Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: OA, Osteoporosis, & Other Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Depression is common in knee osteoarthritis (OA), and leads to reduced physical function, which may mediate the effect of depression on pain. However, research has used self-reported functional measures and assumed that depression is additively related to pain both directly (unmediated) and indirectly (mediated) by physical function. The aim was to assess the direct effect of depression on pain and indirect effect mediated, possibly synergistically, through physical function using an objective physical performance measure among individuals with radiographic knee OA.
Methods: Participants were from the Osteoarthritis Initiative (n=2,484) who had radiographic disease (Kellgren-Lawrence [K-L] grade ≥ 2) and complete data on variables measured at baseline (time t). Depression was measured on a severity continuum using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) Scale as a continuous score (range=0-60) from baseline to third annual follow-up visit (time t+3). Physical performance was assessed via 20-meter gait speed (meters per second [m/s]) from the first (time t+1) through fourth (time t+4) annual follow-up visit. Pain was measured with the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale (rescaled range=0-100) from the second (time t+2) to fifth (time t+5) annual follow-up visit. Time-invariant confounders were age, sex, race, marital status, education, smoking, alcohol consumption, employment status, health insurance, Charlson comorbidity index, and presence of frequent knee symptoms. Time-varying confounders measured concurrent to depression were knee injections, analgesic medication use, body mass index, K-L grade, gait speed, and WOMAC pain. A two-stage marginal structural model approach for effect decomposition in scenarios with exposure-mediator interaction estimated direct, indirect, and total effects between depression, physical performance, and pain (Figure 1).
