Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Since the introduction of the first immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) in 2011, they have become widely utilized in the treatment of malignancy. It is well established that patients with autoimmune disease, such as RA, are at risk for flares of their disease when treated with ICIs. However, there is little information available on patients with RA who receive ICIs. This study aims at evaluating RA disease characteristics, outcomes, and treatment in patients with RA who were treated with ICIs at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Methods: Patients with RA diagnosed at least one year prior to onset of malignancy receiving ICI therapy were included. Full medical record review was performed. Data collected includes type and stage of malignancy, ICI treatment regimen (anti-PD1, anti-PDL1, and/or anti-CTLA4 therapy), RA serologies, RA disease activity at time of cancer diagnosis and ICI start, RA treatment at the time of cancer diagnosis and ICI start, time on ICI therapy, treatment of RA while receiving ICI, treatment of RA flares, immune-mediated adverse events (IRAEs), and overall cancer survival.
Results: A total of 19 patients treated over the past 10 years were identified (Table 1). The most common cancer represented was melanoma (10 patients). Five patients were RF positive, 5 patients were anti-CCP antibody positive, 2 patients were seronegative, and serologies were unavailable for 10 patients. Only 1 patient had active RA by physician’s assessment at time of cancer diagnosis. Fifteen patients were on a DMARD at the time of cancer diagnosis but only 7 remained on a DMARD at the time of ICI initiation. The most commonly continued DMARD was hydroxychloroquine (4) followed by methotrexate (3). Eleven patients had an RA flare (increase in joint pain and/or swelling) with median time to onset of flare of 25 days (range 1 to 185 days) (Table 2). Of the 7 patients on a DMARD at time of ICI start, 4 had RA flares and 3 required glucocorticoids. Ten patients received glucocorticoids for flare (prednisone 10 to 40 mg). Of the 6 seropositive patients, 4 had flares. One of the 2 seronegative patients had a flare and 6 of 11 patients with unknown serologies flared. Six patients had other IRAEs which included hepatitis (2), colitis (2), and pneumonitis (2). Median overall cancer survival was 12 months which includes 11 living patients, some of whom were undergoing active ICI treatment.
Conclusion: Most patients were on DMARDs for RA at the time of cancer diagnosis and all but one were well controlled. However, at the time of ICI start, most patients stopped their DMARDs. Patients with even well-controlled RA can have flares when treated with ICIs. Flares can happen at any time during treatment and risk of flare is not clearly associated with seropositivity. However, most patients stopped or decreased number/dose of immunosuppressive medications when starting ICI therapy which may have contributed to rate of flares. Most flares were treated with prednisone. Only one patient stopped ICI treatment due to RA flare. Prospective studies would be helpful for risk stratification of RA patients receiving ICIs as well as role for DMARDs concomitantly with ICIs.
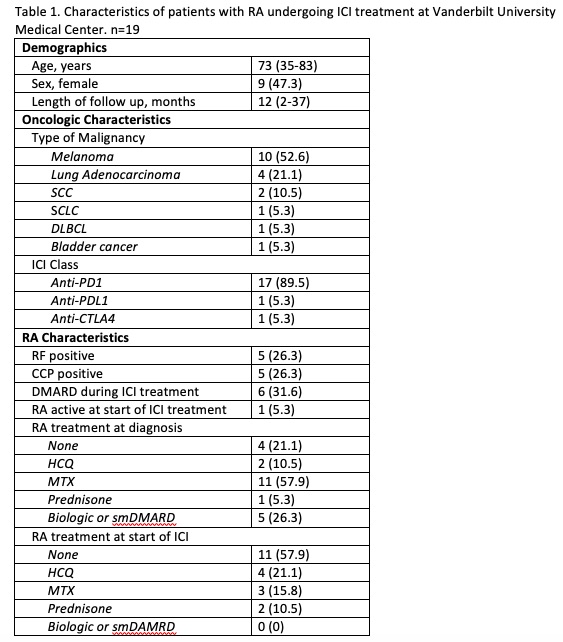 Data presented as median (range) or frequency (percentage). ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; SCLC: small cell lung cancer; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PD1: programmed cell death 1; PDL1: programmed cell death ligand 1; CTLA4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4.
Data presented as median (range) or frequency (percentage). ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; SCLC: small cell lung cancer; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PD1: programmed cell death 1; PDL1: programmed cell death ligand 1; CTLA4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4.
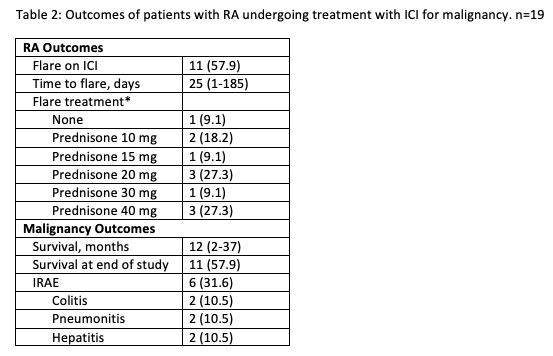 Data presents at frequency (%) or median (range). *n=11. ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; IRAE: immune-related adverse event.
Data presents at frequency (%) or median (range). *n=11. ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; IRAE: immune-related adverse event.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hansen M, Zakria D, Johnson D. Outcomes and Disease Characteristics in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Malignancy at a Single Academic Institution [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-disease-characteristics-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitors-for-malignancy-at-a-single-academic-institution/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-and-disease-characteristics-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitors-for-malignancy-at-a-single-academic-institution/
