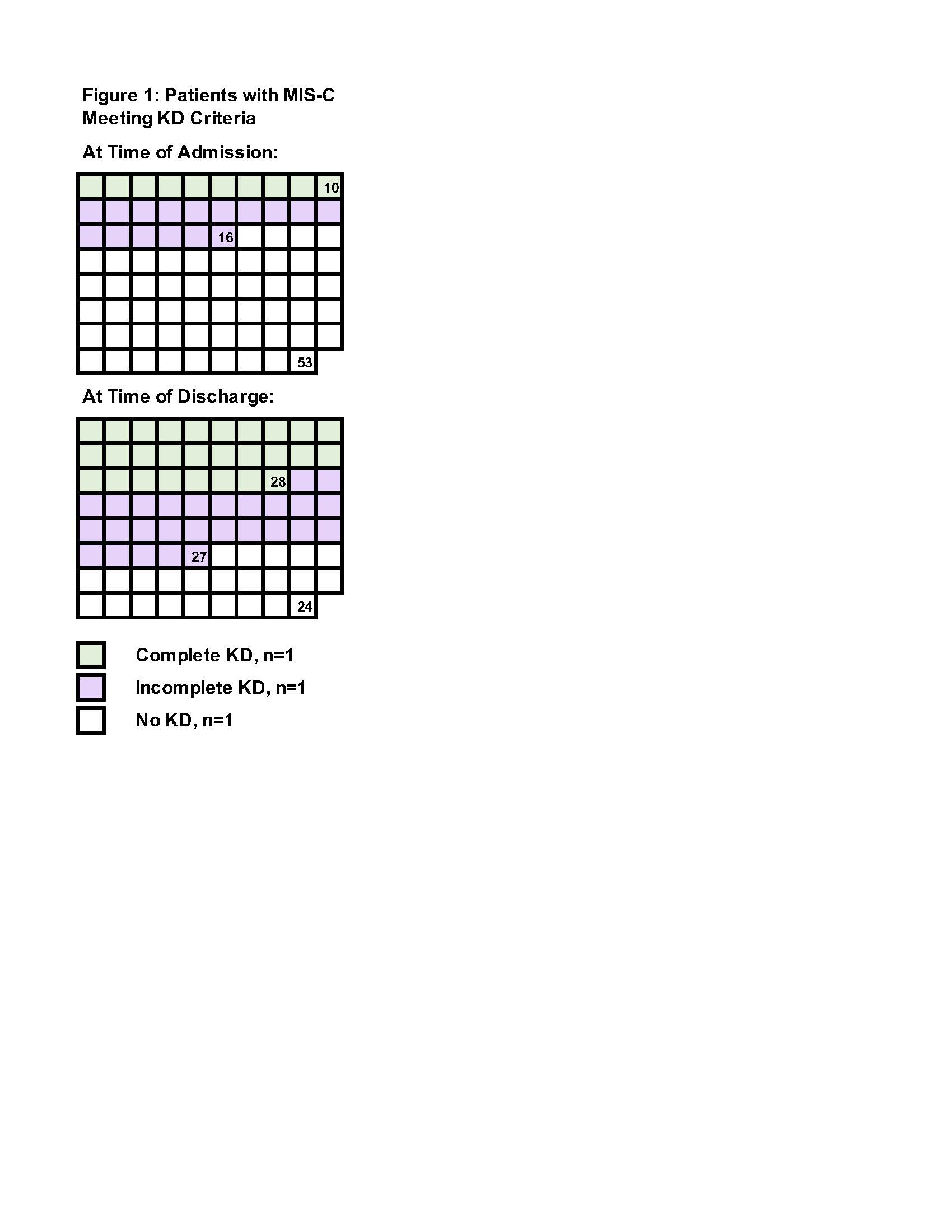 Figure 1: Patients with MIS-C Meeting KD Criteria
Figure 1: Patients with MIS-C Meeting KD Criteria
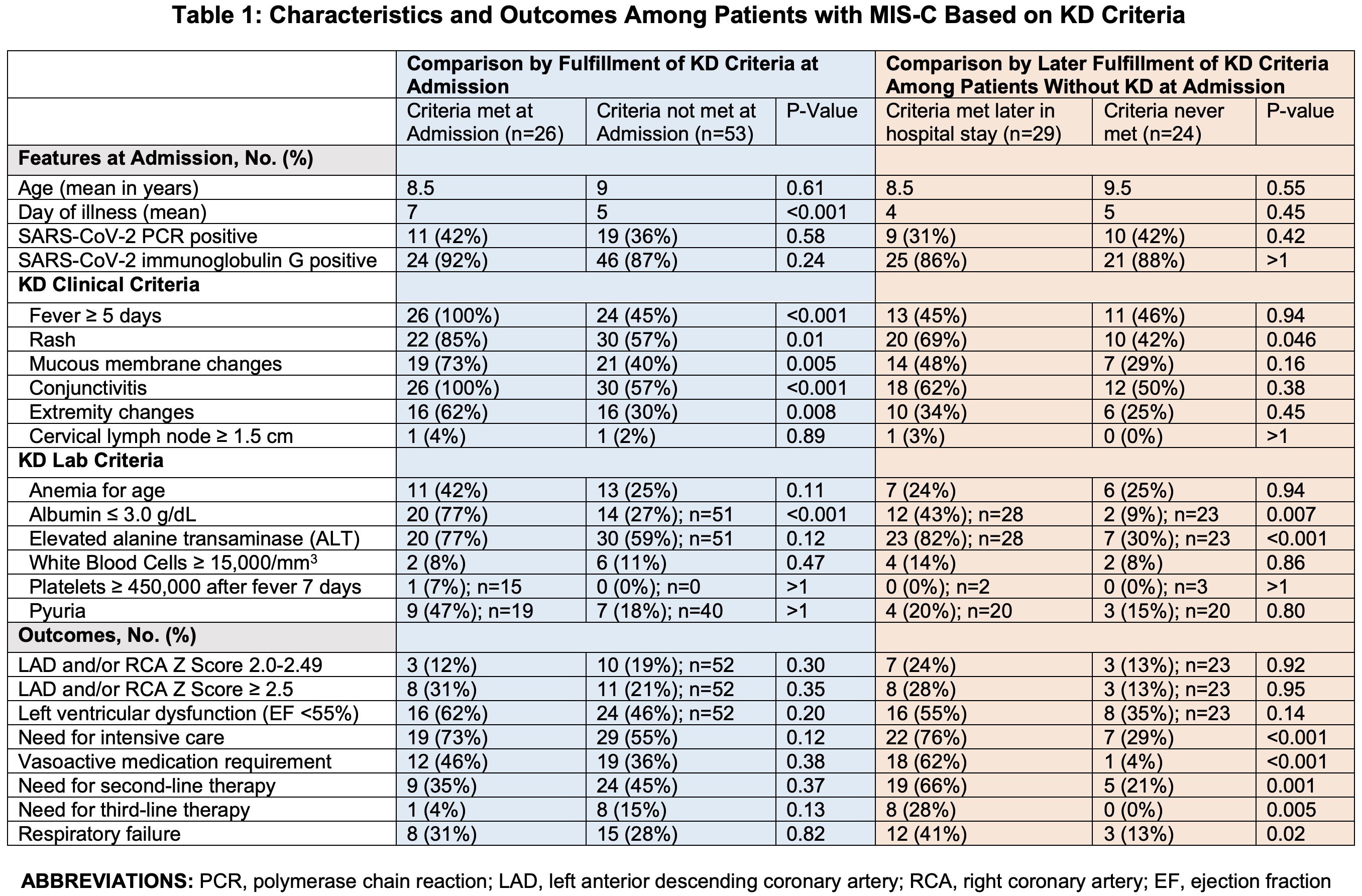 Table 1: Characteristics and Outcomes Among Patients with MIS-C Based on KD Criteria
Table 1: Characteristics and Outcomes Among Patients with MIS-C Based on KD Criteria
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cole L, Anderson M, Heizer H, Hite M, Osborne C, Dominguez S, Jone P. Kawasaki Disease (KD) Criteria Fulfillment and Associated Outcomes in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kawasaki-disease-kd-criteria-fulfillment-and-associated-outcomes-in-multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-mis-c/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kawasaki-disease-kd-criteria-fulfillment-and-associated-outcomes-in-multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-mis-c/
