Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) includes both ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and non-radiographic axial disease (nr-axSpA). Our purpose was to investigate genetic heterogeneity of clinically diagnosed axSpA.
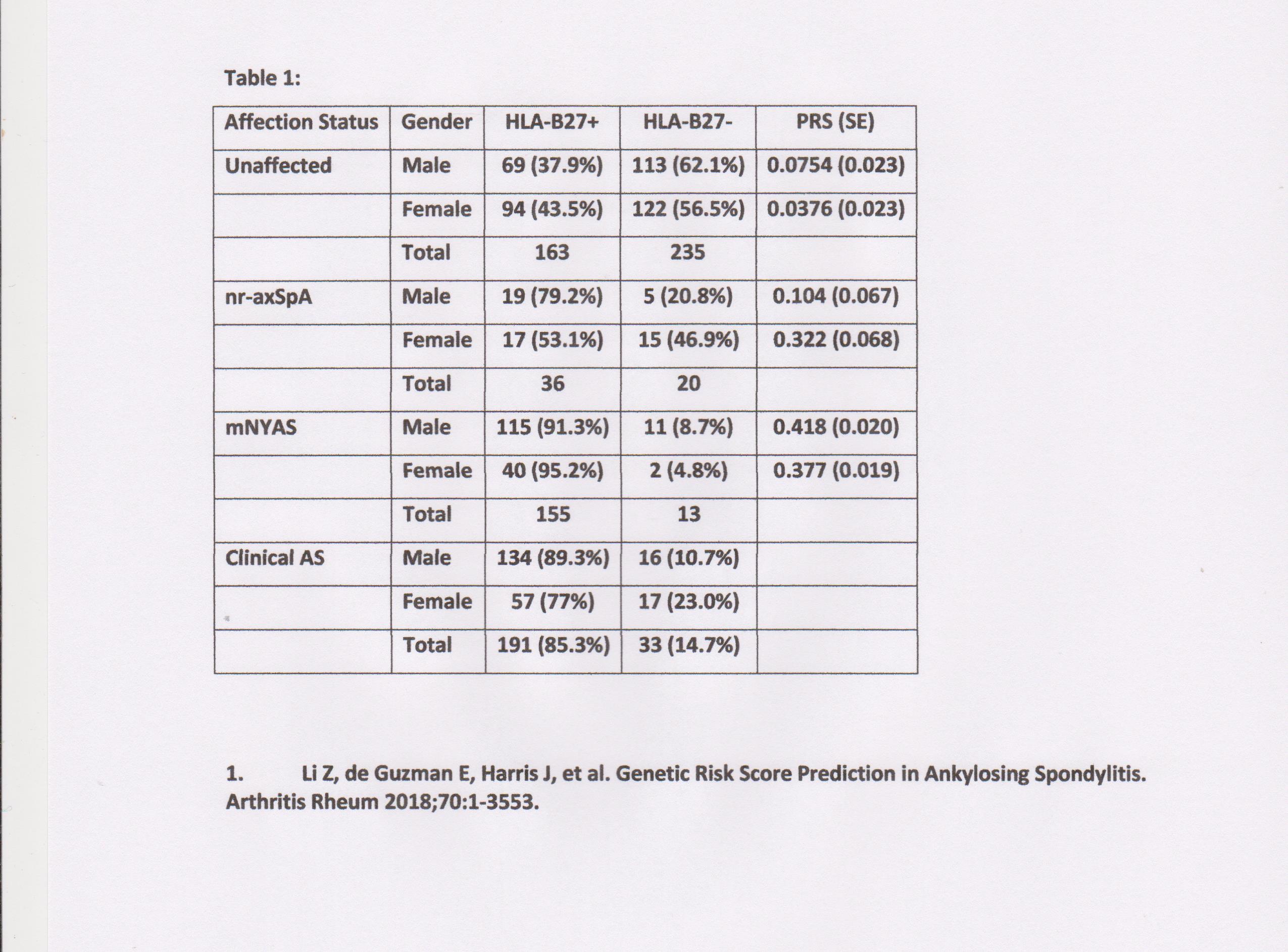
Methods: In 1985 members of the Swiss AS Patient Society who had been diagnosed as having AS by their own physicians, and also their first-degree relatives whether or not they had any rheumatic disease, were invited to participate in this study. 1178 subjects, 355 of them probands, formed our study cohort. Participants completed questionnaires on disease manifestations, underwent rheumatological examination of axial and peripheral joints, and radiography of the sacroiliac joints. Further, they provided blood samples for genetic studies, including HLA-B27. Radiographs were graded according to the modified New York (mNYAS) criteria for AS. Patients diagnosed clinically with AS but with negative radiographs were considered to have nr-axSpA, whereas those with negative clinical diagnoses and radiographs were considered healthy. DNA from 702 participants was genotyped using Illumina CoreExome arrays, and a polygenic risk score (PRS) calculated from this genotype data, as previously reported1. Discriminatory capacity of the PRS between diagnostic groups, and comparing males and females was examined by receiver operator characteristic area under the curve (AUC) analysis.
Results: HLA-B27 was present in 191/224 (85.3%) probands, with HLA-B27 carriage being more common in men than women (odds ratio (OR)= 2.50, p=0.015). The lower HLA-B27 carriage amongst women clinically diagnosed with AS was due to a higher proportion of women with nr-axSpA than with AS being HLA-B27 negative (OR=3.35, P=0.044), with no difference in the HLA-B27 carriage rates of men and women with mNYAS (P=0.41). Considering PRS, both men and women with mNYAS, but only men with nr-axSpA, had higher PRS than healthy subjects (P< 5x10-4 all comparisons). The PRS was higher in men than women with nr-axSpA (0.32 vs 0.10, P=0.029), whereas no difference in PRS was observed comparing men and women with mNYAS (0.80 vs 0.78, P=0.60). Whilst the PRS clearly distinguished males with nr-axSpA from healthy subjects (AUC=0.73, P=1.9×10-4), it was not able to distinguish females with nr-axSpA from healthy subjects (AUC=0.51, P=0.90). The PRS was not able to distinguish men with mNYAS from those with nr-axSpA (AUC=0.50), whereas it clearly distinguished women with mNYAS from those with nr-axSpA (AUC=0.73, P=6.4×10-4).
Conclusion: Whilst men and women with mNYAS have disease that is genetically similar, and men with nr-axSpA had PRS that was similar to mNYAS and distinct from healthy subjects, women with nr-axSpA had similar PRS to healthy subjects and distinct from women with mNYAS. This indicates that women clinical diagnosed with AS, but who are x-ray negative, as a group have a disease that is distinct from mNYAS overall, and from nr-axSpA in men. This study also demonstrates that PRS have good discriminatory performance for nr-axSpA in men.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li Z, Khan M, Khan M, Villiger P, Baumberger H, Zandwijk H, van der Linden S, Brown M. Heterogeneity Amongst Men and Women with Ankylosing Spondylitis and Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-amongst-men-and-women-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-amongst-men-and-women-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/