Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Biomarkers
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ANA testing has been a well-established screening tool for autoimmune conditions such as SLE. Current practice for classification of RA does not include ANA positivity; however, ANA testing is performed in many patients who are ultimately diagnosed with RA. In the general population, ANA positivity is thought to be increasing in prevalence and has been associated with elevated rates of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events (1-2). ANA positivity has also been studied in patients with RA who are taking TNF-α inhibitors who develop “lupus-like syndrome” (3). There is a gap in the understanding of the role a positive ANA has in the management of RA. The aim of this study is to describe differences in the clinical course, treatment, and outcomes of patients with RA who are ANA positive as compared to those who are ANA negative.
Methods: The study design is a retrospective, population-based cohort study of 252 residents of a geographically-defined area who first fulfilled 1987 ACR criteria for RA in 1999-2014 assembled using the resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP). Data was collected on first documentation of joint swelling, RF or CCP antibody testing, ANA level ≥1U by ELISA or IF titer of ≥1:80, and pharmacotherapies. Comparisons between groups were performed using chi-square and rank sum tests.
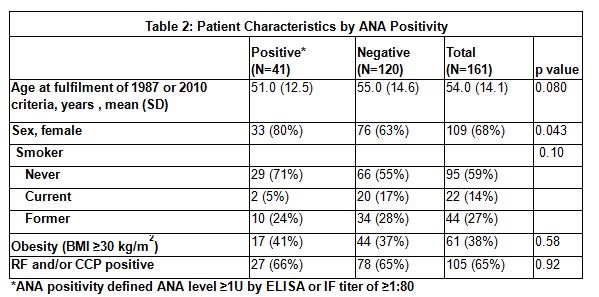
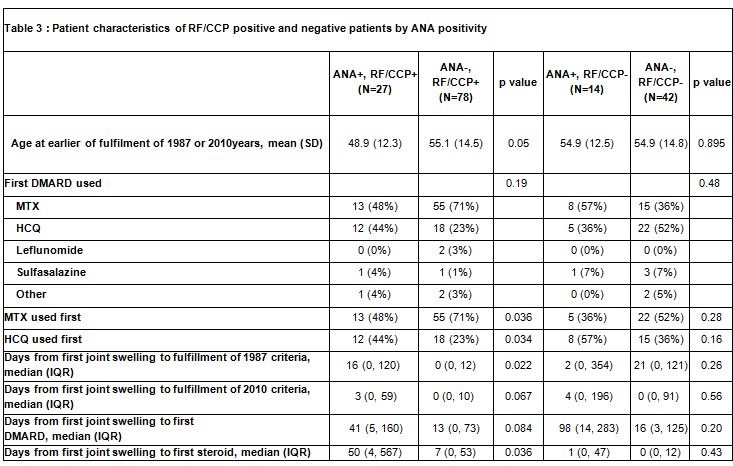
Results: Sixty-four percent of RA patients in the cohort were tested for ANA within ±90 days of RA criteria fulfillment. Patients tested for ANA were more likely to be younger and to be RF or CCP seropositive. In the 161 patients with ANA testing, 25% were ANA positive (Table 1). ANA positive patients were slightly younger, were less likely to be male and somewhat less likely to be current smokers (Table 2). In terms of diagnostics, there were no differences in RF/CCP or RA criteria met, though in patients with seropositivity, the time from joint swelling to fulfillment of RA criteria was increased for ANA positive patients. The length of time to first DMARD initiation in the ANA positive patients was also increased. ANA positive patients were more likely to receive HCQ over MTX as a first treatment (Table 3). ANA positive patients were less likely to receive biologic therapy, but this association did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion: ANA positivity does not differ between seropositive and seronegative RA patients. However, there is a difference in the time to fulfillment of RA criteria, time to treatment with DMARD, as well as in choice of initial pharmacotherapy with more ANA positive patients receiving HCQ over MTX. These findings may indicate a difference in patient presentation or clinical perception of RA patients with ANA positivity. Further research is needed to better understand what drives the treatment rationale for ANA positive, RA patients and what implications that may have for their health outcomes.
References
- Dinse GE, et al. Increasing Prevalence of ANA in the US. Arthritis Rheum 2020;72:1026‐
- Solow EB, et.al. Antinuclear Antibodies Are Associated With All-Cause Mortality and CV Outcomes in the General Population. JACC. 2015;65:2669-2670.
- Latorre IG-D, García-Valladares I. ANA Testing in Patients Treated With Biological DMARDs: Is It Useful? Current Rheum Reports. 2015;17.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paknikar S, Crowson C, Davis J, Thanarajasingam U. Exploring the Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibody Positivity in the Medical Management of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-significance-of-anti-nuclear-antibody-positivity-in-the-medical-management-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-significance-of-anti-nuclear-antibody-positivity-in-the-medical-management-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/