Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Vasculitis – ANCA-Associated Poster I: Epidemiology, Outcomes, and Classification
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Neurologic involvement (NI) in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is common, occurring in approximately one-third of patients, and leads to significant and often chronic functional limitations and bothersome symptoms. There are limited data on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in patients with NI in AAV. This project aimed to report on patient-reported outcome measures in patients with AAV with or without NI.
Methods: Data for this analysis is derived from patients ≥18 years old with AAV [granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)] participating in a multicenter longitudinal observational study from 2006-2021 through the Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium. HRQOL was assessed with the SF-36 health survey that includes physical and mental component summary scores (PCS and MCS, respectively), PROMIS domains (Fatigue, Pain Interference, Physical Function, Applied Cognitive Abilities, Social Isolation and Anxiety) acquired by computer adaptive testing, and patient global assessment (PGA). Patient subsets were compared according to presence or absence of NI.
Results: Data from 1368 patients with GPA or MPA were available. Complete data were available on 1361/1368 patients for SF36, 1359/1368 for PGA, 978/1368 for PROMIS.
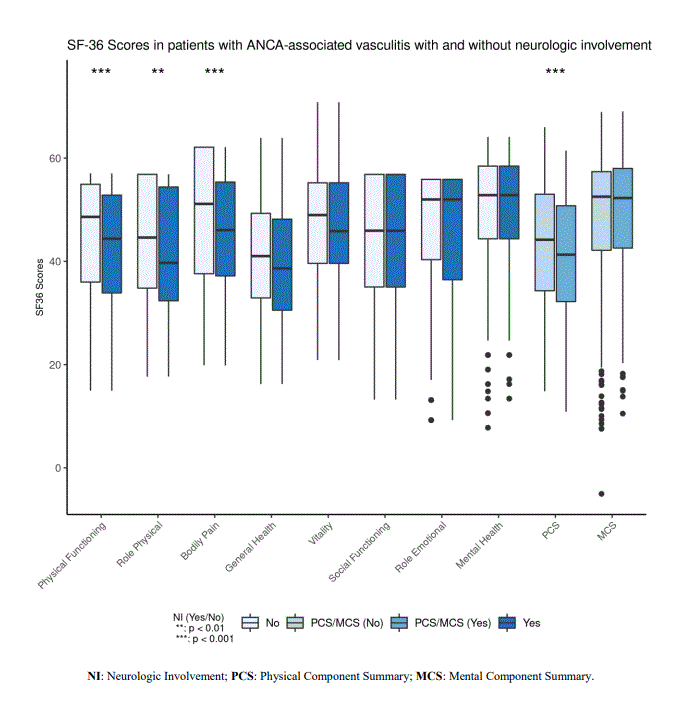
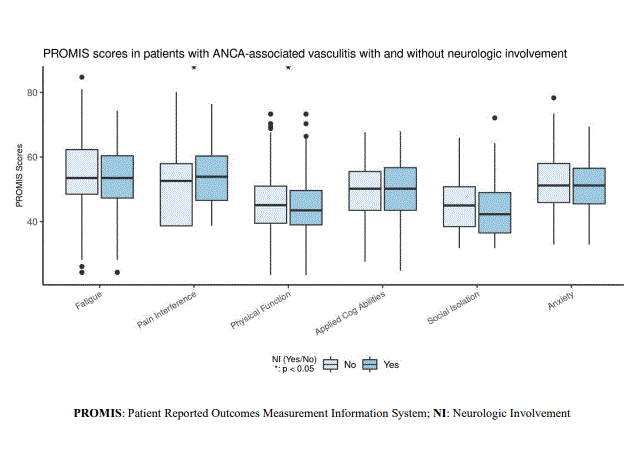
Based on the SF-36, compared to patients without NI, patients with NI have lower scores in Physical Functioning (p < 0.001), Role Limitations (Physical) (p = 0.005), Bodily Pain (p < 0.001), and PCS (p < 0.001) (Figure 1). PROMIS measurements indicated that compared with patients without NI, patients with NI had higher Pain Interference scores (p = 0.033) and lower Physical Function scores (p = 0.047) (Figure 2). Patients with NI reported more vasculitis disease severity as measured by PGA (p = 0.006).
Conclusion: NI in patients with AAV has a negative impact on multiple domains of illness and health-related quality of life. Patients with NI have worse physical functioning, limitations in physical role, and more pain compared to those without NI. These data are informative for clinicians and patients with AAV and should raise the awareness of the impairment in patient with NI in AAV.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hajj-Ali R, Langford C, Zhang C, Calabrese L, Cuthbertson D, Khalidi N, Koening C, McAlear C, Monach P, Moreland L, Pagnoux C, Specks U, Sreih A, Warrington K, Merkel P. Outcome Measures in Patients with Neurologic Involvement in ANCA-associated Vasculitis: Data from Multicenter Longitudinal Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcome-measures-in-patients-with-neurologic-involvement-in-anca-associated-vasculitis-data-from-multicenter-longitudinal-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcome-measures-in-patients-with-neurologic-involvement-in-anca-associated-vasculitis-data-from-multicenter-longitudinal-observational-study/