Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Early in the HIV epidemic, autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were uncommonly encountered. With the advent of combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), patients with HIV-1 live longer and develop rheumatic diseases more similar to the non-HIV population. This study compared characteristics of three categories of arthritides in an outpatient HIV-1 clinic diagnosed over a 29 year period: 1) autoimmune arthritis (RA), 2) immune-mediated arthritis (spondyloarthritis/SpA) and 3) non inflammatory arthritis (primary knee osteoarthritis/ knee OA).
Methods: We examined patients with joint diseases treated at a HIV-1 outpatient rheumatology clinic between 1994 and 2022. At baseline visit, demographic parameters, lymphocyte subsets, HIV-1 viral load, date of diagnosis, pertinent lab findings, and radiographs were collected. Antiretroviral medications were categorized into protease inhibitors, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), and integrase inhibitors. In addition, we compared our SpA population with those with RA and knee OA from our clinic population. Furthermore, we compared and contrast the SpA subgroups (axial SpA, peripheral SpA, and psoriatic arthritis/PsA). All SpA patients met modified New York Criteria for ankylosing spondylitis, ASAS criteria for axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis, and/or CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis. Additionally, all RA and knee OA patients met the ACR classification criteria for their respective diseases. Lastly, univariate analyses were conducted that looked at age, BMI, ethnicity, gender, CD4 count, HIV viral load, and antiretroviral medication use.
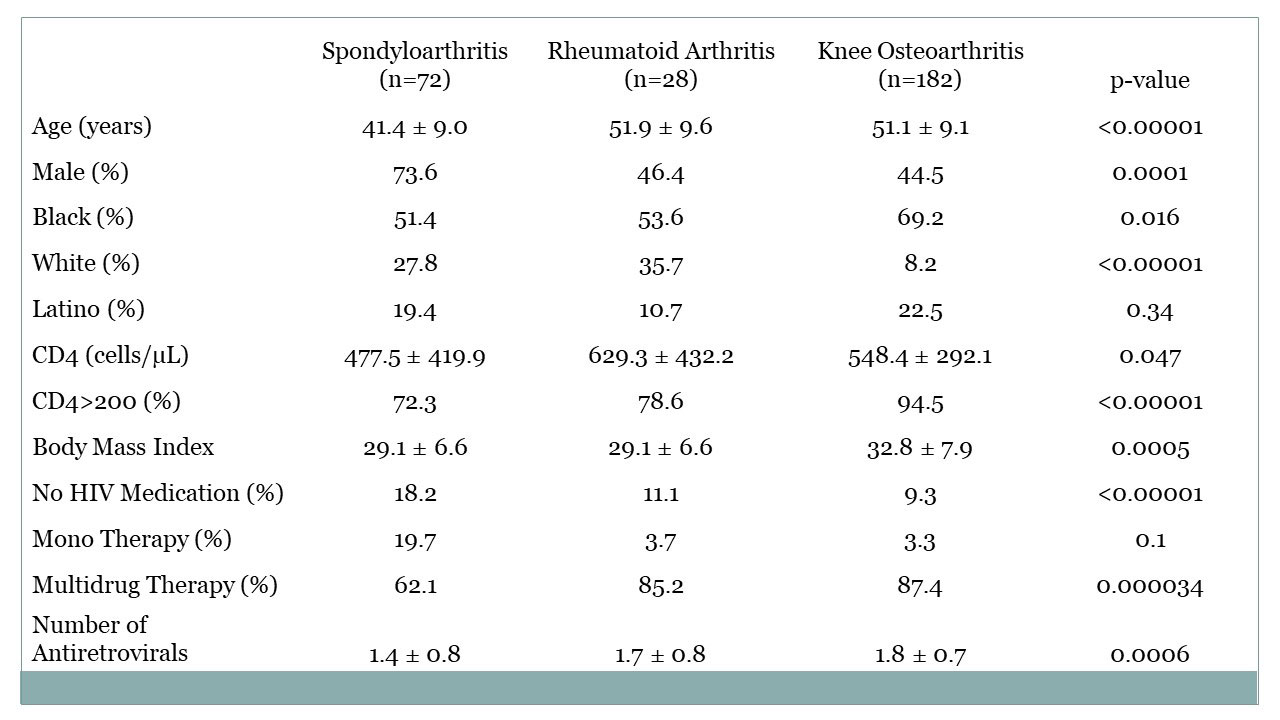
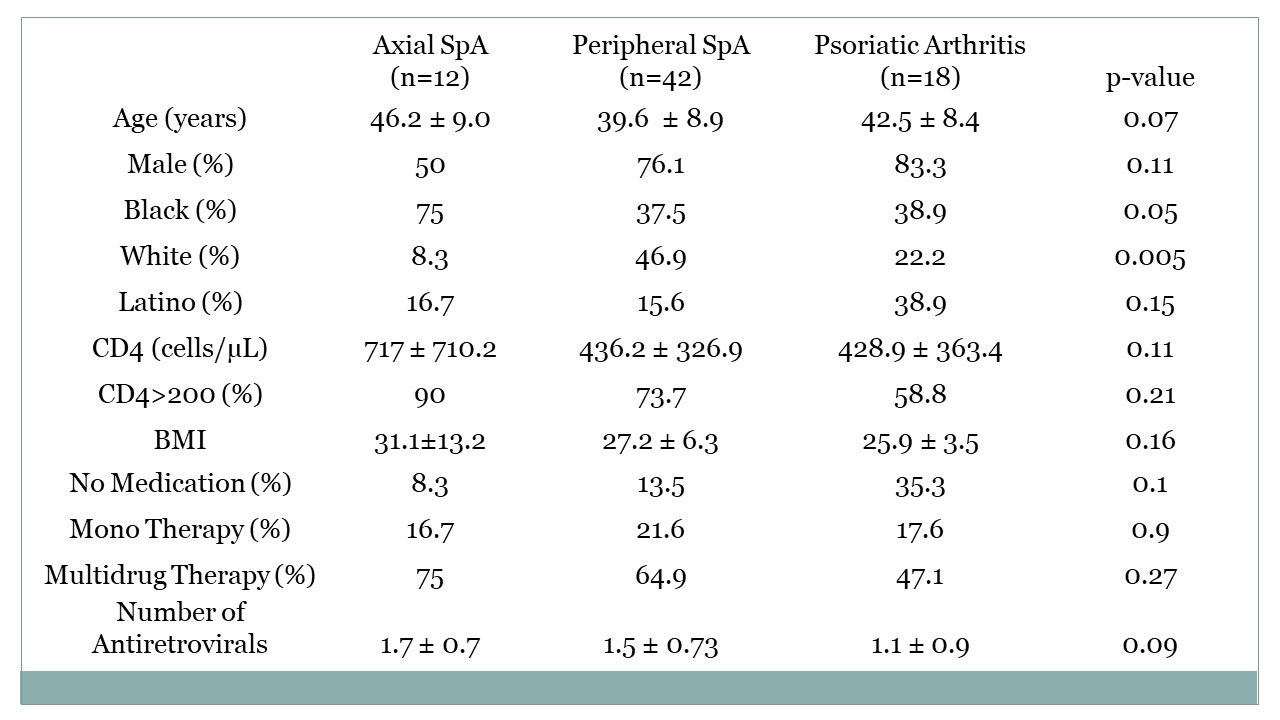
