Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes (1257–1303)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) has a high prevalence of cognitive impairment (CI) (38% (95% confidence interval: 33-43%)). Patient reported outcomes (PROs) capture patient perceptions of their health condition, mood, health related quality of life (HRQoL) and other aspects. We aimed to determine if self-reported fatigue, anxiety, depression, perceived deficits questionnaire (PDQ-20), HRQoL, disease activity scores and cognitive neuro-battery (NB) cluster into distinct groups in SLE patients. We assessed if patients changed clusters at 1 year of follow-up.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of consecutive consenting patients, aged 18-65 years, who attended a single center (Jul 2016 – Mar 2019) and completed baseline and 1 year follow-up visits. Patients completed a comprehensive NB evaluating six cognitive domains: manual motor speed and dexterity, simple attention and processing, visual spatial construction, verbal fluency, learning and memory (verbal and visuospatial) and executive function. We derived a total score for the NB. Patients completed the Beck anxiety, Beck depression, fatigue severity score (FSS), Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) physical (PCS) and mental scores (MCS), and the PDQ-20 (subjective cognitive function). Disease activity was assessed by SLEDAI-2K. Ward’s method was used for clustering and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used to confirm the number of clusters. Clusters were grouped based on symptom intensity, defined as those that had high, medium, and low PROs scores relative to one another. We assessed the stability and movement of clusters at 1 year. Stability was assessed with kappa statistic.
Results: 142 patients were included, 89.4% comprised of females. The mean age and SLE duration at enrolment were 43.1 ± 12.1 and 15.3 ± 10.1 years, respectively.
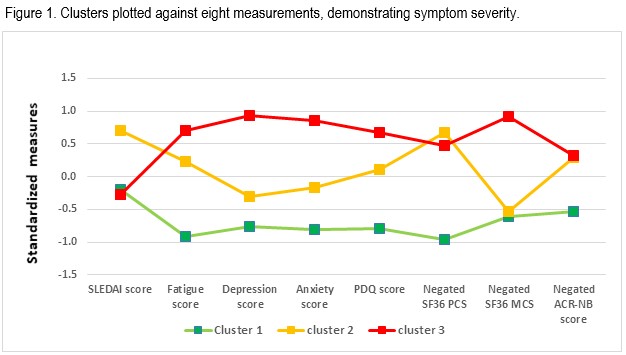
Three clusters were found: Cluster 1 had low symptom intensity, Cluster 2 had moderate symptom intensity and Cluster 3 had high symptom intensity (Figure 1). In Cluster 3, the most severe scores for fatigue, depression, anxiety, PDQ-20, and SF-36 MCS were found. NB scores in Cluster 3 were similar to Cluster 2. SLEDAI-2K was similar in Clusters 1 and 3 and more active in Cluster 2.
At 1 year follow-up, 49% of patients (69/142) remained in their baseline cluster; a fair agreement of stability (Kappa statistic 0.35;95% confidence interval 23.0-47.3) was found. Cluster 1 had the highest stability (77% of patients stayed in the same cluster), followed by Cluster 3 (51%) and Cluster 2 had the lowest stability (3%; Table 1). A minority of patients from Cluster 1 moved to Cluster 3 (19%). In Cluster 3, a larger number moved to Cluster 2 (40%) and less to Cluster 1 (9%).
Conclusion: Three distinct clusters of symptom intensity were defined by PCA in SLE patients in association with cognitive function with Cluster 3 displaying the highest symptom severity and worse cognitive function versus Cluster 1 having the lowest symptom burden and better cognitive function. Patients remained in the same cluster at one year, particularly in Cluster 1 and Cluster 3, and there was a low tendency to move between these two Clusters.
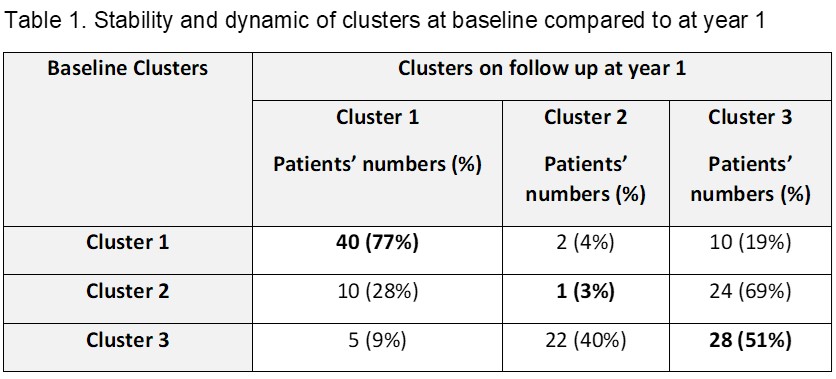 Interpretation for the table: e.g. In Cluster 1, 77% of patients remained in this cluster at year 1 while 4% moved to Cluster 2 and 19% to Cluster 3.
Interpretation for the table: e.g. In Cluster 1, 77% of patients remained in this cluster at year 1 while 4% moved to Cluster 2 and 19% to Cluster 3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta A, Johnson S, Su J, Bingham K, Knight A, Diaz-Martinez J, Kakvan M, Tartaglia M, Ruttan L, Wither J, Choi M, Fritzler M, Bonilla D, Beaton D, Katz P, Green R, Touma Z. Studying Clusters of Patients with SLE According to Cognitive Function, Self-reported Outcomes, Disease Activity, and Clusters Dynamic over 1 Year [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/studying-clusters-of-patients-with-sle-according-to-cognitive-function-self-reported-outcomes-disease-activity-and-clusters-dynamic-over-1-year/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/studying-clusters-of-patients-with-sle-according-to-cognitive-function-self-reported-outcomes-disease-activity-and-clusters-dynamic-over-1-year/