Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) – also referred to as radiographic axial spondyloarthritis – is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the sacroiliac joints and spine. In the recent TORTUGA study, filgotinib (FIL), a preferentially selective Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor, significantly reduced AS disease activity compared with placebo (PBO).1 JAK1 inhibition by FIL has the potential to block multiple inflammatory pathways. Thus, we analyzed circulating biomarker concentrations in samples from adult patients with active AS in TORTUGA and age, gender and BMI-matched healthy volunteers (HV) using exploratory multiplex biomarker panels and high sensitivity immunoassays to assess the impact of disease on circulating biomarkers at baseline and evaluate the effect of FIL treatment over 12 weeks.
Methods: TORTUGA (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT03117270) was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Patients were randomized 1:1 to FIL 200 mg (n=58) or PBO (n=58) once-daily and serum and plasma samples (FIL n=56, PBO n=53) were collected at baseline (BL) and weeks 1, 4 and 12. The samples were analyzed using immunoassays from Meso Scale Diagnostics (Rockville, MD, USA), EMD Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA), Nordic Biosciences (Herlev, Denmark) and Nexelis (Seattle, WA, USA). Biomarker concentration changes from BL were analyzed on paired patient data and reported for weeks 1, 4 and 12, and clustering analysis was performed. Correlation between the biomarkers and selected clinical scores were assessed by Spearman rank correlation analysis. Mean of log-fold-changes in biomarker levels from BL to week 4 and week 12 were compared between arms using PBO-adjusted estimates from a linear mixed effects model.
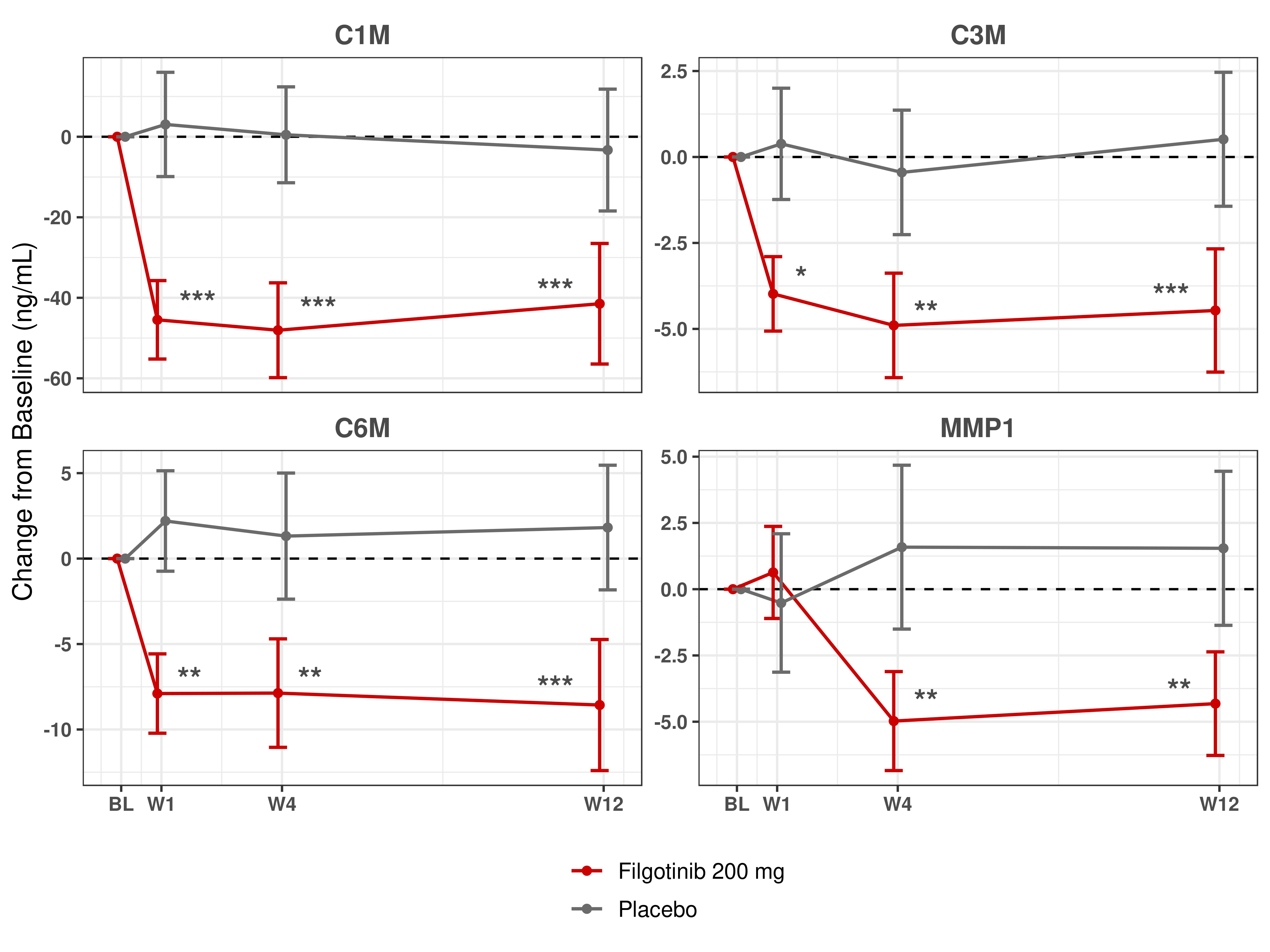
Results: Five clusters of biomarker response were identified based on the kinetics and magnitude of percent changes from BL with FIL treatment. As compared to PBO, a reduction in the inflammatory biomarkers CRP, SAA and IL-6 was observed, as well as a reduction in matrix metalloproteinase-degraded collagen fragments C1M, C3M, C6M and MMP1 (Figure 1). The change in several of these biomarkers correlated with changes in numerous clinical characteristics from BL to week 12, notably a correlation of MMP1, C6M and ICAM1 with Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS), CRP, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) MRI spine score and patient-reported pain. Comparisons to HV were made on a subset of biomarkers and BL ICAM1 and VCAM1 were elevated in AS patients as compared to HV. However, after 1 week of treatment with FIL, both were reduced to levels comparable to HV and remained low for the 12-week duration of the study.
Conclusion: In patients with active AS, FIL treatment reduced the levels of inflammatory cytokines associated with disease including systemic inflammatory cytokines, matrix remodeling biomarkers and cellular adhesion molecules. The observed decrease in biomarkers is consistent with the reduced AS disease activity in TORTUGA and suggest that FIL treatment can rapidly reduce a range of inflammatory cytokines involved in AS pathobiology.
Reference
1. van der Heijde D et al. Lancet 2018;392:2378–87
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Tian Y, Xu J, Barchuk W, Galien R, Besuyen R, Liu Y, Malkov V, Hertz A. Filgotinib Treatment Results in Reduction of Inflammatory and Matrix Remodeling Biomarkers Associated with Disease in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-treatment-results-in-reduction-of-inflammatory-and-matrix-remodeling-biomarkers-associated-with-disease-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-treatment-results-in-reduction-of-inflammatory-and-matrix-remodeling-biomarkers-associated-with-disease-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/