Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful condition leading to joint damage and impaired function. Intra-articular (IA) corticosteroid injections are frequently prescribed to treat pain. Lorecivivint (LOR), a novel IA CLK/DYRK inhibitor that modulates Wnt and inflammatory pathways, appeared safe and demonstrated patient-reported outcome pain and function improvements compared with placebo in a Phase 2b knee OA trial (Yazici, Y. et al. Osteoarthr. Cartil., 2021). While lorecivivint is proposed for stand-alone use, in clinical practice, providers might administer lorecivivint in close time proximity to IA corticosteroid. This open-label, parallel-arm, healthy volunteer study was conducted to assess potential safety and tolerability (primary objectives), and pharmacokinetic (PK) interactions (secondary objective), between lorecivivint and triamcinolone acetonide (TCA) when the two medications were administered 7 days apart.
Methods: Healthy volunteers were randomized to Treatment Arm 1 (IA 40 mg TCA on Day 1 followed by IA 0.07 mg lorecivivint on Day 8) or Treatment Arm 2 (IA 0.07 mg lorecivivint on Day 1 followed by IA 40 mg TCA on Day 8). All injections were performed on the right knee. For each treatment arm, treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were categorized by “epoch”, with Epoch 1 spanning from first until second injection, and Epoch 2 spanning from second injection until end of study. In Treatment Arm 1, plasma TCA levels were assessed on Days 1 (before TCA dosing and up to 12 h after), 2 (24 h after), 3, 5, 8 (before lorecivivint dosing and up to 8 h after), 11, and 15. Plasma lorecivivint concentrations were assessed on Day 8 (before lorecivivint dosing and up to 8 h after). In Treatment Arm 2, plasma lorecivivint levels were assessed on Days 1 (before lorecivivint dosing and up to 8 h after), 8 (up to 8 h after TCA dosing), 9 (24 h after), 10, and 12. Plasma TCA levels were assessed on Days 8 (before TCA dosing and up to 12 h after), 9 (24 h after), 10, 12, 15, 18, and 22.
