Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III: Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Diclofenac sodium gel 1% (DSG), a topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is effective for the relief of osteoarthritis (OA) pain in the elbows, wrists, hands, feet, ankles, and knees. Over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, including DSG, carry label warnings for systemic side effects, such as gastrointestinal (GI), cardiovascular (CV), and hepatic events. However, in controlled clinical trials, DSG had similar rates of these adverse events as placebo, with only application-site reactions reported more frequently. This study was conducted to support the switch of DSG from a prescription to an OTC product in the USA (OTC approved February 2020) and to further evaluate DSG for NSAID-associated events of interest (EOIs) in a real-world setting.
Methods: This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study sourced data from the United States Department of Defense Military Health System (MHS) electronic health records database. The study period was 01Jan2007 to 31Dec2016. Individuals with ≥1 prescription for DSG dispensed between 01Jan2008 and 30June2016 (screening period) and ≥1 year of continuous enrollment/eligibility in the MHS prior to their first DSG prescription fill in the screening period (index date) were included. ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM diagnosis, ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-PCS procedure codes, and medications (as proxy) were used to identify specific EOIs (ie, GI, hepatic, or renal injury/disease, CV event/disease, incident or exacerbated hypertension, skin reactions, misuse/abuse, and death). These were assessed from the index date until earliest occurrence of last DSG treatment episode end date, disenrollment from MHS, death, or end of study (follow-up period).
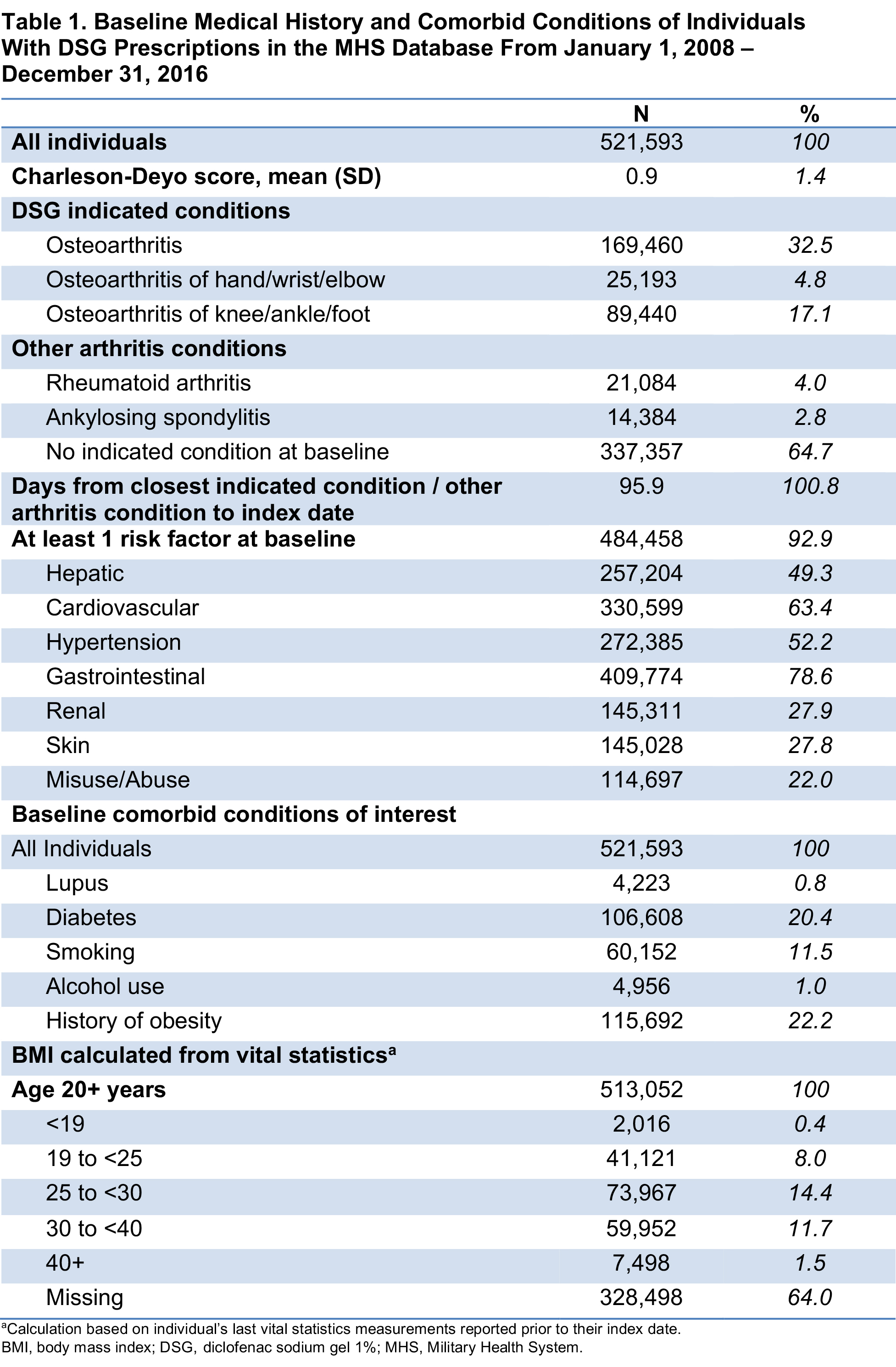
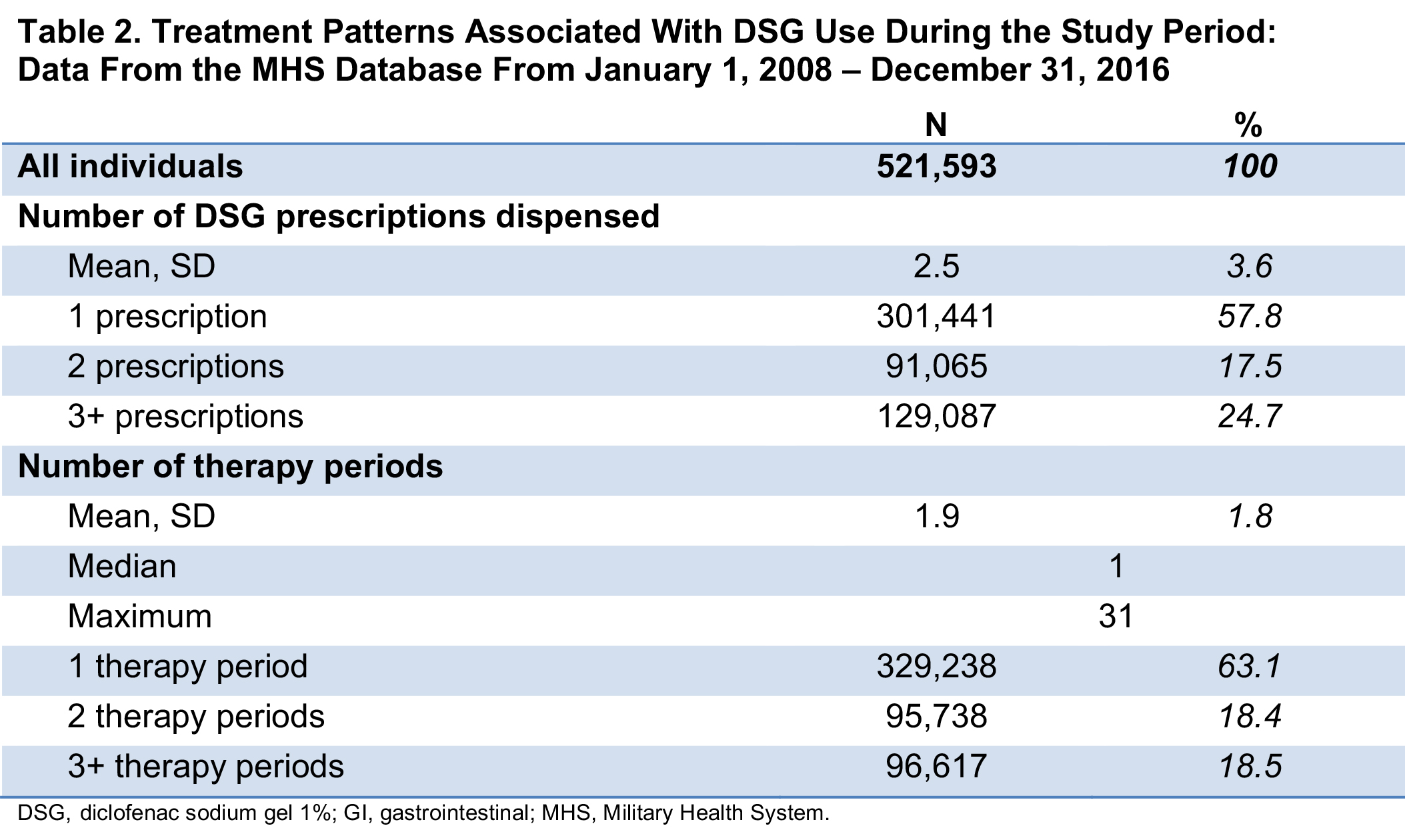
