Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II (1565–1583)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Previous analyses in the CANTOS trial demonstrated a benefit of canakinumab (CAN; IL-1β inhibitor) on gout flares. We aimed to quantify the mediating role of early inflammatory suppression of high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) in explaining the protective role of CAN. If mediation is substantial, hsCRP may be a useful biomarker indicating treatment benefit.
Methods: We conducted a post-hoc analysis for gout flares in CANTOS, an RCT originally undertaken to examine the potential CV benefit of CAN compared to placebo. Our outcome of interest was time to first gout flare after hsCRP and other biomarkers, measured at 3 months. Based on previous analyses with similar gout benefits, we combined 3 different dosages of CAN.
We examined several biomarkers as mediators that may explain some proportion of the protective effect of CAN on future gout flares. hsCRP was the main biomarker of interest. We also analyzed serum urate (SU) as a “negative control mediator” (i.e., not expected to mediate CAN effect but known risk factor for gout flare). In approximately 50% of patients in the biomarker cohort, we also examined IL-6 (hypothesized to be like hsCRP) and IL-18 (not affected by CAN like SU).
We used the regression-based causal mediation analysis. The 3-month change in the log biomarker was the mediator and its relationship with CAN was examined in linear regression. We used Cox regression for the gout flare outcome modeling. We estimated the total effect (TE), natural direct effect (NDE; non-mediated part of TE), natural indirect effect (NIE; mediated part of TE), and proportion mediated (PM). On the hazard ratio (HR) scale, TE=NDE×NIE. We examined the cohort overall as well as stratified by prevalent gout at baseline.
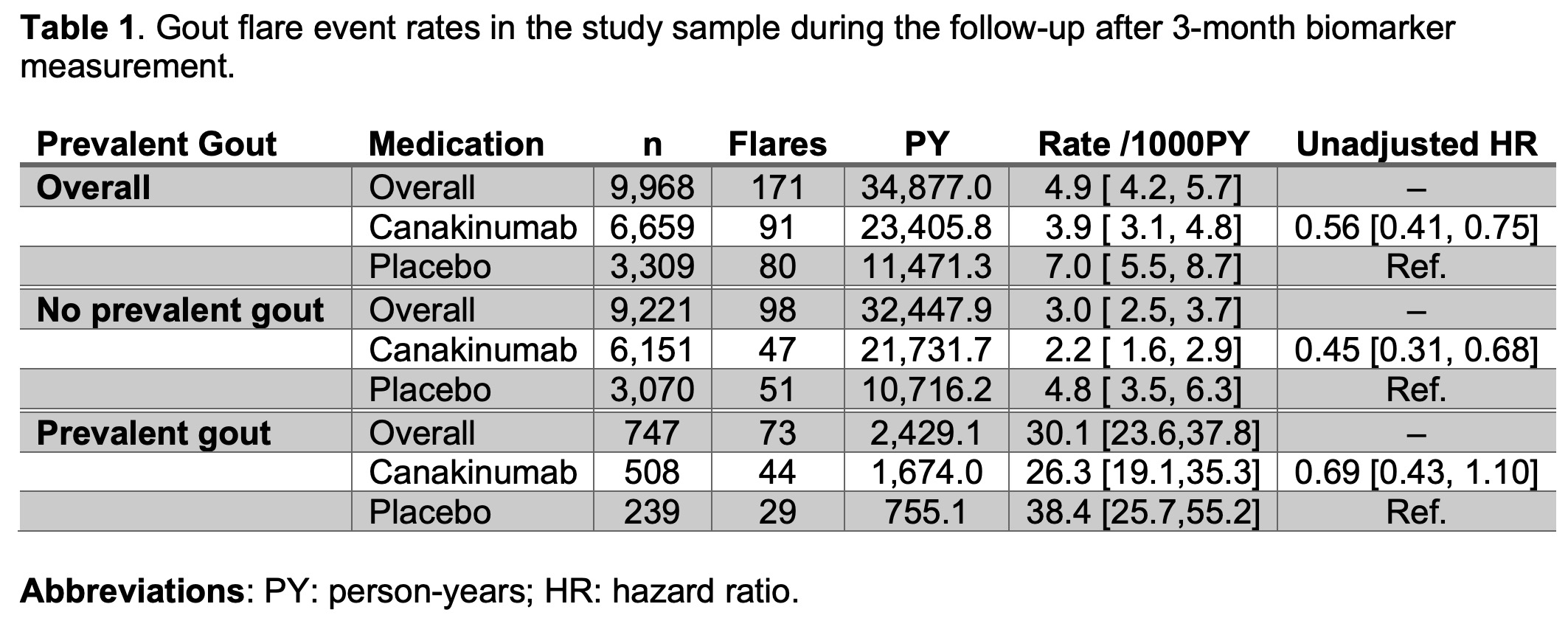
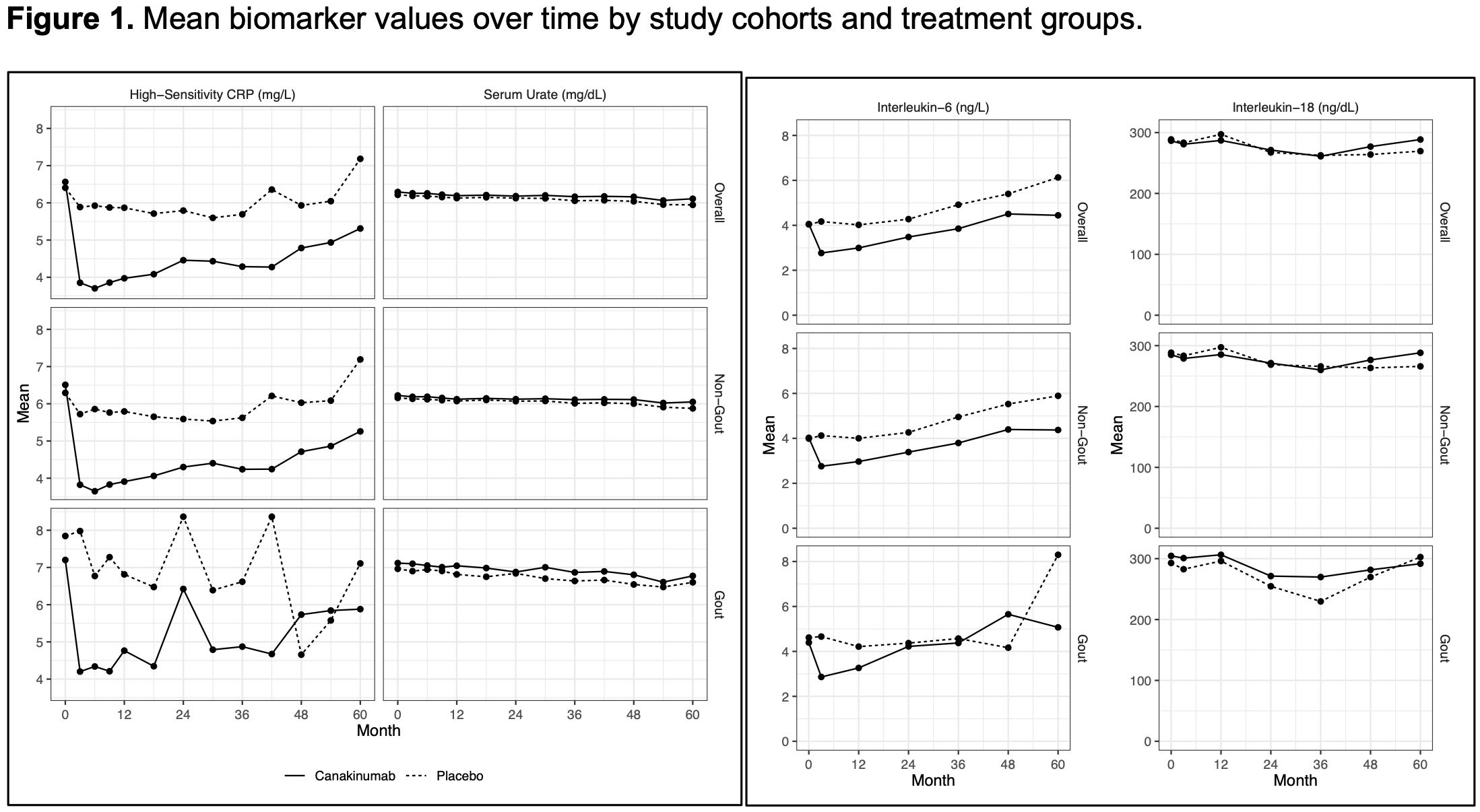
Results: 9,221 patients without known prevalent gout at baseline and 747 with a known prevalent f gout were analyzed. Unadjusted analyses (Table 1) showed similar relative protective effects of CAN on future gout flares regardless of baseline gout. Figure 1 shows that CAN is associated with early decreases of hsCRP and IL-6, but not SU or IL-18.
