Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Combined thermal and ultrasound (US) imaging modalities in detecting joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has not been evaluated relative to thermal or US imaging alone. Therefore, we aim to compare outcomes of the combined imaging modalities versus single imaging modality using the routinely performed 28-joint disease activity score (DAS28).
Methods: Thermography and ultrasonography were performed on 22 joint sites (bilateral hands and wrists) at the same study visit. Maximum (Tmax), minimum (Tmin) and average (Tavg) temperatures at each joint were recorded. For each patient, the lowest Tmin temperature among all joints testing negative for joint inflammation by both US power Doppler (PD) and grey-scale (GS) was defined as the patient’s control temperature and subtracted from Tmax, Tmin and Tavg temperatures at all 22 joints for that patient. Differences with the control temperature for the respective parameters (Tmax, Tmin and Tavg) were then summed across all joints to obtain MAX, MIN and AVG values for each patient. US PD and GS joint inflammation scores (graded semi-quantitatively 0-3 at each joint recess), respectively, were summed for the 22 joints to obtain Total PD and Total GS scores per patient. MAX (PD), MIN (PD) and AVG (PD) represent the results of combined thermal and US PD imaging. As a greater PD vascularity indicates more inflammation at the joints, when a patient’s Total PD score was greater than the median value, to increase its weightage to the combined imaging scores, the patient’s MAX (PD), MIN (PD) and AVG (PD) were derived by multiplying MAX, MIN and AVG by a factor of 2. Otherwise, the patient’s MAX (PD), MIN (PD) and AVG (PD) remained the same as the MAX, MIN and AVG (without multiplying by 2).
Results: In this cross-sectional study, 814 joints were studied in 37 RA patients with the following patients’ baseline characteristics: mean (SD) age, 56.5 (13.8) years; majority female, 28/37 (75.7%); majority Chinese, 28/37 (75.7%); mean (SD) disease duration of 30.9 (45.3) months; mean (SD) DAS28 of 4.43 (1.12); 31/37 (83.8%) patients were on one or more DMARDs (methotrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine and/or tofacitinib). Table 1 summarizes results of the correlation analysis between the imaging parameters and DAS28. Specifically, only MAX (PD) and AVG (PD) exhibited statistically significant correlation with DAS28 scores (MAX (PD): correlation coefficient (95% CI) 0.393 (0.079, 0.636), P=0.016; AVG (PD): 0.376 (0.060, 0.624), P=0.022). Figure 1 shows the scatter plots for the combined thermal and US imaging parameters versus DAS28. Table 2 summarizes the results of the simple linear regressions between the imaging parameters and DAS28. Specifically, only MAX (PD) and AVG (PD) were shown to be significantly correlated with DAS28 (MAX (PD): coefficient (95% CI), 0.0086 (0.0019, 0.0153); P=0.0161); AVG (PD): coefficient (95% CI), 0.0112 (0.0021, 0.0203); P=0.0217).
Conclusion: For the first time ever, combined thermal and US imaging in RA have been shown to be superior to either imaging modality alone in terms of correlation with DAS28. Longitudinal studies testing the use of combined thermal and US imaging in RA will be required.
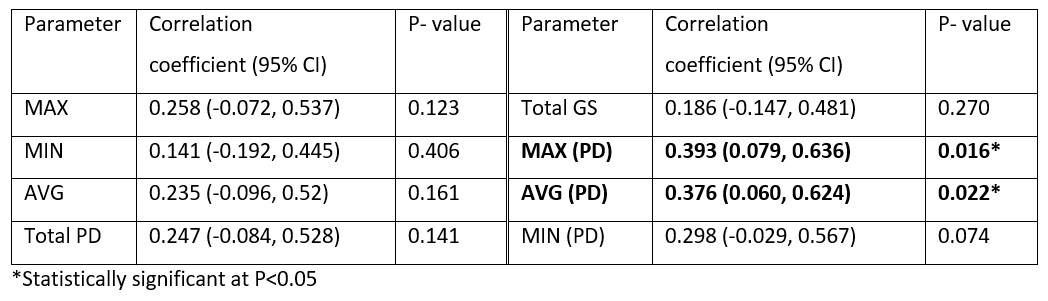 Table 1. Correlation between imaging parameters and DAS28.
Table 1. Correlation between imaging parameters and DAS28.
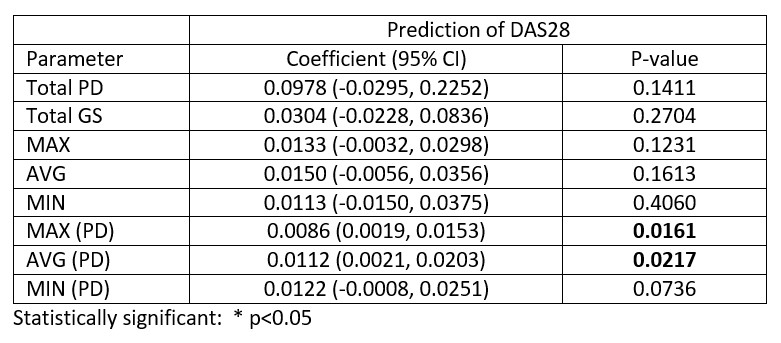 Table 2. Results of linear regression between the imaging parameters and DAS28.
Table 2. Results of linear regression between the imaging parameters and DAS28.
 Figure1. Scatter plots for the combined thermal and ultrasound imaging parameters versus DAS28.
Figure1. Scatter plots for the combined thermal and ultrasound imaging parameters versus DAS28.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tan Y, Hong C, Li H, Allen Jr J, Thumboo J. Combined Thermal and Ultrasound Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Superior to Either Imaging Alone in Terms of Correlation with the 28-joint Disease Activity Score [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combined-thermal-and-ultrasound-imaging-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-superior-to-either-imaging-alone-in-terms-of-correlation-with-the-28-joint-disease-activity-score/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combined-thermal-and-ultrasound-imaging-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-superior-to-either-imaging-alone-in-terms-of-correlation-with-the-28-joint-disease-activity-score/
