Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) is a parameter that represents the number of lymphocytes (B, T, and NK cells) in the blood, and lymphopenia often accompanies rheumatologic disease. Lymphopenia, even in those without rheumatologic disease, has been associated with worse survival due to cardiovascular disease (CVD), especially when accompanied by other pro-inflammatory surrogates, including increased red cell distribution width (RDW). The connection between rheumatic disease and increased risk of atherosclerotic disease has been established, but there is lack of data on ALC levels in patients with psoriatic arthritis. We sought to test the hypothesis that alterations in immunohematologic abnormalities in the setting of psoriatic arthritis may in part reflect traditional cardiovascular risk factors, but are also driven by inflammation.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review study examining the relationship between ALC, RDW, and traditional atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk in a cohort (n=170) of patients with psoriatic arthritis at the Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center. All patients had an ICD-10 diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis and either a rheumatologist confirmed diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis or met CASPAR criteria. ASCVD risk was quantified using the pooled cohort equation risk model (based on age, gender, race, presence of hypertension or diabetes, lipid profile, and smoking status). We examined patient treatment history and recorded laboratory values in relation to treatment to understand the effect of immunomodulation on these parameters. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for statistical analysis.
Results: ALC was negatively correlated with ASCVD score (r=-0.28, p=0.001) (Figure 1). Positive correlations were observed between ASCVD score and RDW (r= 0.339, p=0.01), ASCVD score and ESR (r=0.20, p=.02), and negative correlations were observed between ASCVD score and albumin (r=-.20, p=.01), and ASCVD score and hemoglobin (r=-.22, p=.009). When evaluating parameters over the course of therapy, those who were started on TNF-inhibitor therapy (n=60) had an increase in ALC between time 0 and 6 months (p = 0.007), and this was maintained at twelve months (p = 0.032) (Figure 2). Patients on TNF-inhibitor therapy also experienced a decline in RDW at 6 months (p = 0.004) and at 12 months (p = 0.014) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Our data shows that abnormal lymphocyte levels and RDW are associated with traditional cardiovascular risk factors but also tend to revert with anti-TNF therapy. Thus, correlates of immunohematologic dysfunction relevant to CVD risk may be dynamic and modified by reducing inflammation, at least in psoriatic arthritis. Future studies to define whether trajectories of ALC or RDW can improve cardiovascular disease risk stratification both in psoriatic arthritis and in the general population are warranted.
 Figure 1: There was a negative, statistically significant, correlation between ALC and ASCVD risk score. As ASCVD score increased, ALC value decreased.
Figure 1: There was a negative, statistically significant, correlation between ALC and ASCVD risk score. As ASCVD score increased, ALC value decreased.
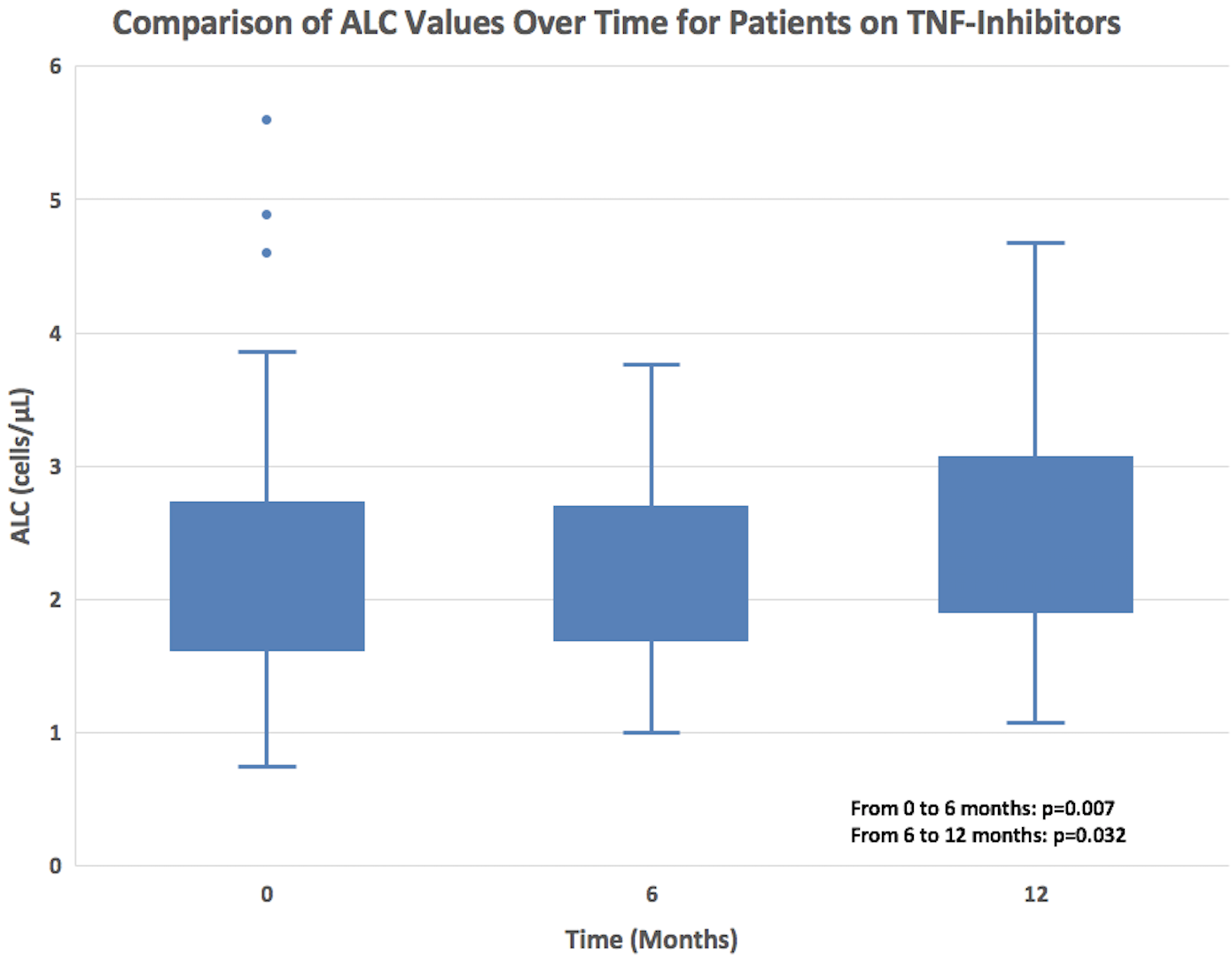 Figure 2: Patients on TNF-inhibitor therapy exhibited a statistically significant increase in ALC over the course of 12 months.
Figure 2: Patients on TNF-inhibitor therapy exhibited a statistically significant increase in ALC over the course of 12 months.