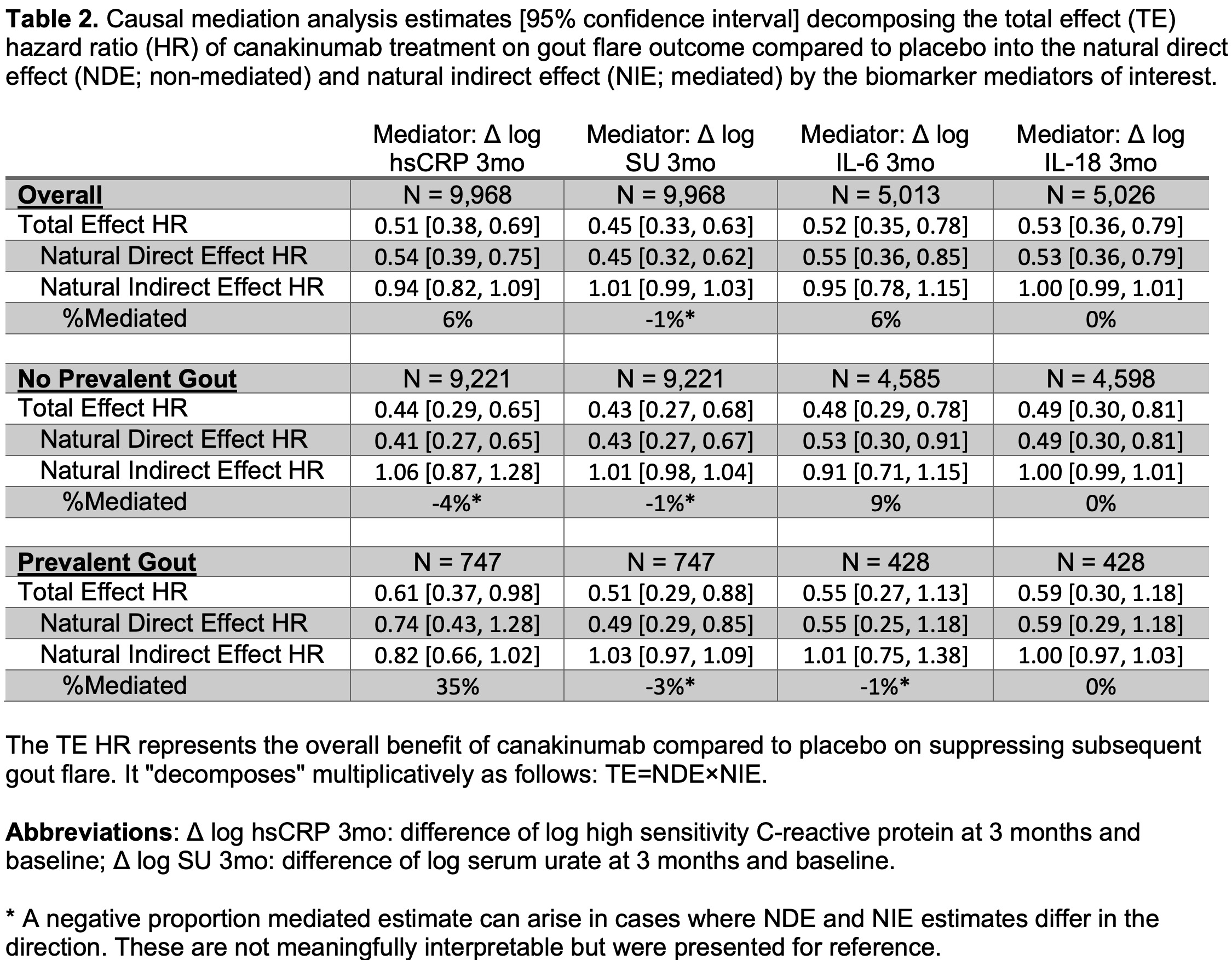
Table 2 summarizes the mediation results. As hypothesized, SU and IL-18 analyses consistently gave near-zero PM estimates. For the hsCRP analysis, the overall cohort result was HR 0.51=0.54×0.94, giving a PM of 6%. Mediation was inconsistent in the no prevalent gout cohort (HR 0.44=0.41×1.06). Upon closer examination, this unclear mediation was due to the poor prediction of future gout flare by the first 3-month change in hsCRP with CAN. In the gout cohort, HR 0.61=0.74×0.82 (PM35%). This mediation was primarily driven by the interaction between be CAN and hsCRP reduction in the outcome model. That is, the first 3-month hsCRP reduction, when driven by CAN, is protective of gout flares. The overall cohort IL-6 analysis was similar although subgroup results did not concur.
Conclusion: The first 3-month reduction in hsCRP explained 6% of its protective effect on future gout flare suppression with a larger proportion mediated (35%) among prevalent gout patients. There may be a potential role of early hsCRP reduction under canakinumab therapy as a treatment benefit biomarker for future gout flares in addition to its role as a treatment benefit biomarker for future CVD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoshida K, Glynn R, Choi H, Everett B, Li Y, MacFadyen J, Ridker P, Solomon D. Causal Mediation Analysis of the Relationship of Canakinumab’s Protective Effect Against Gout Flares and High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein in the CANTOS Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/causal-mediation-analysis-of-the-relationship-of-canakinumabs-protective-effect-against-gout-flares-and-high-sensitivity-c-reactive-protein-in-the-cantos-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/causal-mediation-analysis-of-the-relationship-of-canakinumabs-protective-effect-against-gout-flares-and-high-sensitivity-c-reactive-protein-in-the-cantos-trial/