Results: For 521,593 individuals with ≥1 DSG prescription fill who met study criteria, mean age was 57 years and 60% were female; the median duration of follow-up was 60 days. Overall, 79% of the study population had baseline diagnoses of musculoskeletal and/or connective tissue diseases, and 32% had a baseline diagnosis of OA (Table 1). Comorbidities included obesity, diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, and lupus (Table 1). At baseline, >50% of patients also had filled prescriptions for NSAIDs or opioids. Overall, 93% of the population had risk factors at baseline associated with ≥1 of the 7 study EOIs (excluding death; Table 1); baseline risk factors for GI, CV, hypertension, and hepatic events were 79%, 63%, 52%, and 49%, respectively. In presence of baseline risk factors, 26% of the population experienced ≥1 EOI during the study period; mean (SD) time from index date to first event was 244 (369) days. An average of 2.5 DSG prescription fills per patient was dispensed during the study period (Table 2).
Conclusion: The >500,000 DSG users in this retrospective study were generally older, more likely to be female, and had baseline comorbidities and risk factors of interest. Over half had a history of NSAID or opioid use at baseline. This study found that few DSG users (< 15%) had any single EOI despite baseline comorbidities and risk for these events, and that the EOIs on average occurred after the last prescription fill when DSG was no longer being used.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kenneally A, Bariguian F, Petruschke R, Tave A, Edison J, Sicignano N, Barbone F. Profile of Topical Diclofenac Sodium Gel 1% (Voltaren®) Users in a United States Longitudinal Electronic Health Records Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/profile-of-topical-diclofenac-sodium-gel-1-voltaren-users-in-a-united-states-longitudinal-electronic-health-records-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/profile-of-topical-diclofenac-sodium-gel-1-voltaren-users-in-a-united-states-longitudinal-electronic-health-records-database/