Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: X-inactive-specific transcript (XIST) has been shown to silence linked genes on the X chromosome that may be related to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in female patients. However, the function of XIST in SLE at other levels remains unclear. The present study aimed to clarify the correlations between XIST expression and SLE clinical features and the contribution of XIST to SLE pathogenesis at the transcriptome level.
Methods: Expression of XIST in 79 SLE patients and 23 healthy controls was detected by quantitative-polymerase chain reaction. Bioinformatics methods were used to explore the function and regulatory mechanism of XIST.
Results: Expression of XIST was significantly upregulated in SLE patients compared with healthy controls (Figure 1A, p = 0.0043), and had a high diagnostic value for SLE (Figure 1B, AUC = 0.762, 95% CI: 0.658 to 0.867, p = 0.000136). Compared with male patients and older patients, XIST was significantly upregulated in female patients (Figure 1C, p = 0.0162) and younger patients (Figure 1D, p = 0.0429). Moreover, XIST was highly expressed in patients with arthralgia (Figure 1E, p = 0.0222). Importantly, SLE patients with high expression of XIST tended to have elevated levels of total T cells and CD8+ T cells, but reduced levels of Treg cells and NK cells. Bioinformatics analyses suggested that XIST may regulate the expression of OLFM4 and CEACAM8 by acting as a spongy body for miR-20a, miR-92a, miR-106a, and miR-449a (Figure 2). Furthermore, OLFM4 and CEACAM8 are significantly upregulated in SLE patients and had significant positive correlations with expression of XIST.
Conclusion: We propose that XIST may alter the balance of peripheral blood immune cells in SLE by acting as a spongy body for the miR-17-92 cluster and promoting the expression of OLFM4 and CEACAM8, resulting in immune dysregulation and tissue damage in SLE.
 Figure 1 expression of lncRNA XIST and its diagnostic value for SLE. A. Expression of XIST in SLE patients and healthy controls. B. ROC curves of XIST in the two groups. C and D. XIST is significantly upregulated in female (C) and young (D) patients. E. XIST is highly expressed in patients with arthralgia.
Figure 1 expression of lncRNA XIST and its diagnostic value for SLE. A. Expression of XIST in SLE patients and healthy controls. B. ROC curves of XIST in the two groups. C and D. XIST is significantly upregulated in female (C) and young (D) patients. E. XIST is highly expressed in patients with arthralgia.
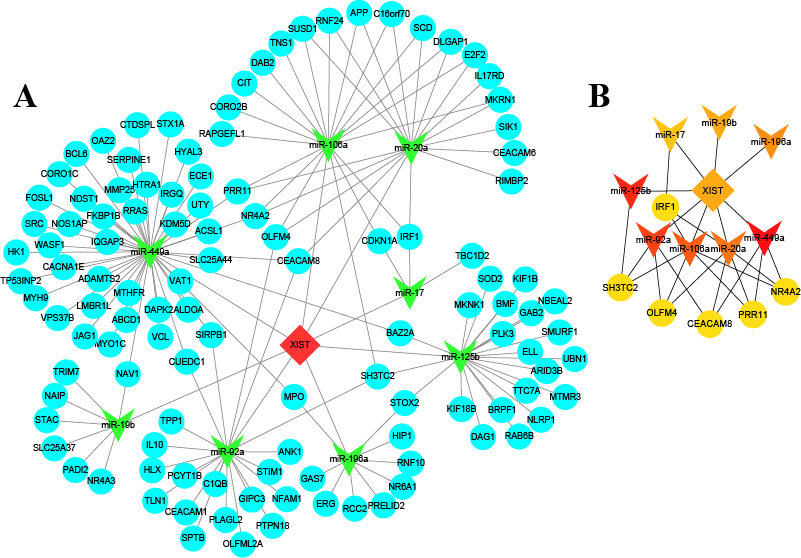 Figure 2 Function and regulatory mechanism of XIST at transcriptome level. A.The ceRNA network was composed of 1 lncRNA, 8 miRNAs, 115 mRNAs, and 150 edges. Each edge represents one interaction between two transcripts. Red diamond, lncRNA; green V, miRNA; sky-blue circle, mRNA. B. Subnetwork of hub transcripts constructed by Cytoscape and its plug-in Cytohubba.
Figure 2 Function and regulatory mechanism of XIST at transcriptome level. A.The ceRNA network was composed of 1 lncRNA, 8 miRNAs, 115 mRNAs, and 150 edges. Each edge represents one interaction between two transcripts. Red diamond, lncRNA; green V, miRNA; sky-blue circle, mRNA. B. Subnetwork of hub transcripts constructed by Cytoscape and its plug-in Cytohubba.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng Q, Chen M, Chen x, zhang p, wu h, du y. LncRNA XIST Alters the Balance of Peripheral Blood Immune Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Regulating the miR-17-92/OFLM4 and CEACAM8 Axis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lncrna-xist-alters-the-balance-of-peripheral-blood-immune-cells-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-by-regulating-the-mir-17-92-oflm4-and-ceacam8-axis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lncrna-xist-alters-the-balance-of-peripheral-blood-immune-cells-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-by-regulating-the-mir-17-92-oflm4-and-ceacam8-axis/
