Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Gender disparities in PsA can affect natural course of disease, clinical presentation and response to medication1. The German non-interventional study AQUILA provides real-world data on the influence of gender of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) on therapeutic effectiveness and retention rate under treatment with secukinumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin-17A.The aim of this interim analysis is to describe selected baseline (BL) demographics, to evaluate secukinumab treatment outcomes on disease activity, depressive mood and retention rate depending on the gender of PsA patients.
Methods: AQUILA is an ongoing, multi-center study including more than 3000 patients with active PsA or ankylosing spondylitis. Patients were observed from BL up to week (w) 52. Real-world data was assessed prospectively and analyzed as observed. Data was collected on impact of disease (Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease – 12 items, PsAID-12 score), skin disease activity (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, PASI), joint counts and severity of depressive mood (Beck´s Depression Inventory version II, BDI-II), in addition to patient´s global assessment (PGA). Moreover, retention rates (time from study inclusion until premature secukinumab treatment discontinuation) were assessed through Kaplan-Meier plots. This interim analysis focuses on the subgroups of male and female PsA patients.
Results: At BL, 1278 PsA patients were included: 41.5% (n=531) male and 58.5% (n=747) female. Demographic data (Table 1) of male and female PsA patients differed most obviously regarding proportion of overweight patients, smokers, pretreatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and biologicals/biosimilars (b-bsDMARDs).
