Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Cardiovascular Pulmonary Disease (0268–0295)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Pulse pressure (PP) is defined as the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure and represents arterial compliance and reflective properties of blood flow. It is well known that gender, age, and ethnicity are intrinsic factors of the patient that influence PP. Brachial PP has recently been associated with subclinical cardiovascular disease after adjustment with traditional cardiovascular risk factors in the general population. However, this relationship has not been studied in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its identification would allow earlier adjustments of cardiovascular therapies in this high-risk group.
The aim of the study is to analyze the difference of PP between patients with RA and healthy controls. Additionally, to analyze the difference between RA patients with carotid plaque (CP) and without CP.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional, observational, and comparative study of 92 patients with RA aged 40-75 years and who fulfilled the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria. Also, we included 92 controls without RA, matched by gender, age and comorbidities. A carotid ultrasound was performed in RA patients and they were divided into two subgroups, patients with CP and without CP. Blood pressure measurement was taken after 15 minutes of rest on the left arm of all study subjects. Distribution was evaluated with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Descriptive analysis was done using measures of central tendency. Chi-square, Student’s t test and Mann-Whitney U test were used for comparations between groups.
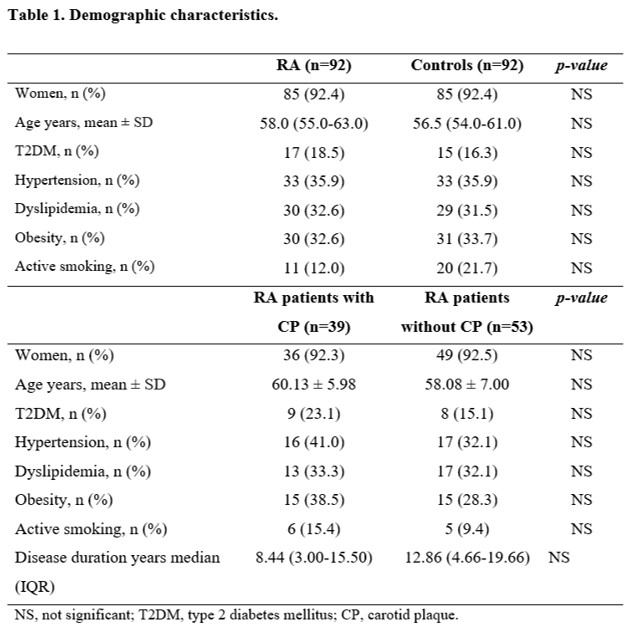
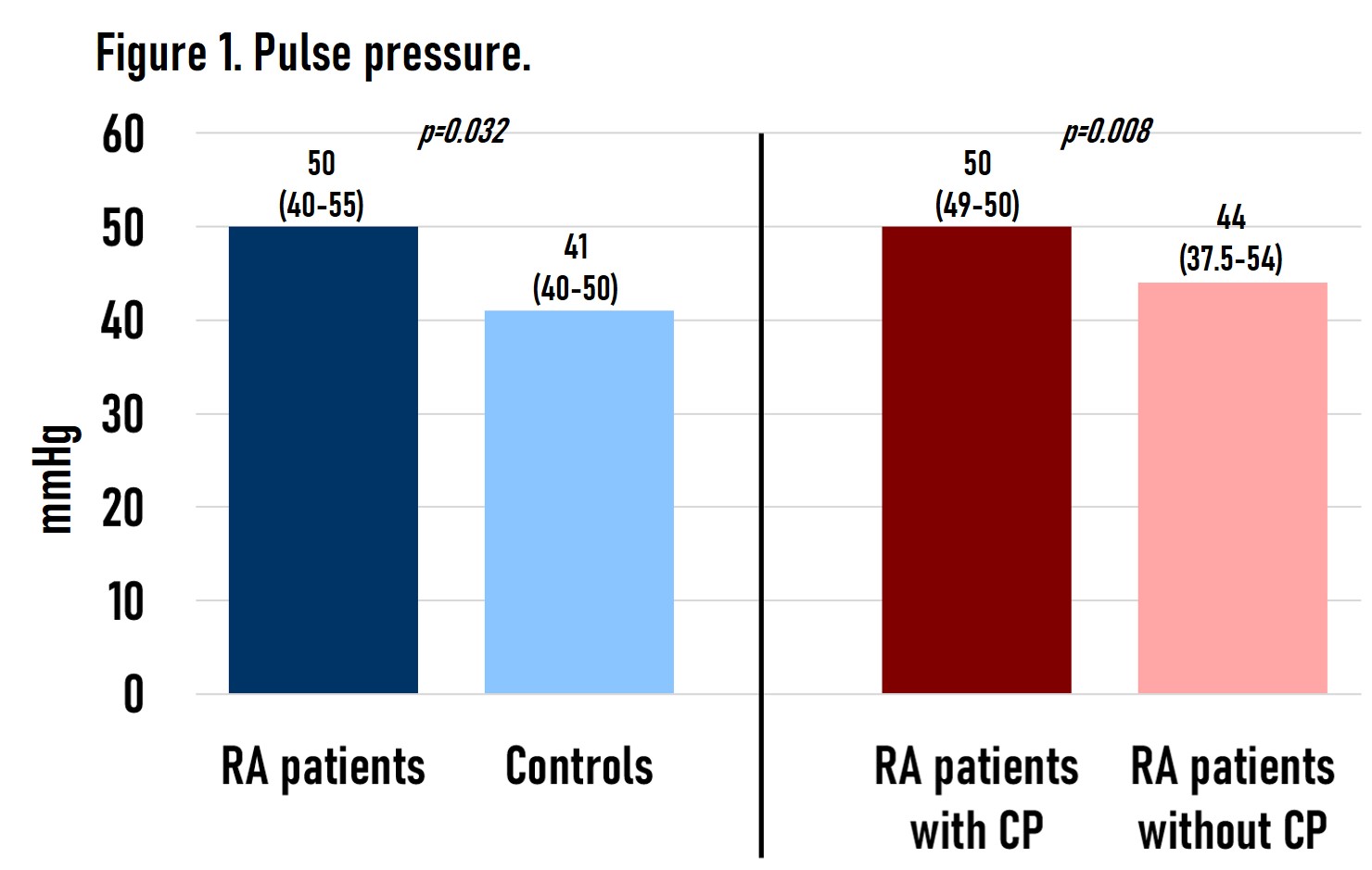
Results: We found no differences between groups regarding age, gender, and comorbidities (type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and active smoking) (Table 1). There was a significant difference in PP between patients with RA and controls (50 mmHg vs 41 mmHg respectively, p=0.032). When comparing RA patients there was a significant difference in PP of patients with CP and without CP (50 mmHg vs 44 mmHg respectively, p=0.008) (Figure 1). When performing a binary logistic regression, it was found that PP was the only independent risk factor for the presence of CP in patients with RA, OR 1.054 (95% CI 1.008-1.101, p=0.020).
Conclusion: Patients with RA had a higher PP than controls. Binary logistic regression showed PP as the only independent risk factor for the presence of subclinical atherosclerosis in RA patients. PP is a parameter that all rheumatologists should consider when evaluating cardiovascular risk in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guajardo-Jauregui N, Colunga-Pedraza I, Azpiri-Lopez J, Galarza-Delgado D, Rodriguez-Romero A, Loya-Acosta J, Meza-Garza A, Cardenas-de La Garza J, Lugo-Perez S, Castillo-Treviño J. Pulse Pressure as a Predictor of Carotid Plaque in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pulse-pressure-as-a-predictor-of-carotid-plaque-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pulse-pressure-as-a-predictor-of-carotid-plaque-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/