Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster III: Miscellaneous Rheumatic Disease (1614–1644)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) engage in less physical activity than their healthy peers. The Canadian 24-h Movement Guidelines recommend children take part in at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) per day to help maintain optimal health. Meeting these physical activity guidelines may be even more important for children with JIA, as research suggests they may be at increased risk for accelerated cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to compare cardiovascular health indicators in children with JIA who meet and do not meet the MVPA guidelines.
Methods: Children with single diagnosis of JIA between 7 to 17 years of age were recruited from McMaster Children’s Hospital and completed 2 study visits. During Visit #1, height, weight, and body fat were measured. Participants then wore an accelerometer for 7 consecutive days to estimate habitual levels of MVPA. During Visit #2, cardiovascular health indicators were assessed in a fasted state. Carotid artery b-stiffness and intima-media thickness (cIMT) were measured by ultrasound. Whole body arterial stiffness was assessed as carotid – foot pulse wave velocity (PWV). Endothelial function was measured using flow-mediated dilation (FMD) of the brachial artery. Participants were divided into two groups based on meeting (MET) or not meeting (NOT) guidelines of an average of ≥60-min MVPA per day. Participant characteristics, carotid artery b-stiffness and cIMT for MET and NOT were compared using independent sample t-tests, while PWV and FMD were assessed using analysis of covariance, with height or baseline artery diameter as a covariate, respectively.
Results: Twenty-one participants (12 girls) completed this study. Nine children (43%) were in the MET group and had a mean MVPA of 72.9±16.2 min/day, while 12 children (57%) were in the NOT group and engaged in 38.6±13.2 min/day. There were no between group differences in age, height, weight, or body fat (Table 1). There were no between group differences in cardiovascular health indicators including carotid b-stiffness, cIMT and relative FMD (Table 2). There was a trend towards MET having better PWV than NOT (4.8±0.42 m/s vs. 5.2±0.35 m/s, F(1,18)=2.7, p=0.083, partial h2 = 0.129; Figure 1).
Conclusion: Over half of children with JIA in our sample did not meet physical activity guidelines. While we did not find any significant differences in cardiovascular health indicators between children who meet and did not meet the MVPA guidelines, these results, and particularly PWV, may be underpowered to detect differences. These findings highlight the need for further investigation of physical activity and cardiovascular health in JIA.
This study was funded by a Grant-in-Aid from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada.
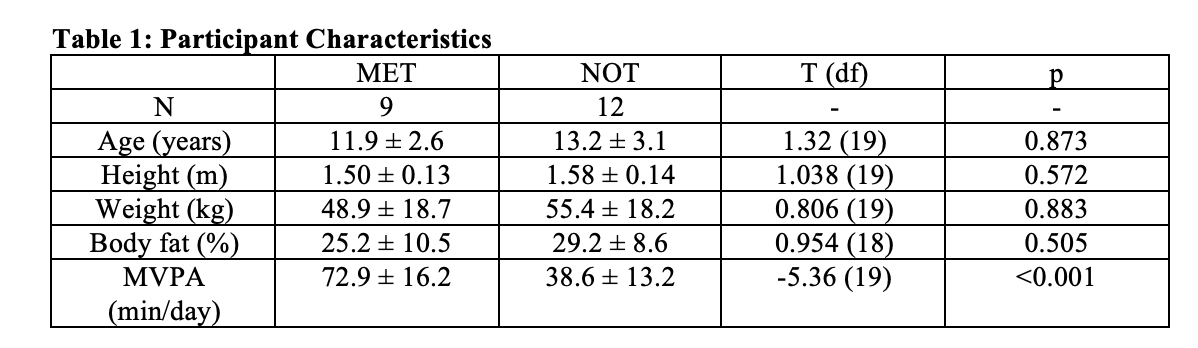 df = degrees of freedom; MVPA = moderate-to-vigorous physical activity. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
df = degrees of freedom; MVPA = moderate-to-vigorous physical activity. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
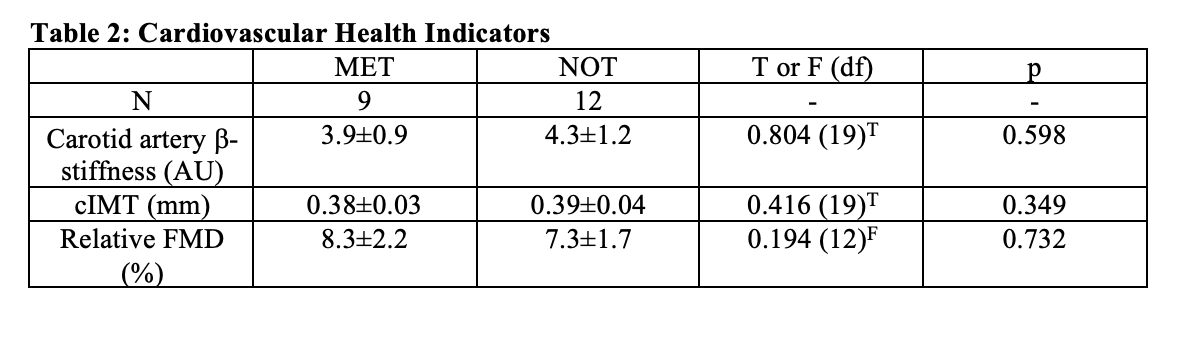 cIMT = carotid intima media thickness; FMD = flow-mediated dilation. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. T = T statistic (degrees of freedom); F = F statistic (degrees of freedom).