Mean PsAID-12 values over time were higher in women; nevertheless, PsAID-12 improved comparably for both genders from BL to week 52 (♂: 4.8 at BL to 2.9 at w52, ♀: 5.3 at BL to 3.5 at w52, Fig. 1A). This was similar to the course of improvements for mean PGA across genders (♂: 4.9 at BL to 3.0 at w52, ♀: 5.6 at BL to 3.5 at w52). In terms of PASI scores, both BL mean values and improvements over time were similar across genders (♂: 6.8 at BL to 1.9 at w52, ♀: 7.0 at BL to 1.0 at w52). Mean joint counts (tender/swollen) also improved similarly (♂: 6.8/3.7 at BL to 3.1/0.9 at w52, ♀: 7.3/3.7 at BL to 2.8/0.9 at w52). Over time, male patients showed overall reduced BDI-II values; nevertheless, BDI-II reductions were comparable across the genders (♂: 10.2 at BL to 8.1 at w52, ♀: 13.0 at BL to 10.6 at w52). Secukinumab treatment retention rate for men was (not significantly) higher than for women (Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: In a real-world setting, secukinumab improved disease activity and depressive mood of PsA patients in both men and women. Women showed overall higher burden of disease. Altogether, this interim analysis shows that secukinumab is an effective treatment up to 52 weeks with high treatment retention rates in real-world setting, irrespective of gender.
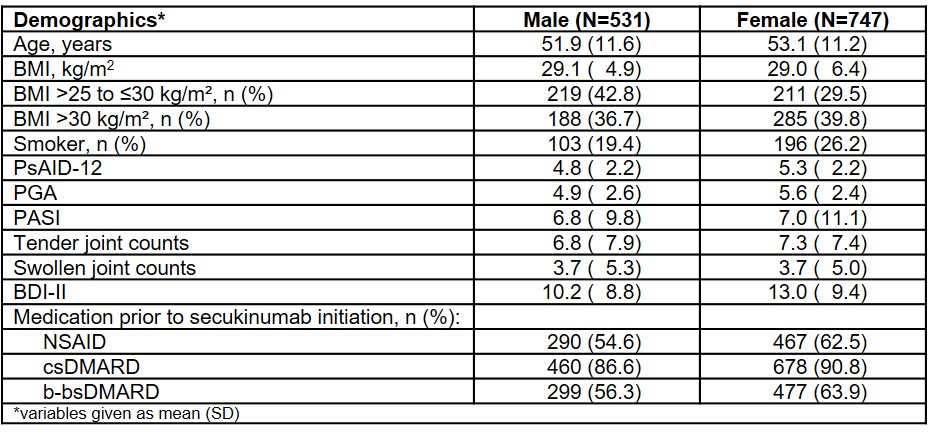 Table 1: Overview of baseline characteristics in PsA patients depending on gender
Table 1: Overview of baseline characteristics in PsA patients depending on gender
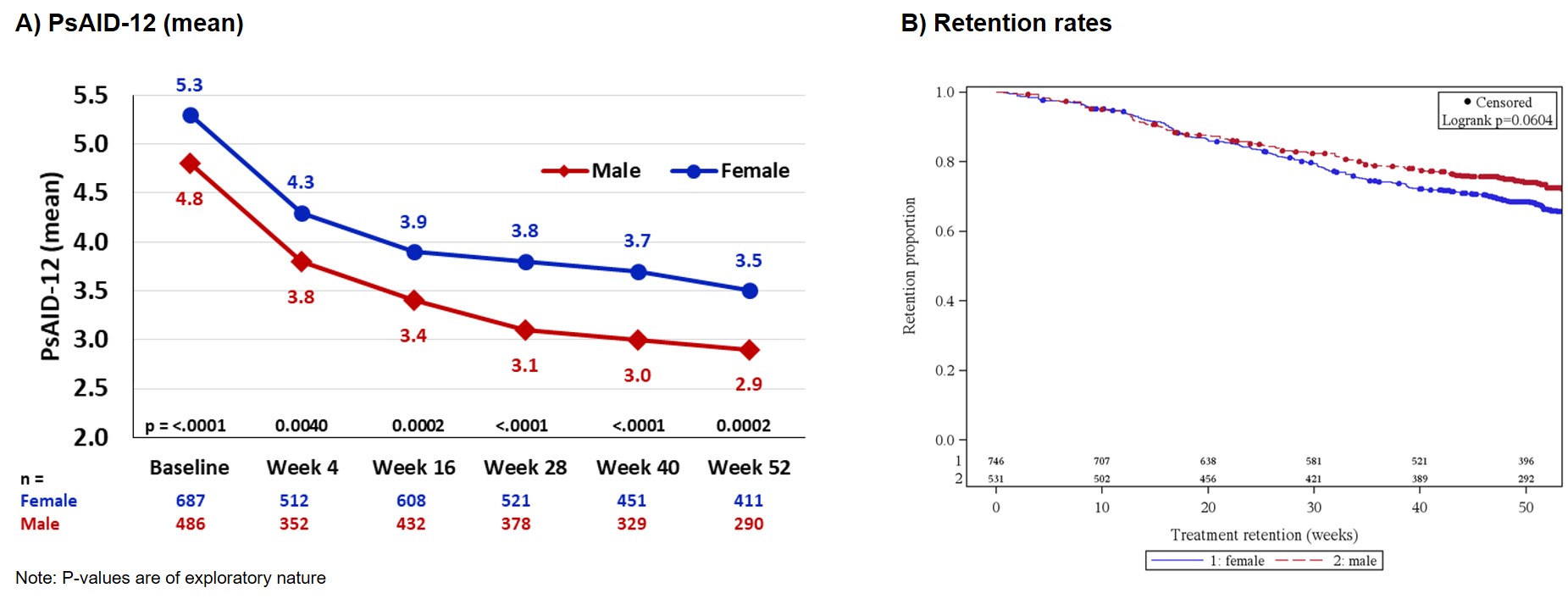 Figure 1: Impact of disease and treatment retention in PsA patients stratified by gender
Figure 1: Impact of disease and treatment retention in PsA patients stratified by gender
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Brandt-Jrgens J, Kästner P, Riechers E, Peterlik D, Tony H. How Does Gender Affect Secukinumab Treatment Outcomes and Retention Rates in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis? – Real World Data from a German Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-does-gender-affect-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-and-retention-rates-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-data-from-a-german-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-does-gender-affect-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-and-retention-rates-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-data-from-a-german-observational-study/
