Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Bench to Bedside
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Despite improvement in management and outcomes of pregnancies complicated by SLE, the risk of adverse events and preeclampsia (PE) continues to exceed that of healthy women. Activation of the complement system has been associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes (APO). This study extends prior observations and addresses whether detection of erythrocyte complement receptor 1 (ECR1) and C4d bound to erythrocytes (EC4d) predict APO
Methods: Pregnant women fulfilled ACR or SLICC criteria for SLE. Serum complement proteins C3 and C4 were measured by immunoturbidimetry and anti-dsDNA by ELISA. ECR1 and EC4d were measured by quantitative flow cytometry and are expressed as net mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Disease activity was evaluated by the SLE Pregnancy Disease Activity Index (SLEPDAI) and the physician global assessment (PGA on a 0 to 3 scale) without knowledge of study analytes. Statistical analysis consisted of t-test and determination of diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) to evaluate association of inflammatory biomarkers (including ECR1 and EC4d) with APO (defined as neonatal death, pre-term delivery [< 36 weeks due to placental insufficiency], < 5th percentile for gestational age [SGA]) and PE at any time.
Results: A total of 51 women (33% white, 27% black, 18% Asians, 18% Hispanics, 4% of other races) had a total of 56 pregnancies (mean age 32 years, range 17 to 42) and 168 visits (median=3) during their pregnancy (n=34, 59, and 49 in first, second, and third trimesters, respectively) or postpartum period (n=26). The average SLEPDAI was 2.8, 3.5, and 2.9 in first, second, and third trimesters, respectively and PGA was 0.39, 0.54, and 0.40. APO and PE data are reported in the Figure. Overall 22% of pregnancies resulted in an APO. Specifically, 12 pregnancies resulted in a total of 19 APO (3 neonatal deaths; 8 births < 36 weeks [range 25 – 35.9 weeks] and 8 SGA). Eleven pregnancies in 10 women resulted in PE. ECR1, EC4d, and C4 were significantly associated with APO when all visits that occurred during pregnancy (n=142) were analyzed. ECR1 and EC4d also associated with PE. Anti-dsDNA and C3 were not associated with any of these outcomes (Table; top). Analysis of the individual APO showed that ECR1 was associated with preterm delivery (Table; top). For preterm delivery, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of ECR1 was 0.697 (95% CI: 0.585-0.808). At ECR1 < 5.5 net MFI (optimum cutoff), sensitivity and specificity were 72% and 79%, respectively (Youden index = 0.51). Low ECR1 (< 5.5 net MFI) remained significant for preterm delivery when only baseline visits that occurred in the first trimester (n=32 visits with 7 pregnancies experiencing 9 APO) were analyzed (DOR = 30.67) (Table; bottom).
Conclusion: This prospective study demonstrates that low ECR1 and elevated EC4d are associated with APO and late PE in SLE pregnancies. Of the traditional biomarkers in SLE (C3, C4, dsDNA) only low C4 associated with APO. Importantly, low ECR1 early in pregnancy predicted preterm delivery and, to a lesser extent, other APO. In conclusion, complement activation as measured by EC4d and ECR1 may be a predictor of pregnancy complications.
 Table. T-test and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of complement markers (EC4d, ECR1, serum C3, and serum C4) and anti-dsDNA to evaluate association and prediction of APO, preeclampsia (PE) and preterm delivery. Data of all visits during pregnancy (post-partum visits excluded, n=142; TOP) and of baseline visits that occurred in the first trimester (n=32; BOTTOM) were analyzed. Two women had 2 visits each in the first trimester; thus, there was a total of 34 visits in the first trimester, of which 32 were baseline. Note that some patients had baseline visits after the first trimester. For t-test, continuous variables were analyzed, while variables were considered positive or negative (based on the cutoffs indicated in the table) for DOR calculation. DOR is reported with 95% confidence intervals [95% CI]. Significant p values ( < 0.05) are bolded.
Table. T-test and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of complement markers (EC4d, ECR1, serum C3, and serum C4) and anti-dsDNA to evaluate association and prediction of APO, preeclampsia (PE) and preterm delivery. Data of all visits during pregnancy (post-partum visits excluded, n=142; TOP) and of baseline visits that occurred in the first trimester (n=32; BOTTOM) were analyzed. Two women had 2 visits each in the first trimester; thus, there was a total of 34 visits in the first trimester, of which 32 were baseline. Note that some patients had baseline visits after the first trimester. For t-test, continuous variables were analyzed, while variables were considered positive or negative (based on the cutoffs indicated in the table) for DOR calculation. DOR is reported with 95% confidence intervals [95% CI]. Significant p values ( < 0.05) are bolded.
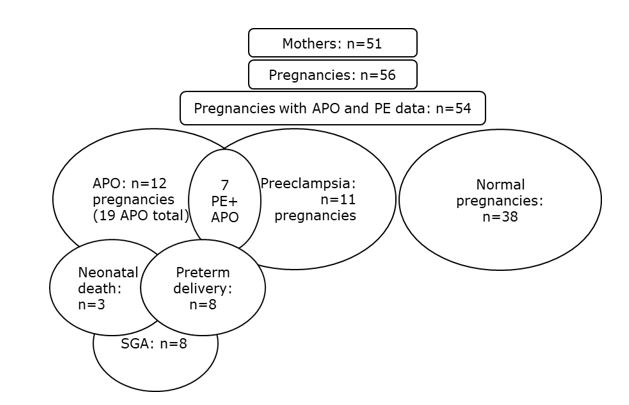 Figure. Flowchart of the patient population
Figure. Flowchart of the patient population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buyon J, Conklin J, Golpanian M, Ligayon J, Dervieux T, Izmirly P, Belmont H, Salmon J, Alexander R. Erythrocyte Complement Receptor 1 (ECR1) and Erythrocyte Bound C4d (EC4d) Associate with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/erythrocyte-complement-receptor-1-ecr1-and-erythrocyte-bound-c4d-ec4d-associate-with-adverse-pregnancy-outcomes-and-preeclampsia-in-pregnant-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/erythrocyte-complement-receptor-1-ecr1-and-erythrocyte-bound-c4d-ec4d-associate-with-adverse-pregnancy-outcomes-and-preeclampsia-in-pregnant-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/
