Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: The Heart of the Matter (0484–0488)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in the lowest LDL group (< 70mg/dl) experience unexpectedly high cardiovascular risk. We first explored whether this group (Group 1) had higher coronary atherosclerosis burden compared to other LDL groups (Group 2: 70≤ LDL ≤130 and Group 3: LDL >130). We then evaluated whether differences in LDL particle composition, oxidation, or inflammation associated with low LDL in Group 1.
Methods: One hundred fifty RA patients without cardiovascular disease underwent coronary atherosclerosis evaluation with computed tomography angiography. Coronary artery calcium, number of segments with plaque (segment involvement score), stenotic severity (segment stenosis score), and extensive ( >4 segments with plaque) or obstructive disease ( >50% stenosis) were assessed. Lipoprotein classes and subclasses were directly measured. Oxidized LDL (oxLDL) was measured with monoclonal antibody E06. Chemiluminescence Elisa quantified IgG and IgM antibodies to oxLDL (anti-oxLDL) and apoB100 immune complexes. Proinflammatory cytokines were measured with Erenna Immunoassay. Robust linear and logistic regression models- adjusted for Framingham D’Agostino score and statin treatment- evaluated associations between LDL groups and plaque outcomes. Similar models evaluated adjusted differences in LDL subclasses, oxLDL, anti-oxLDL, ApoB100 immune complexes, and cytokines across LDL groups.
Results: Patients in Group 1 had higher coronary plaque burden (Figure 1A) and 2.8 times greater likelihood of extensive or obstructive disease (adjusted OR 2.82 [95% CI 1.12-7.17], P = 0.031) compared to LDL >70 groups. Group 1 had higher anti-oxLDL IgG and ApoB100 IgG immune complexes compared to other groups (Figure 2A). Among statin naïve patients, those with LDL< 70 also had higher oxLDL (Log transformed EMM 2.55 [95%CI 2.34-2.77] vs. 2.27 [95%CI 2.19-2.36], P = 0.018 for LDL >70). LDL subclass relative content in the LDL particle differed across groups. Lp(a) was higher in LDL particles in Group 1 (EMM 16.04% [95% CI 11.75-20.33], vs. 10.48% [95% CI 8.20-12.75] in Group 2, p = 0.026 and 7.41% [95% CI 0.77-14.04] in Group 3, p = 0.033). Notably, Lp(a) content strongly associated with oxLDL overall (r = 0.83, p< 0.0001). This association was stronger for Group 1 compared to others (p< 0.005, Figure 2B). No differences in RA activity, CRP, TNF-α, IL-17A, or IL-17F were seen across groups. However, Group 1 had higher IL-6 (log-transformed EMM= 1.98 [95% CI 1.64- 2.32] vs. 1.57 [1.45-1.70],P = 0.028 in Group 2 and 1.32 [95% CI 0.84-1.80],
P = 0.031 in Group 3). IL-6 associated with both IgG anti-oxLDL (p=0.015) and apoB100 immune complexes (p=0.016). IL-6 further associated with higher CAC (adjusted B 0.41 [95% CI 0.01-0.81], P= 0.049).
Conclusion: RA patients with LDL< 70 had higher coronary atherosclerosis burden. Low circulating LDL in that group may reflect higher oxidation; this was mostly linked to the larger Lp(a) relative content of LDL and its significantly higher oxidation potential in that group. Greater oxLDL further associated with higher IL-6 elaboration which may in turn augment atherosclerosis burden in Group1.
