Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster IV: COVID-19 (1589–1613)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Following the introduction of the COVID-19 vaccines, there has been uncertainty as to whether receiving the COVID-19 vaccine would result in overactivation of the immune system and subsequently lead to a rheumatoid arthritis flare. Noteworthy, the mRNA vaccines studies that were conducted excluded patients with rheumatic diseases who are on immunosuppressive therapy, therefore it is still unclear whether the mRNA covid vaccines might provoke flares of underlying rheumatologic diseases.
The purpose of our study is to assess whether rheumatoid arthritis patients who received the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed a flare of their disease.
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective study at the Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center. We included all patients with RA who are actively on immunosuppressive therapy and received the Pfizer vaccine. Those patients were contacted by phone and a survey questionnaire was used to collect data about their RA, immunosuppressive therapy, and development of symptoms post vaccinations. We included 60 patients in this abstract. Our primary end point was to calculate the percentage of any flare up of RA after COVID-19 vaccine. Secondary end points were to estimate the side effect profile from the vaccine among this population, to check if patients developed a COVID infection after they received the vaccine, and to evaluate whether patients stopped their immunosuppressive medications around the time of the vaccine.
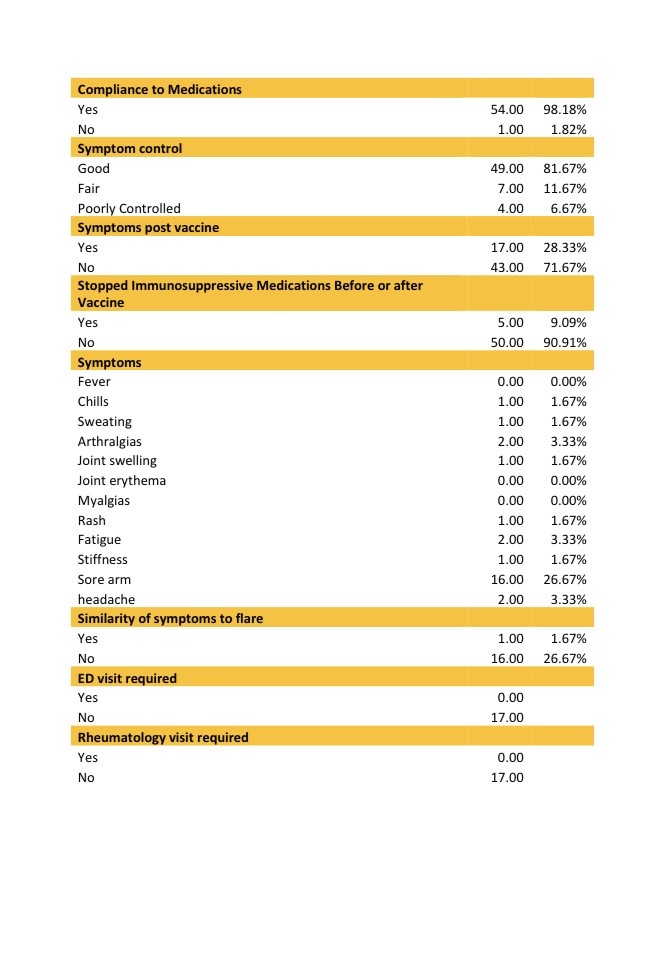
Results: Between 3/9/2021 and 5/27/2021, a total of 60 patients were contacted. One out of the sixty patients (1.67%) reported symptoms of RA flare up after taking the vaccine. Most common side effects in our patients were soreness over the injection site (26.27%), fatigue for one day (3.33%), headaches (3.33%) and arthralgias (3.33%), similar to what was reported in the general population. Most of the patients did not stop their immunosuppressive medications before or after the vaccine (90.91%). None of the patients developed COVID-19 infection following the vaccine up till the date of the phone call. Among our RA patients, one patient developed an RA exacerbation after the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine administration. This patient had poor symptoms control before taking the vaccine however he had worsening of his symptoms following the second dose. Most of the patients had minimal side effects. The question remains as to whether COVID-19 vaccine would confer adequate immune protection in these patients with altered immune response either from underlying rheumatic disease or secondary to disease modifying agents. Some of the Limitations we faced were the small number of patients, and potential recall bias from phone surveys.
Conclusion: Rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving the COVID-19 Pfizer vaccine did not develop major symptoms, flares or side effects following the vaccine. The mRNA COVID vaccine was mostly safe and patients with RA are recommended to receive it. Further research with larger numbers of patients is needed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine within patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases.
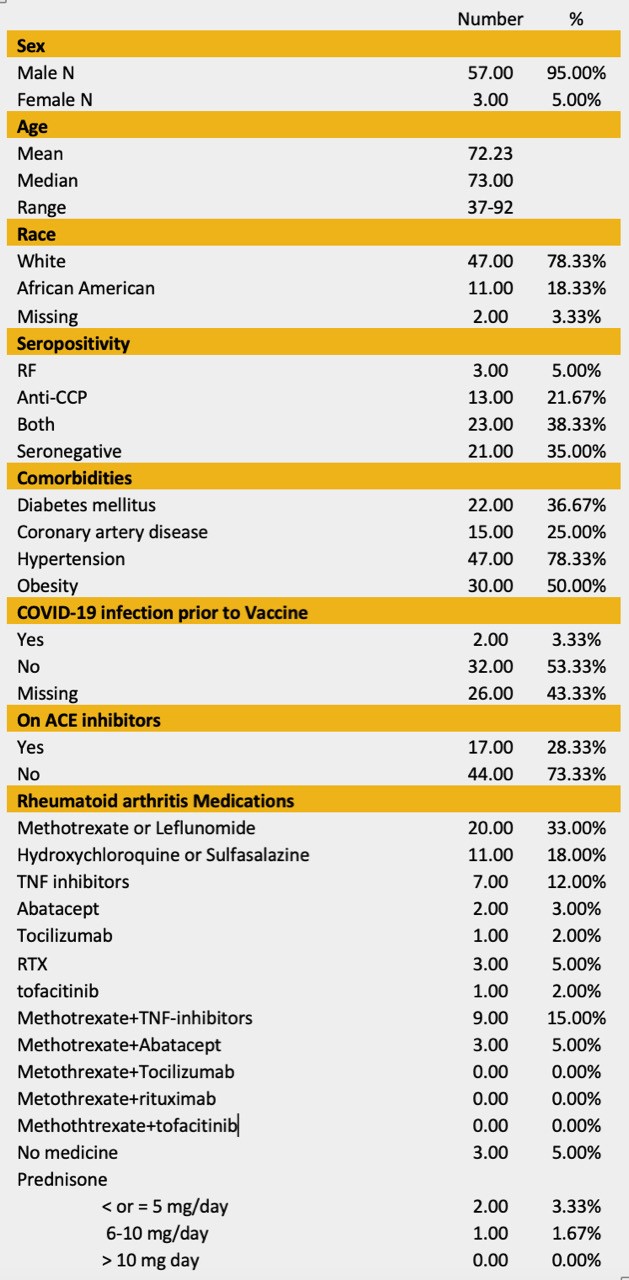 Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abi Doumeth S, Silversteyn L, Anthony D, Mattar M. COVID-19 Vaccination Experience in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated at the Cleveland VA Medical Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-experience-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-at-the-cleveland-va-medical-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-experience-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-at-the-cleveland-va-medical-center/