Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is a potent oral selective janus kinase 1 inhibitor which is currently being investigated as an agent to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In the FINCH 2 study (NCT02873936), FIL in combination with conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD therapy significantly improved the signs and symptoms of RA in patients with an inadequate response to a biologic (b)DMARD compared with placebo (PBO). Chronic inflammatory diseases such as RA substantially affects a broad range of aspects of patients’ health related quality of life, including work participation.1 The aim of this post-hoc analysis is to evaluate the rate and magnitude of change on work productivity and activity scores from the FINCH 2 study.
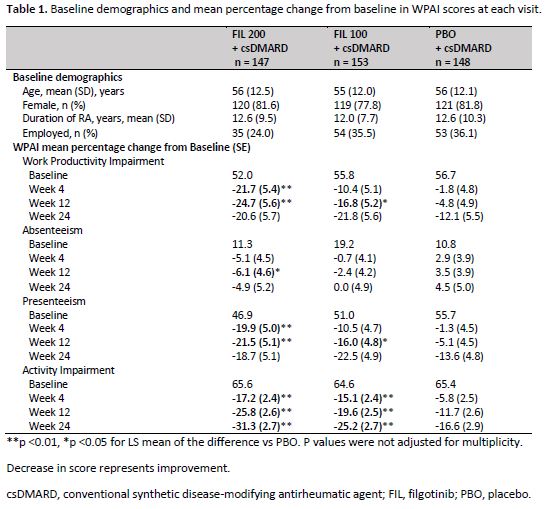
Methods: Patients with active RA were randomized to receive FIL 200 mg (n = 147), FIL 100 mg (n = 153), and PBO (n = 148) for 24 weeks. The activity impairment, work productivity impairment, presenteeism, and absenteeism in the past 7 days were evaluated at baseline and at weeks 4, 12 and 52 on treatment, using the self-administered 6-item Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Rheumatoid Arthritis (WPAI:RA). The WPAI-RA contains the activity impairment as a single item score evaluated among all subjects, while work productivity impairment (employed patients only) is absenteeism and presenteeism. The 4 subscale scores ranged from 0%-100%, with higher scores indicating greater impairment. Percentage changes from baseline in WPAI: RA score were analyzed using mixed effect models for repeated measures (MMRM), and missing data were not imputed. All analyses were exploratory without multiplicity adjustment, nominal P values are reported.
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar across all treatment arms. Patients were (mean ± SD) 56 ± 12 years old, 80% female, and 32% employed. Statistically significantly greater improvement in WPAI scores from baseline compared to PBO was reported as early as week 4 with both doses of FIL for work productivity and activity. Similar statistically significant improvement occurred as early as week 4 for presenteeism with FIL 200mg and as early as week 12 for FIL 100mg. (Table 1). At 12 weeks, FIL 200mg resulted in 21.5-24.7%% improvement in work productivity and presenteeism compared to 4.8-5.1% in PBO. Both doses of FIL improved activity impairment score by 19.6-25.8% from baseline compared to 11.7% in PBO at week 12 and was maintained through week 24.
Conclusion: Improvement in work productivity, presenteeism and activity was greater with both doses of FIL in combination with csDMARD compared to PBO + csDMARD in RA patients who had inadequate response to bDMARDs.
Reference:
- Kim et al. J Rheumatol. 2017;44(8):1112-1117.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Younossi Z, Stepanova M, Gerber L, Lee S, Lee I, Hendrikx T, Boonen A, Alten R, Combe B, Walker D. Filgotinib Improved Work Productivity and Activity Impairment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Biologic DMARDs: Results from the FINCH 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-improved-work-productivity-and-activity-impairment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards-results-from-the-finch-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-improved-work-productivity-and-activity-impairment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards-results-from-the-finch-2-study/