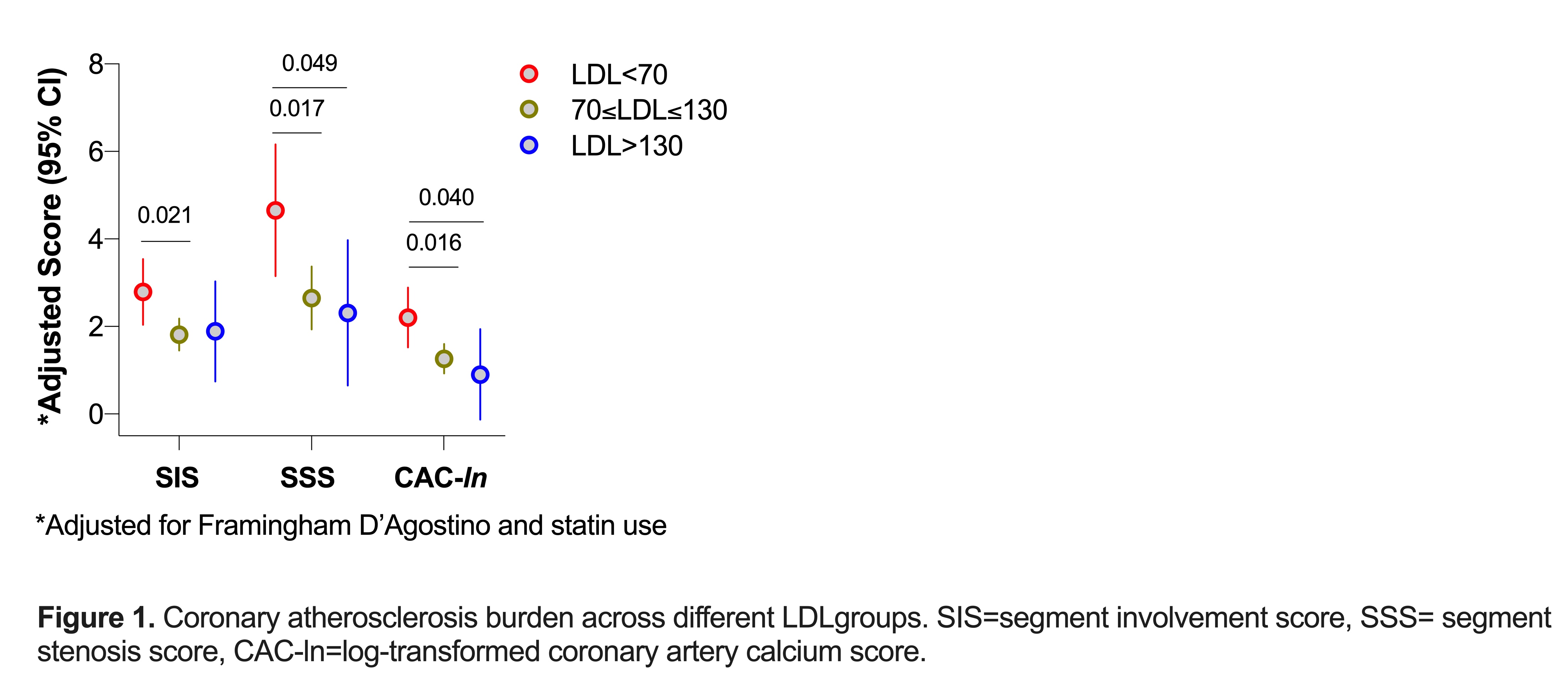 Figure 1. Coronary attherosclerosis burden across different LDLgroups. SIS=segment involvement score, SSS= segment stenosis score, CAC-ln=log-transformed coronary artery calcium score.
Figure 1. Coronary attherosclerosis burden across different LDLgroups. SIS=segment involvement score, SSS= segment stenosis score, CAC-ln=log-transformed coronary artery calcium score.