Results: Incremental effects for one-unit differences in CES-D score indicated that associations (Figure 2) increased with higher depression severity. Direct effects of depression on pain were 0.126 (95% CI: 0.124, 0.128) and 0.130 (95%: 0.128, 0.132) WOMAC units for a CES-D score difference of 1 vs. 0 compared to 16 vs. 15, respectively. Indirect effects of depression on pain mediated by physical performance were smaller in magnitude but showed larger proportional increases: CES-D score 1 vs. 0 = 0.003 (95% CI: 0.002, 0.004) WOMAC units; and CES-D score 16 vs. 15 = 0.066 (95% CI: 0.003, 0.009) WOMAC units. Cumulative effects (Figure 3) implied a 16-unit CES-D score difference (16 vs. 0) yielded a direct effect of 2.082 (95% CI: 2.052, 2.112) WOMAC units and indirect effect mediated by physical performance of 0.105 (95% CI: 0.054, 0.157) WOMAC units.
Conclusion: Effects of depression on pain increase with higher depressive symptom severity, but the proportion of the association mediated by physical performance is small. Findings suggest that exercise interventions for depression may reduce pain by acting directly on depressive symptoms or by increasing physical activity rather than function.
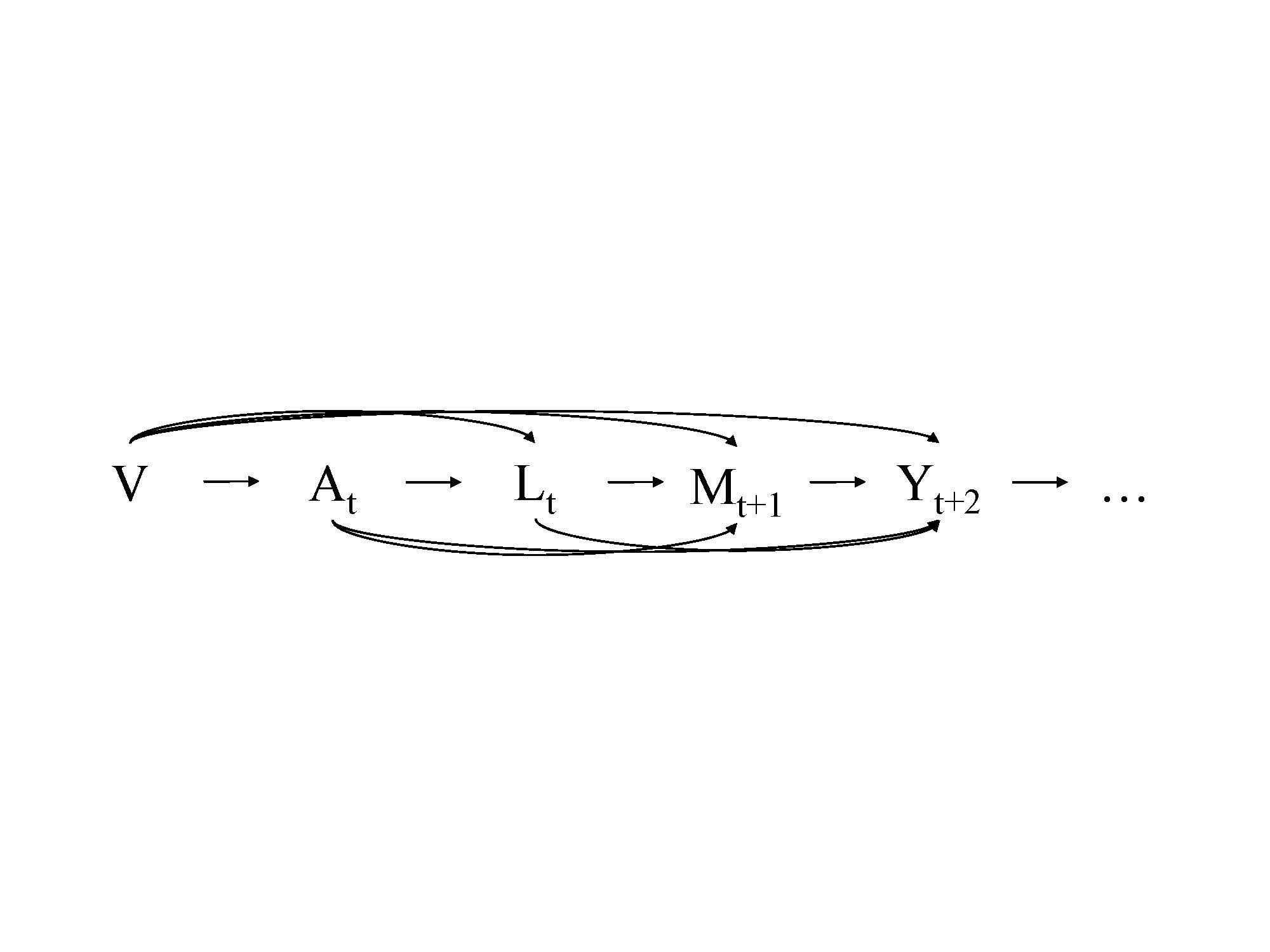 Figure 1. Directed acyclic graph illustrating the repeated measures study design with time-invariant confounders (V), and time-varying depression exposure (A), confounders (L), and physical performance mediator (M), as well as pain outcome (Y), where the subscript t corresponds to time point.
Figure 1. Directed acyclic graph illustrating the repeated measures study design with time-invariant confounders (V), and time-varying depression exposure (A), confounders (L), and physical performance mediator (M), as well as pain outcome (Y), where the subscript t corresponds to time point.
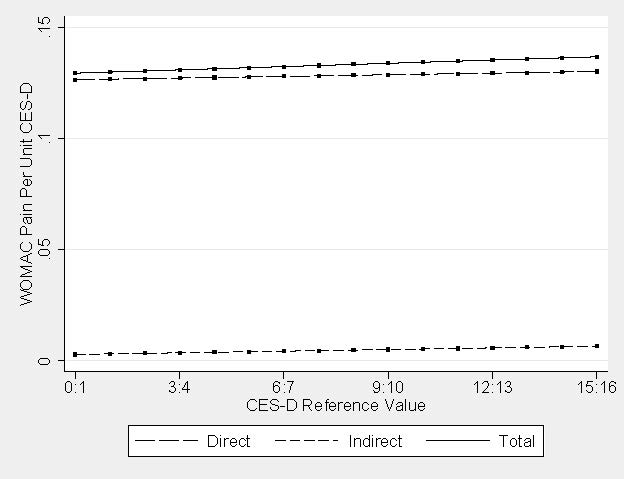 Figure 2. Incremental direct, indirect, and total effects.
Figure 2. Incremental direct, indirect, and total effects.
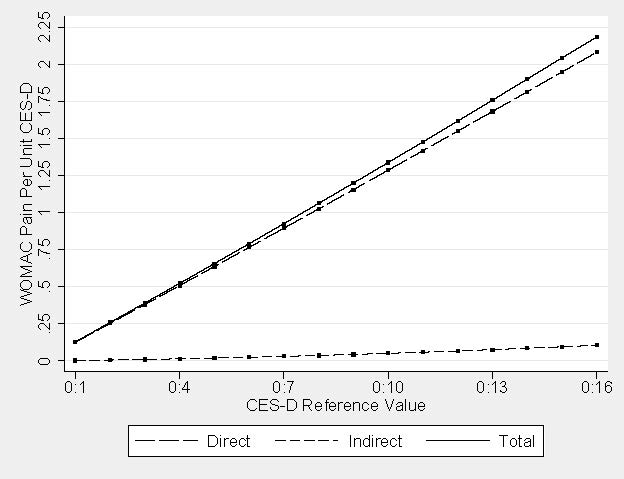 Figure 3. Cumulative direct, indirect, and total effects.
Figure 3. Cumulative direct, indirect, and total effects.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rathbun A, Stuart E, Shardell M, Nguyen T, Ryan A, Gallo J, Yau M, Schuler M, Hochberg M. Physical Performance as a Mediator of the Association Between Depression and Pain in Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physical-performance-as-a-mediator-of-the-association-between-depression-and-pain-in-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/physical-performance-as-a-mediator-of-the-association-between-depression-and-pain-in-knee-osteoarthritis/