Results: Of 1656 unduplicated patients seen between 2/1/94 and 1/31/22, 72 were diagnosed with SpA, 28 with RA, and 182 with knee OA. Of these,18 (25%) of those with SpA were seen before 1998, when cART became widely available in our clinic, compared to 5 (2.8%) of those with knee OA and none of the 28 RA patients (p< 1×10-8, OR=13.7). Patients with HIV-associated SpA were more likely to be younger, male, have baseline CD4 counts below 200 cells/microliter, the level associated with immunosuppression, and to be taking no HIV medication or at least not multidrug therapy (Table 1). Of those with SpA, whites more more likely to have peripheral SpA and blacks axial SpA (Table 2). There was nonsignificant trend toward more PsA in Latinos.
Conclusion: To date, this is the largest cohort of concomitant HIV-1 and SpA, RA and knee OA patients followed longitudinally to date. Whites were more likely to have peripheral SpA and blacks axial SpA .Those with knee OA were more likely to be black and have higher BMI’s. Patients with HIV-associated SpA were more likely to have been encountered in the pre-cART era, and were more likly to be male, younger, to have lower CD4 counts and to be taking monotherapy or no HIV treatment compared to those with HIV-associated RA and knee OA. The increased frequency of an immune-mediated disease such as SpA where greater immunosuppression was present and in the face of less comprehensive treatment of HIV suggest different mechanisms of disease than autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naovarat B, Reveille J, Hwang M, Williams F, Salazar G. Comparison of Spondyloarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Knee Osteoarthritis Occurring in the Setting of HIV Infection [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-spondyloarthritis-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-knee-osteoarthritis-occurring-in-the-setting-of-hiv-infection/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-spondyloarthritis-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-knee-osteoarthritis-occurring-in-the-setting-of-hiv-infection/