Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: With the advent of combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), patients with HIV-1 began living longer and started to develop diseases associated with aging such as osteoarthritis (OA). This study examined the epidemiologic, clinical, and immunological data in patients with concomitant HIV-1 and knee OA.
Methods: We examined with knee OA treated at a HIV-1 outpatient clinic seen between 1994 and 2020. At baseline visit, demographic parameters, lymphocyte subsets, HIV-1 viral load, knee OA date of diagnosis, pertinent lab findings, knee radiographs, and relevant clinical information were collected. All patients met the American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for knee OA. Antiretroviral medications were categorized into protease inhibitors, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), and integrase inhibitors. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted that looked at age, BMI, ethnicity, gender, CD4 count, HIV viral load, antiretroviral medication use, and time of knee OA diagnosis on the risks of developing knee OA.
Results: Comparing the pre-HAART (1994-1997) to the era after the introduction of HAART (1998-2020), the frequency of DILS and reactive arthritis fell whereas the osteoarthritis, particularly of the knee, and carpal tunnel syndrome rose dramatically (Table 1). A total of 217 patients with HIV-1 infection and knee OA were identified out of the 1671 patients referred to the HIV Rheumatology Clinic. Patients with knee OA were more likely to be female and to be black or Latino than white (Table 2). The knee OA patients were older (average age of 51.1 [±9.1] years compared to 46.7 [±9.8] years in the non-knee OA group). In addition, knee OA patients had a greater body mass index (BMI-average of 32.8 [±7.9] compared to 28.5 [±6.6] in the non-knee OA group). Patients with knee OA were more likely to have CD4 >200 cells/μL at baseline than those with other diagnoses. Medication use with NRTI and integrase inhibitors respectively, were significantly associated with knee OA. However, on multivariable analysis, independent associations of CD4 count, HIV viral load, NRTI and integrase inhibitor usage were not observed. When stratifying antiretroviral usage into the categories of no therapy, mono-drug therapy, and multi-drug therapy, those on multidrug-therapy had higher odds of having knee OA that those on no therapy. However, in the multivariable analysis, this association was not independently observed. Moreover, between the period of 1994 and 2020, we noted an increase in the frequency of knee OA over time on both the univariable (p< 0.001) and multivariable analyses (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: To date, this is the largest cohort of concomitant HIV-1 and knee OA patients followed longitudinally to date. Our cohort confirmed the risk factors of BMI, age, ethnicity, and female gender as well as demonstrating that there is a relationship with CD4 >200 cells/μL and an increase in the frequency of knee OA diagnoses over the period 1994-2006, probably reflecting the longer survival of patients with HIV with effective treatment and factors associated with HIV treatment itself.
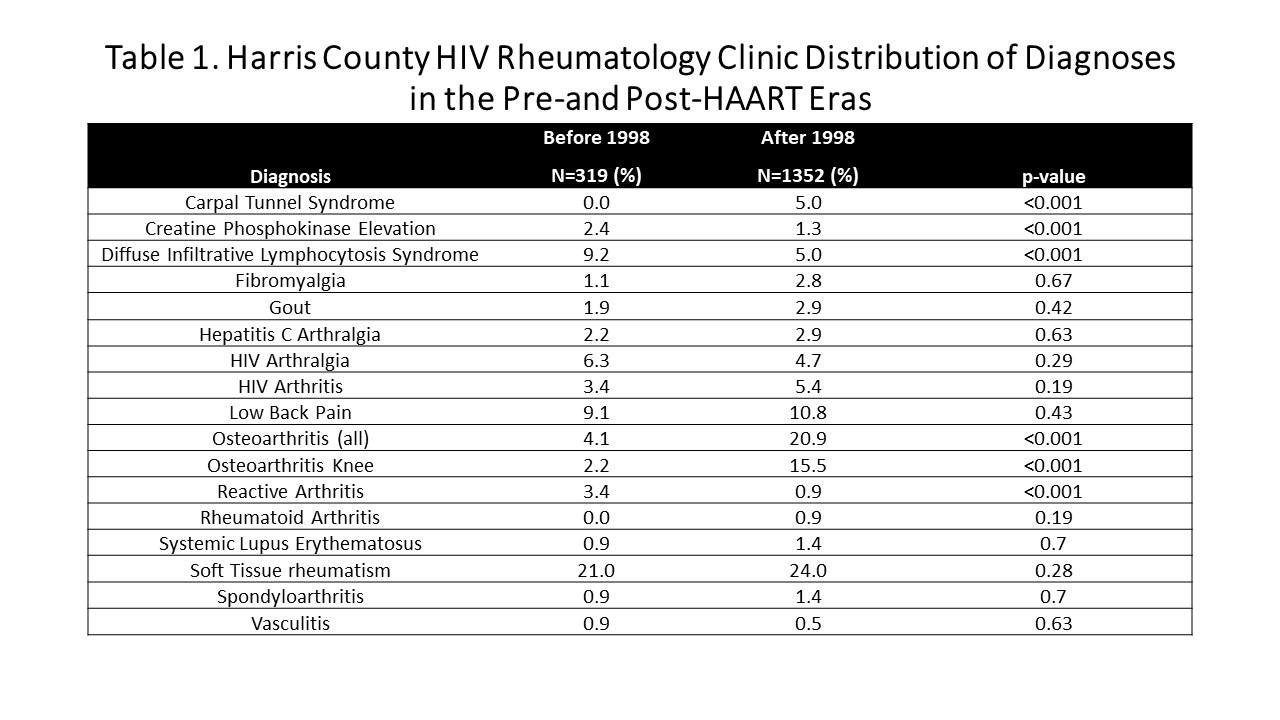 Table 1. Harris County HIV Rheumatology Clinic Distribution of Diagnoses in the Pre-and Post-HAART Eras
Table 1. Harris County HIV Rheumatology Clinic Distribution of Diagnoses in the Pre-and Post-HAART Eras
 Table 2. Demographic and Clinical Parameters in HIV Rheumatology Patients with and without Knee OA
Table 2. Demographic and Clinical Parameters in HIV Rheumatology Patients with and without Knee OA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naovarat B, Williams F, Dau J, Lyons M, Nguyen B, Salazar G, Reveille J. Factors Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis in an Outpatient HIV-1 Clinic over a 26 Year Interval [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-knee-osteoarthritis-in-an-outpatient-hiv-1-clinic-over-a-26-year-interval/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-knee-osteoarthritis-in-an-outpatient-hiv-1-clinic-over-a-26-year-interval/
