Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Skeletal myopathy in systemic sclerosis (SSc) is underappreciated yet an important manifestation of SSc. While it has been reported that there are distinct histopathologic subsets of myopathy, Multiparametric muscle magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) patterns are unknown and the degree of involvement is yet quantified. In order to determine whether unique mpMRI muscle tissue signatures exist in SSc associated myopathy, we implemented advanced mpMRI muscle techniques in the evaluation of SSc in patients with muscle weakness.
Methods: SSc patients were identified as having a skeletal myopathy as defined by proximal weakness and at least one abnormal diagnostic test such as muscle enzymes, EMG, MRI or muscle biopsy. Eligible SSc patients with a myopathy and age matched healthy controls were prospectively recruited. The mpMRI protocol consisted of anatomical and advanced functional sequences that included T1– and T2-weighted, T2 mapping, STIR, Dixon, and diffusion weighted images(DWI) and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Water (ADC) maps for detection and quantification the burden of muscle involvement in SSc associated myopathy. MpMRI between muscle groups in each cohort were tested using a paired t-test and significance was set at p< 0.05.
Results: There were a total of 10 patients, seven who met the 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria for systemic sclerosis and three healthy controls, who underwent the research mpMRI. Six of seven (86%) had diffuse cutaneous SSc. Four of the 7 patients had prior muscle biopsies and demonstrated muscle heterogeneity ranging from a fibrosing myopathy (n=1), necrotizing myopathy (n=2), and dermatomyositis (n=1). Five of the seven were on at least 1 immunosuppressant and/or IVIG for the treatment of myopathy. Mean creatine kinase was 152 + 111 within 3 months of the mpMRI. There were significant differences between abnormal and normal obturator muscle groups (external and internal) using mpMRI T2 map values (p=0.02). (Internal Right Side:130±28 versus 87±16 msec and Left Side:138±23 versus 91±16 msec), (External Right Side:157±26 versus 87±16 msec and Left Side:155±26 versus 100±33 msec). Similarly, the ADC values were significantly different in these muscle groups. Figure 1 depicts a representative case where the white arrows show the increased signal intensity in the obturators on the STIR, T2 maps and ADC maps in a patient compared to a normal control.
Conclusion: In this preliminary study of SSc patients with skeletal myopathy, we demonstrated that by using advanced mpMRI, techniques, the obturator muscles of the pelvis were preferentially affected by SSc compared to healthy controls. Advanced muscle mpMRI could be a useful non-invasive imaging biomarker for muscle disease in SSc associated myopathy that provides new quantifiable metrics.
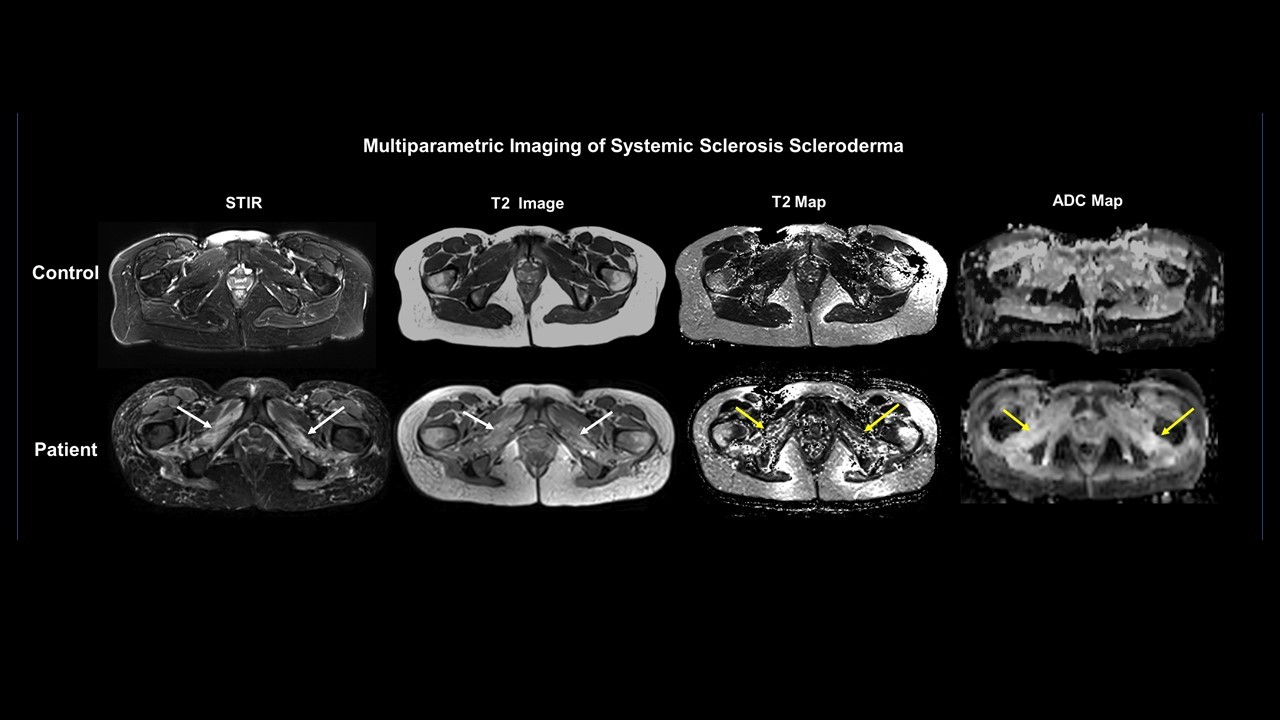 Representative cases of Multiparametric muscle MRI in a control and SSc patient
Representative cases of Multiparametric muscle MRI in a control and SSc patient
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paik J, Wigley F, Fayad L, Hummers L, Jacobs M. Advanced Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Muscle for Detection and Quantification of Muscle Disease in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/advanced-multiparametric-magnetic-resonance-imaging-of-muscle-for-detection-and-quantification-of-muscle-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/advanced-multiparametric-magnetic-resonance-imaging-of-muscle-for-detection-and-quantification-of-muscle-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/