cIMT = carotid intima media thickness; FMD = flow-mediated dilation. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. T = T statistic (degrees of freedom); F = F statistic (degrees of freedom).
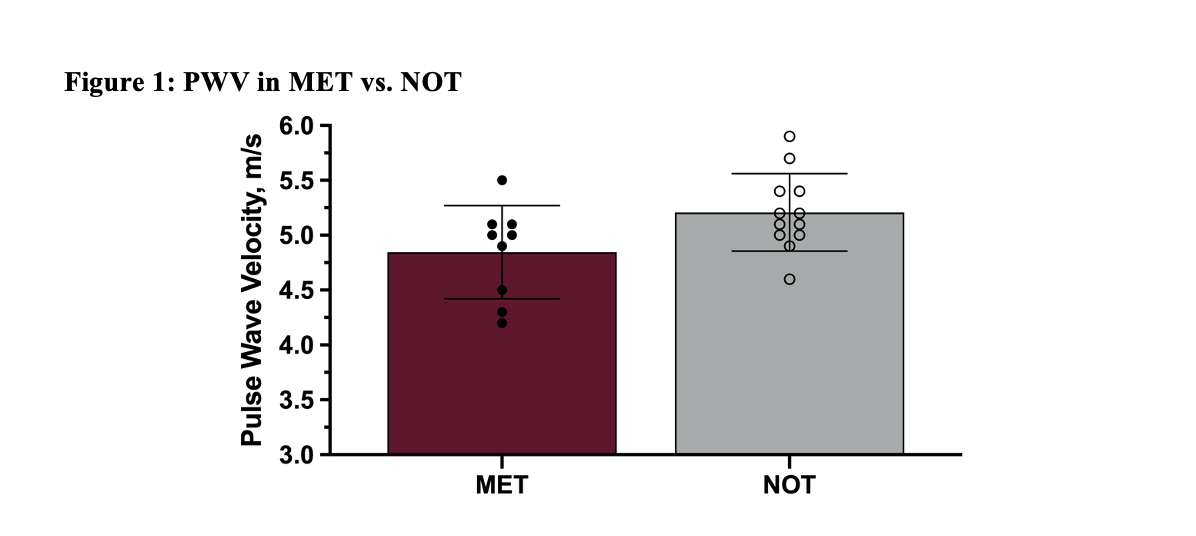 Data are presented as mean ± SD, with individual data displayed in closed circles for MET and open circles for NOT.
Data are presented as mean ± SD, with individual data displayed in closed circles for MET and open circles for NOT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Byra M, Proudfoot N, Chen S, MacDonald M, Cellucci T, Batthish M, Timmons B, Obeid J. A Comparison of Cardiovascular Health Indicators in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Who Meet and Do Not Meet the Physical Activity Guidelines [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-cardiovascular-health-indicators-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-who-meet-and-do-not-meet-the-physical-activity-guidelines/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-cardiovascular-health-indicators-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-who-meet-and-do-not-meet-the-physical-activity-guidelines/