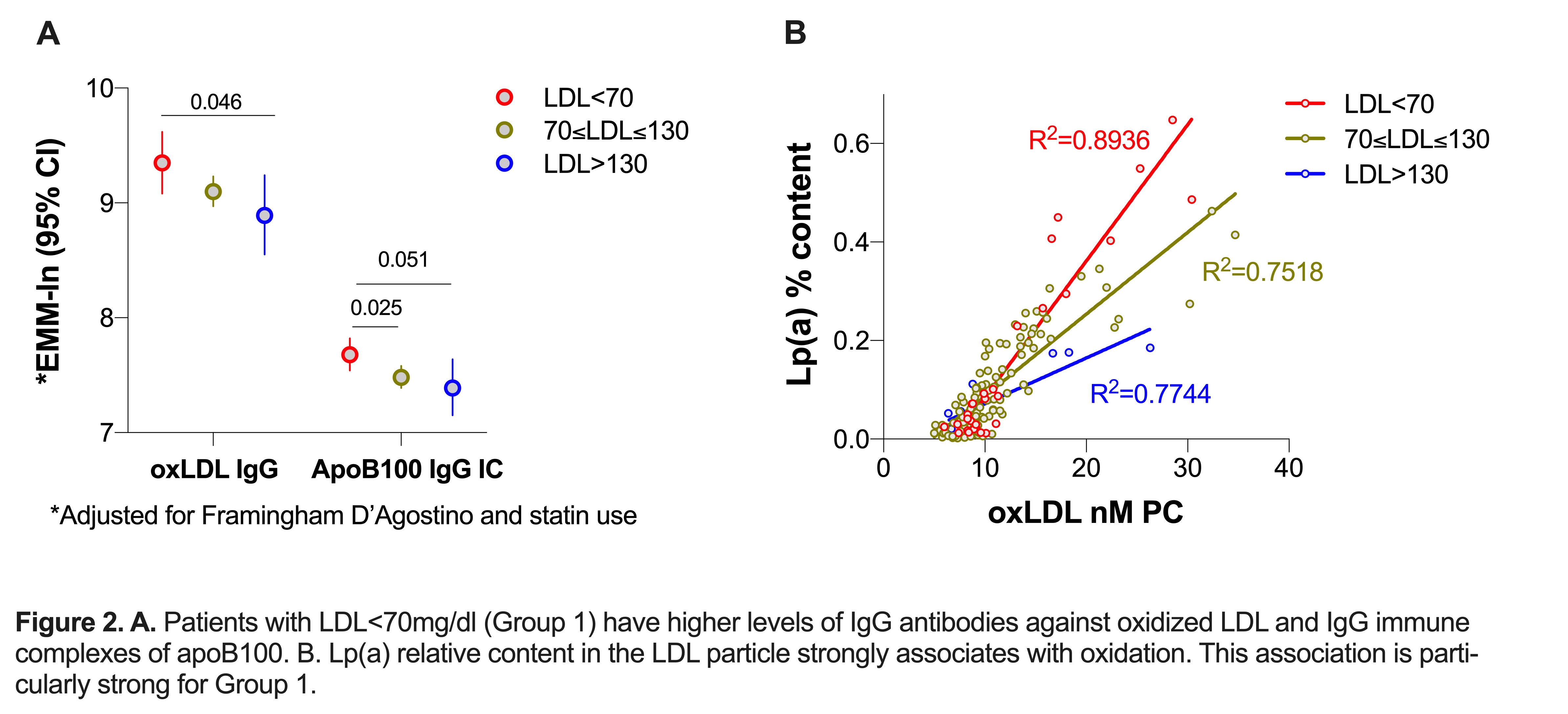 Figure 2. A. Patients with LDL < 70mg/dl (Group 1) have higher levels of IgG antibodies against oxidized LDL and IgG immune complexes of apoB100. B. Lp(a) relative content in the LDL particle strongly associates with oxidation. This association is parti- cularly strong for Group 1.
Figure 2. A. Patients with LDL < 70mg/dl (Group 1) have higher levels of IgG antibodies against oxidized LDL and IgG immune complexes of apoB100. B. Lp(a) relative content in the LDL particle strongly associates with oxidation. This association is parti- cularly strong for Group 1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Ormseth S, Hernandez E, Budoff M. Differences in Low-density Lipoprotein (LDL) Particle Composition and Oxidation May Underlie the Paradoxical Association of Low LDL with Higher Coronary Atherosclerosis Burden in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differences-in-low-density-lipoprotein-ldl-particle-composition-and-oxidation-may-underlie-the-paradoxical-association-of-low-ldl-with-higher-coronary-atherosclerosis-burden-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differences-in-low-density-lipoprotein-ldl-particle-composition-and-oxidation-may-underlie-the-paradoxical-association-of-low-ldl-with-higher-coronary-atherosclerosis-burden-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
