Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Cardiopulmonary Aspects
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To assess the Cardiovascular Risk (CV) in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients using carotid ultasonography additionally to the traditional CV risk factors.
Methods: A single center cross-sectional case control study was performed. Inclusion criteria were adult patients who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2010 RA criteria (cases) and matched healthy adults in terms of age, sex and CV risk factors (controls). Population over 75 years old, patients with established CV disease and/or chronic kidney disease (from III Stage) were excluded. Controls with other inflammatory diseases, pregnant women or any malignancy were also excluded. This study was performed from July-2019 to January-2020.
CV risk assessment included risk factors collection such as serum biomarkers (glucose, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, Triglycerides, Creatinine, Glomerular filtrate [CKD-EPI], uric acid, C reactive protein [CRP], Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate [ESR]), Body Mass Index, life style habits, family history of early CV disease.
The US evaluator was blinded to the case/control condition and evaluated the carotid artery by using B-mode imaging of the arterial wall, color doppler flow analysis, presence of plaques, plaque number and measured the intima-media thickness in both right and left carotid.
Statistical analysis was performed with R software (3.6.1 version) and included a multivariate variance analysis (Manova) and a negative binomial regression adjusted by confounding factors.
Results: Overall, a total of 200 cases and 111 healthy controls were included in the study. Demographical and clinical variables were comparable between cases and controls and are shown in table 1. In both groups a relationship between age, BMI and high blood pressure was detected (p< 0.001). RA disease characteristics are displayed in table 2.
US study revealed a higher IMT in both right and left carotid arteries with greater presence of plaques in patients than in controls (CI 95% [1.542; 3.436], p< 0.001). Plaques were found in both carotid arteries in the 32% of cases and 9.91% of controls. The longer duration of RA was related to a higher presence of carotid plaques (95% [1.015; 1.056], p< 0.001). The age was also related to plaque development (CI 95% [1.051; 1.094], p< 0.001) as seen with high blood pressure (CI 95% [1.124; 2.27], p=0.012). Female sex protected against carotid plaques presence (CI 95% [0.367; 0.856], p=0-009). US and blood test results are shown in table 3.
Conclusion: RA leads to a higher intima-media thickness and this is related to the disease duration. Traditional risk factor may explain only partially the global CV risk in RA. These findings might support that RA acts as an independent cardiovascular risk factor.
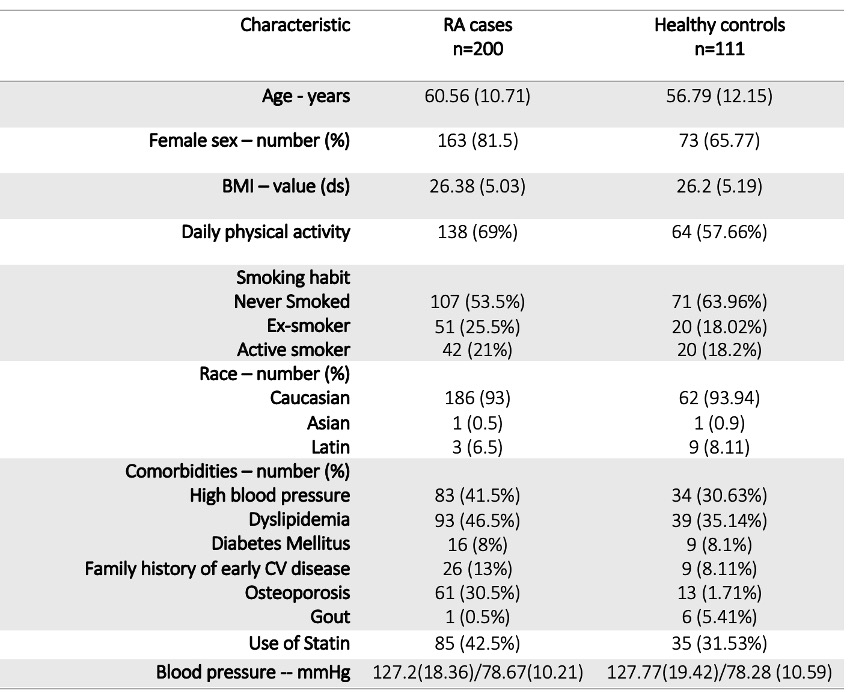 Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients and controls.
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients and controls.