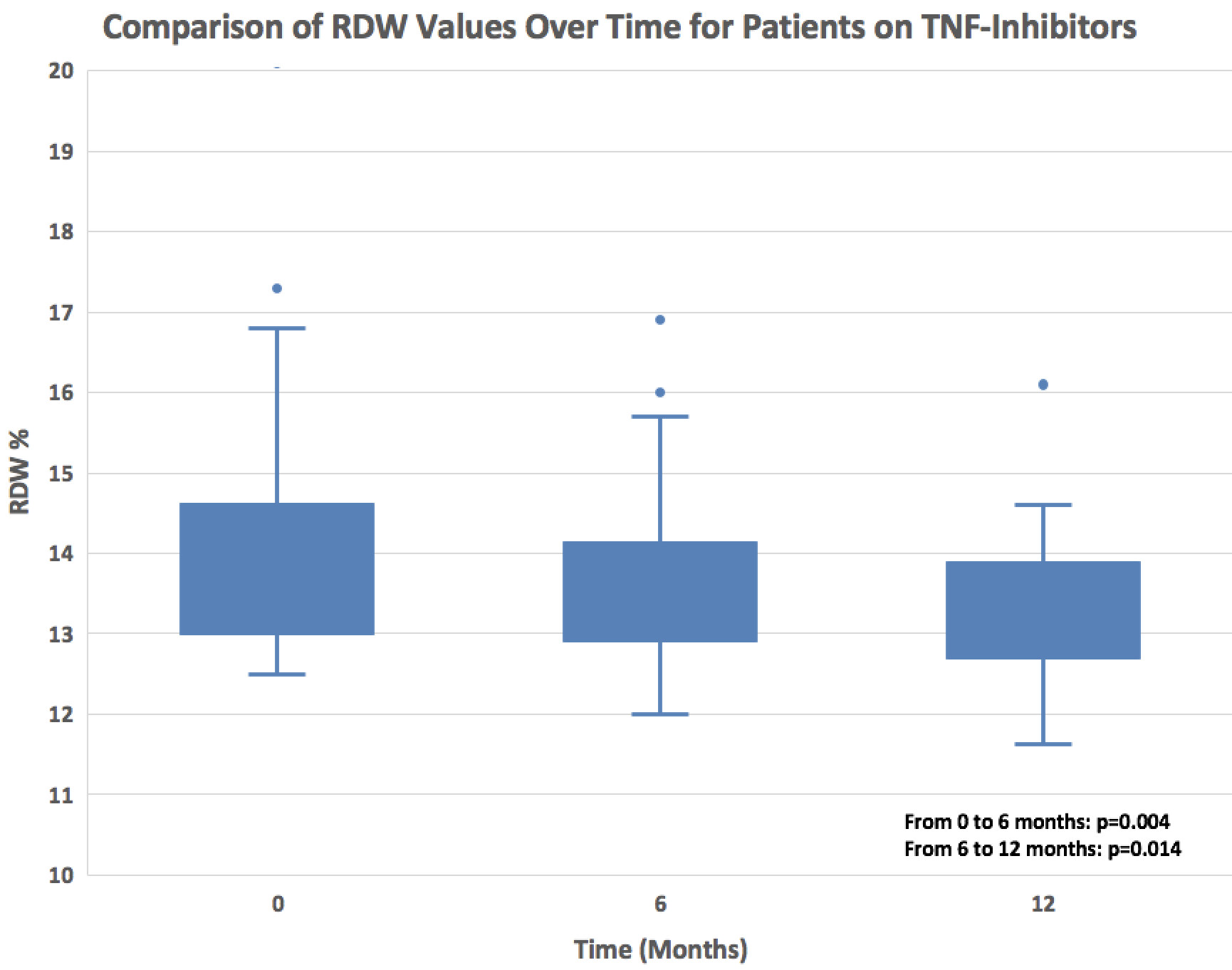 Figure 3: Patients on TNF-inhibitor therapy exhibited a statistically significant decline in RDW over the course of 12 months.
Figure 3: Patients on TNF-inhibitor therapy exhibited a statistically significant decline in RDW over the course of 12 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta A, Damjanovska S, Lange A, Wilson B, Bej T, Mattar M, Zidar D, Anthony D. Absolute Lymphocyte Count Is Negatively Correlated with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score and Red Cell Distribution Width in Psoriatic Arthritis and Increases with TNF-Inhibitor Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-lymphocyte-count-is-negatively-correlated-with-atherosclerotic-cardiovascular-disease-risk-score-and-red-cell-distribution-width-in-psoriatic-arthritis-and-increases-with-tnf-inhibitor-therap/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-lymphocyte-count-is-negatively-correlated-with-atherosclerotic-cardiovascular-disease-risk-score-and-red-cell-distribution-width-in-psoriatic-arthritis-and-increases-with-tnf-inhibitor-therap/
