Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The use of large administrative health datasets is increasingly important in Rheumatology for disease trends and outcome research. We established the West Australian Rheumatic Disease Epidemiological Registry containing longitudinal health data for over 10000 patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Western Australia (WA). Accuracy of coding for RA is essential to validity of the datasets. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) based discharge codes for RA at WA’s largest tertiary hospital.
Methods: Medical records for RA patients randomly selected from the hospital discharge database with ICD 10 codes (M05.00–M06.99) from 2008–2020 were retrospectively reviewed. Rheumatologist‐reported diagnosis and ACR/EULAR classification were used as gold standards to determine positive predictive value (PPV) with 95% Confidence Interval (CI) for RA primary diagnostic codes.
Results: Medical chart review was completed for 87 patients (mean age 64.7 years, 67% female). Total of 80 (92%) patients had specialist confirmed RA diagnoses, while seven patients (8%) had alternate clinical diagnoses providing a PPV of 93.5% (95%CI: 89.9 to 95.86). Overall, 69 out 87 patients (79.3%) fulfilled ACR/EULAR classification criteria based on RA primary diagnostic codes with a PPV of 80.5% (95%CI: 76.81 to 83.7). A combination of a diagnostic RA code with biologic infusion codes in two or more codes increased the PPV to 97.9%.
Conclusion: Hospital discharge diagnostic codes in WA identify RA patients with a high degree of accuracy. Combining a primary diagnostic code for RA with biological infusion codes can further increase the PPV.
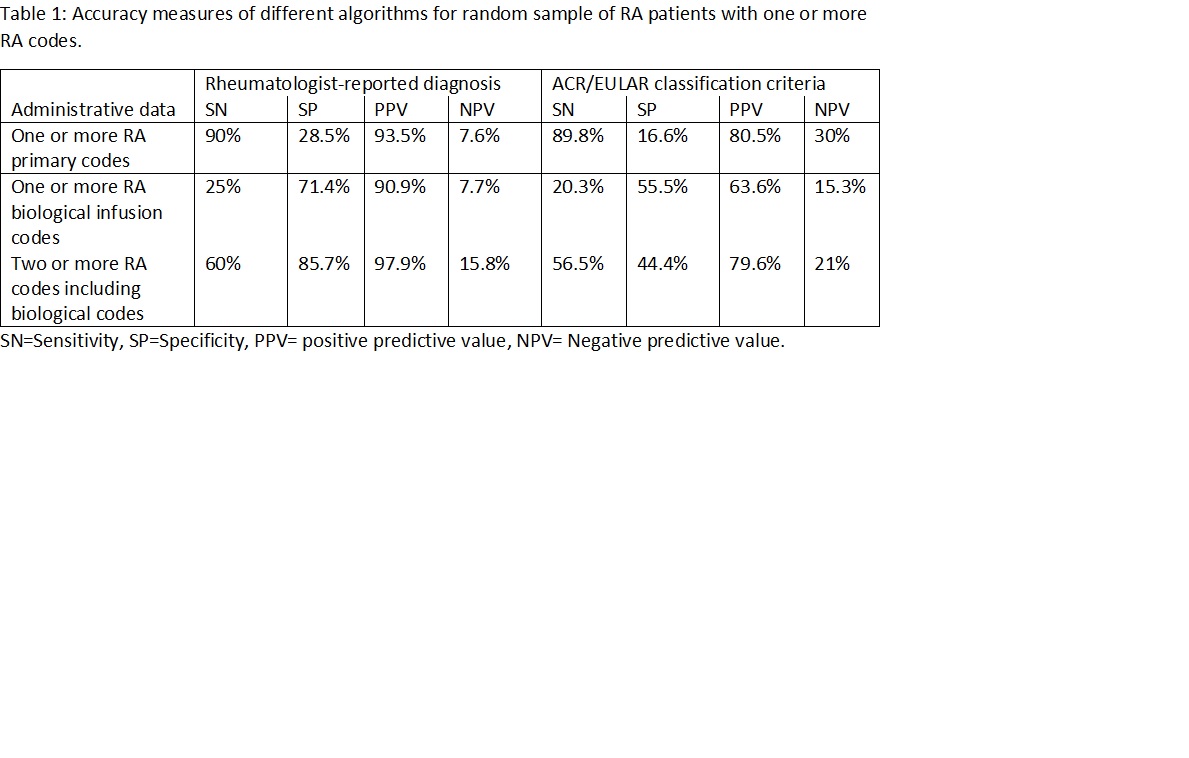 Table 1: Accuracy measures of different algorithms for random sample of RA patients with one or more RA codes.
Table 1: Accuracy measures of different algorithms for random sample of RA patients with one or more RA codes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almutairi K, Nossent J, Preen D, Keen H, Rogers K, Inderjeeth C. The Accuracy of Administrative Health Data for Identifying Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Validation Study Using Medical Records in Western Australia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-accuracy-of-administrative-health-data-for-identifying-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-validation-study-using-medical-records-in-western-australia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-accuracy-of-administrative-health-data-for-identifying-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-validation-study-using-medical-records-in-western-australia/