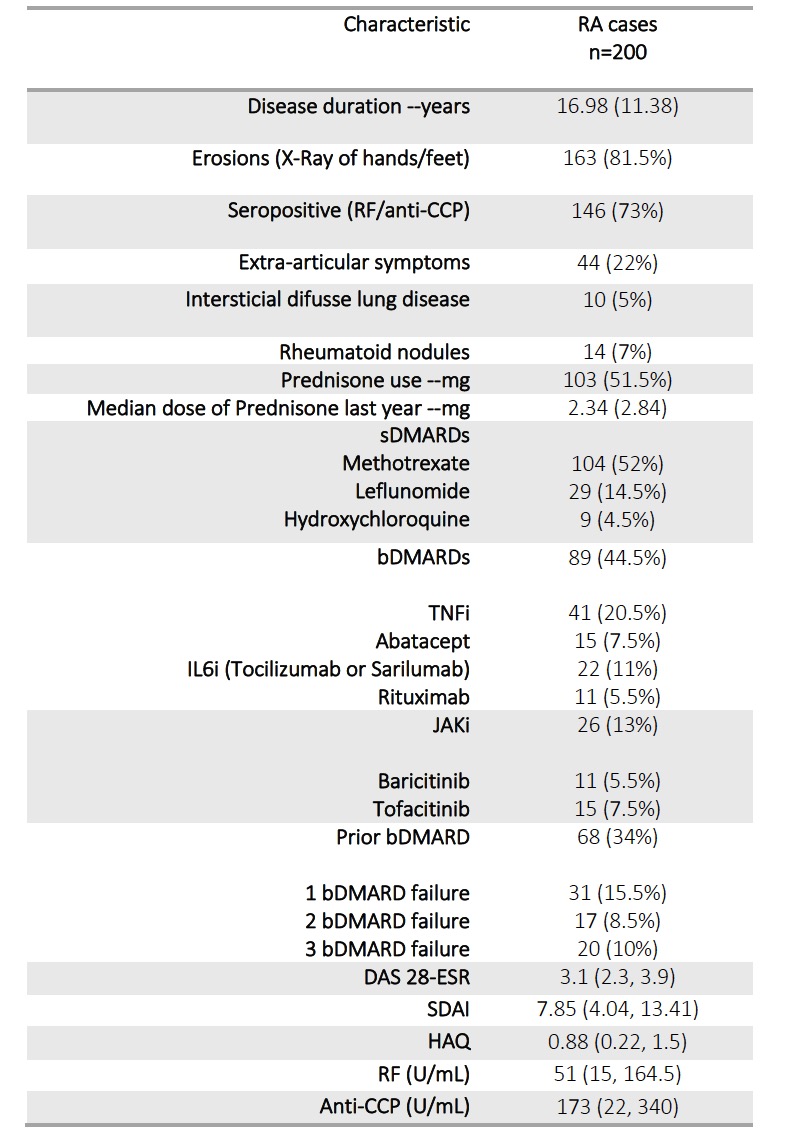 Table 2. Rheumatoid Arthritis disease characteristics among patients included.
Table 2. Rheumatoid Arthritis disease characteristics among patients included.
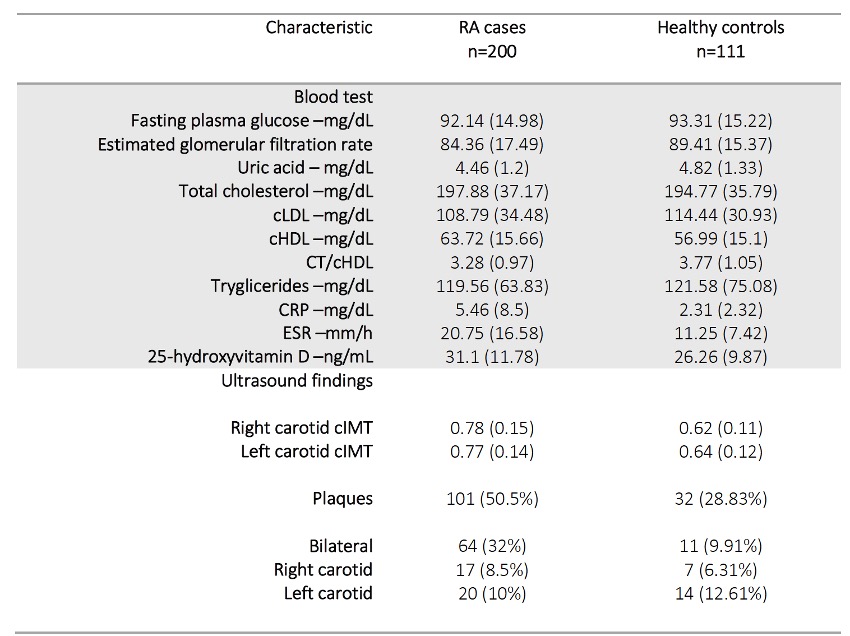 Table 3. Blood test and Ultrasound Results in patients and controls.
Table 3. Blood test and Ultrasound Results in patients and controls.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez Mazario R, Fragio Gil J, De la Rubia Navarro M, Pavez Perales C, Leal Rodriguez S, Ivorra Cortes J, Gonzalez Puig L, Grau Garcia E, Vicens Bernabeu E, Ortiz-Sanjuan F, Negueroles Albuixech R, Alcañiz Escandell C, Oller Rodriguez J, Chalmeta Verdejo I, Martinez Cordellat I, Najera Herranz C, Canovas Olmos I, Cañada Martínez A, Roman Ivorra J. Cardiovascular Risk Assessment with Carotid Ultrasonography in Addition to the Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-assessment-with-carotid-ultrasonography-in-addition-to-the-traditional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-assessment-with-carotid-ultrasonography-in-addition-to-the-traditional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-case-control-study/