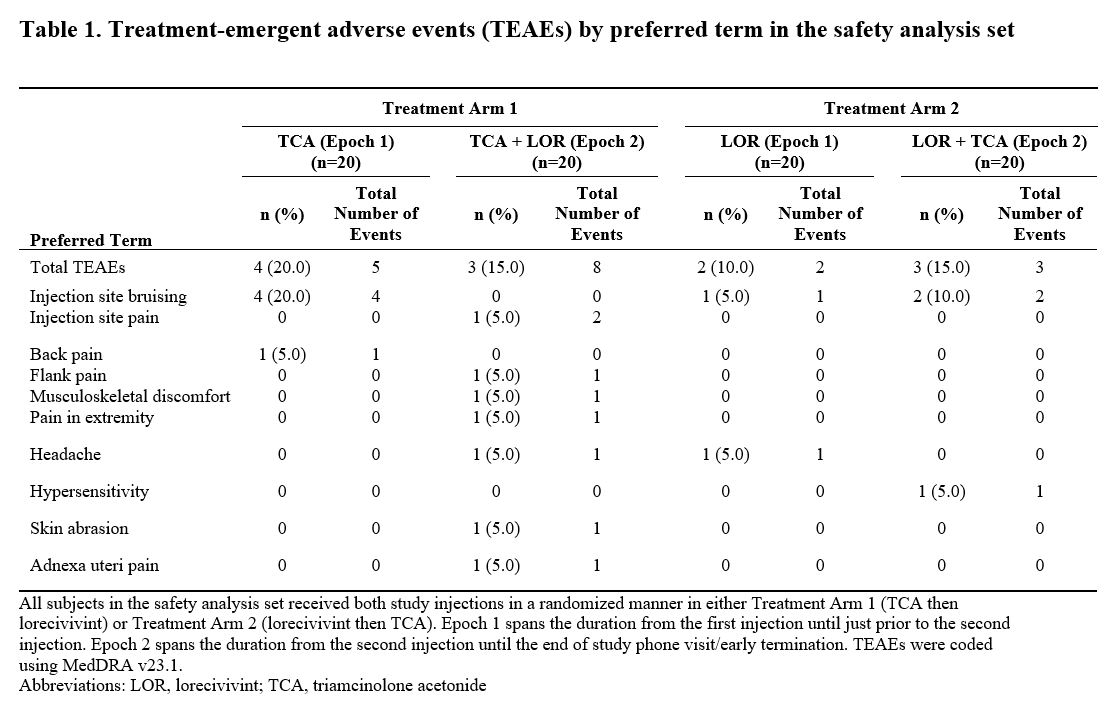
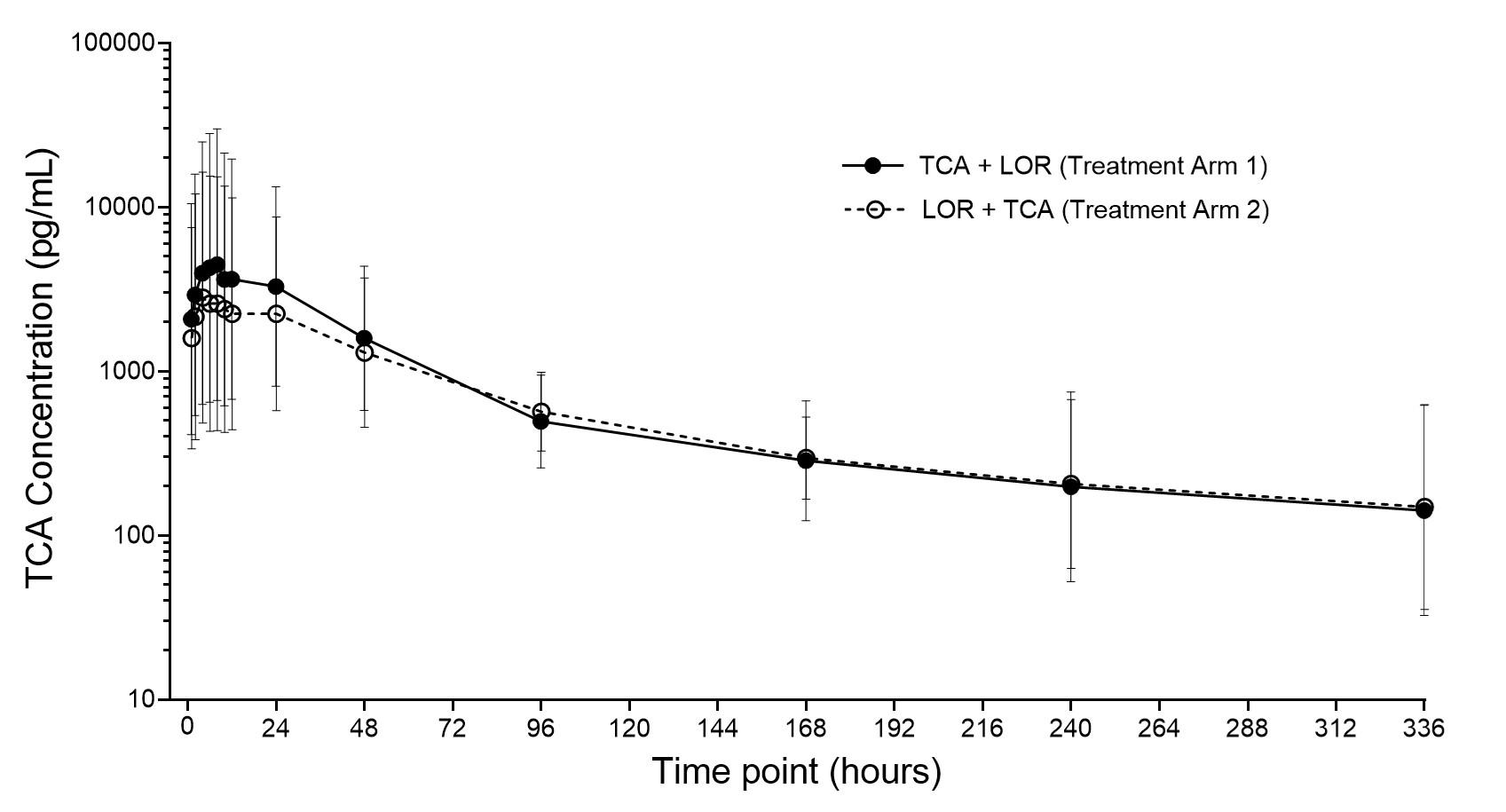
Results: Forty subjects (n=20/arm; age 41.3±7.2 years; BMI 27.8±2.98 kg/m2; female 40.0%) were evaluated. A total of 18 TEAEs were reported by 11 (27.5%) subjects (Table 1). TEAEs were similar between arms and there were no serious adverse events. In all subjects and at all time points, plasma lorecivivint concentrations were below the limit of quantification (0.1 ng/mL). Geometric mean concentrations (Figure 1) and PK parameters for TCA were similar between treatment arms.
Conclusion: There were no quantifiable plasma concentrations of lorecivivint in either treatment arm, and the PK of TCA was unaffected by previous lorecivivint injection. No safety signals were observed. These results suggest that IA administration of lorecivivint and triamcinolone in close proximity (7 days apart) should not pose a safety concern.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halseth A, Lane N, Kennedy S, Swearingen C, Lopez V, Simsek I, Fineman M, Yazici Y. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of an Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injection Administered 7 Days Before or After Intra-articular Lorecivivint Injection into the Same Knee of Healthy Volunteers: An Open-Label, Parallel-Arm Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-tolerability-and-pharmacokinetics-of-an-intra-articular-corticosteroid-injection-administered-7-days-before-or-after-intra-articular-lorecivivint-injection-into-the-same-knee-of-healthy-volun/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-tolerability-and-pharmacokinetics-of-an-intra-articular-corticosteroid-injection-administered-7-days-before-or-after-intra-articular-lorecivivint-injection-into-the-same-knee-of-healthy-volun/