Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Scleroderma (systemic scleroderma or systemic sclerosis, SSc), is a highly heterogeneous autoimmune disease of unknown etiology, with a high rate of therapeutic failure and a progression of the disease. Although recently it has been noted a decrease in mortality It is still high, therefore SSc treatment is considered a therapeutic challenge. The immunomodulatory capacity of the mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), has increased the attention of the scientific community, considering them an alternative therapy that could potentially exceed the efficacy of available therapeutic options; we consider to evaluate through a systematic literature review (SLR), the efficacy, and safety of MSC in patients with SSc.
Methods: A SLR was conducted by two independent researchers (following PRISMA guidelines) in Medline/OVID, Lilacs, Embase and Cochrane/OVID databases (up until February 2019, no language restriction). All clinical study types were considered: Patients over 18 years of age, with SSc who received treatment with MSC (all clinical outcomes). Exclusion criteria: Animal Models, Bone marrow stromal cell transplant, Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Narrative reviews, Letters to the editor. The specified MeSH terms and keywords were used on the search strategy. Rayyan® Microsoft Excel® and review Manager ® 5.2 software were used for the different steps of the SLR. Data extraction (using a predesigned data extraction form) and quality assessment was also undertaken independently by two reviewers with disagreements resolved by discussion or by a third reviewer. Joanna Briggs Institute quality appraisal checklist was used to appraise the quality of studies. The Oxford Centre classifications for levels of evidence were used.
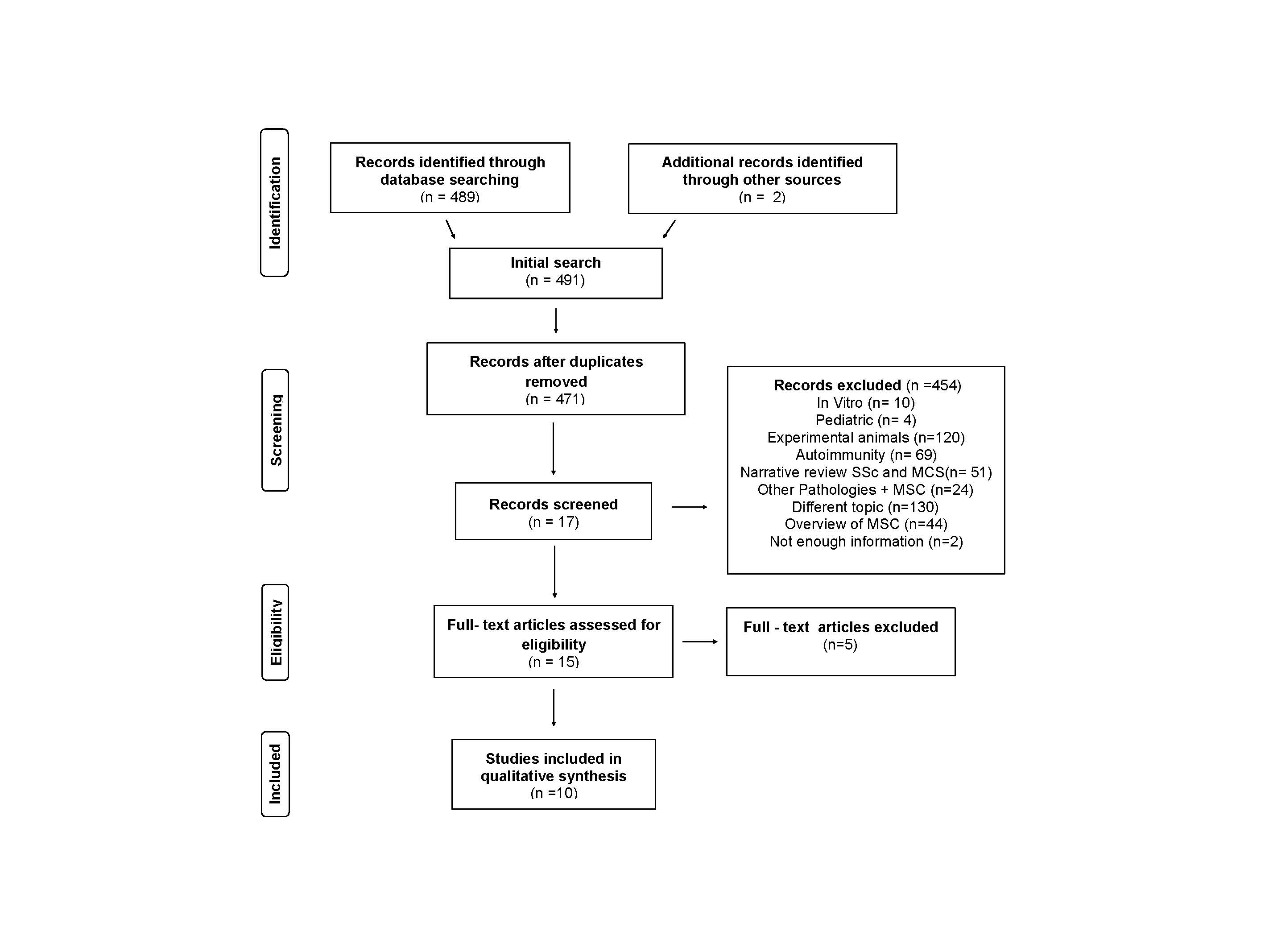
Results: Once the search was done on electronic bases and the grey literature, it was identified a total of 491 items. Duplicate articles were resolved, obtaining 471. 17 articles were screened by title and abstract, of which 15 articles were chosen and by full text 10 were included (6 case report, 3 Case series, and 1 pilot study). Figure1
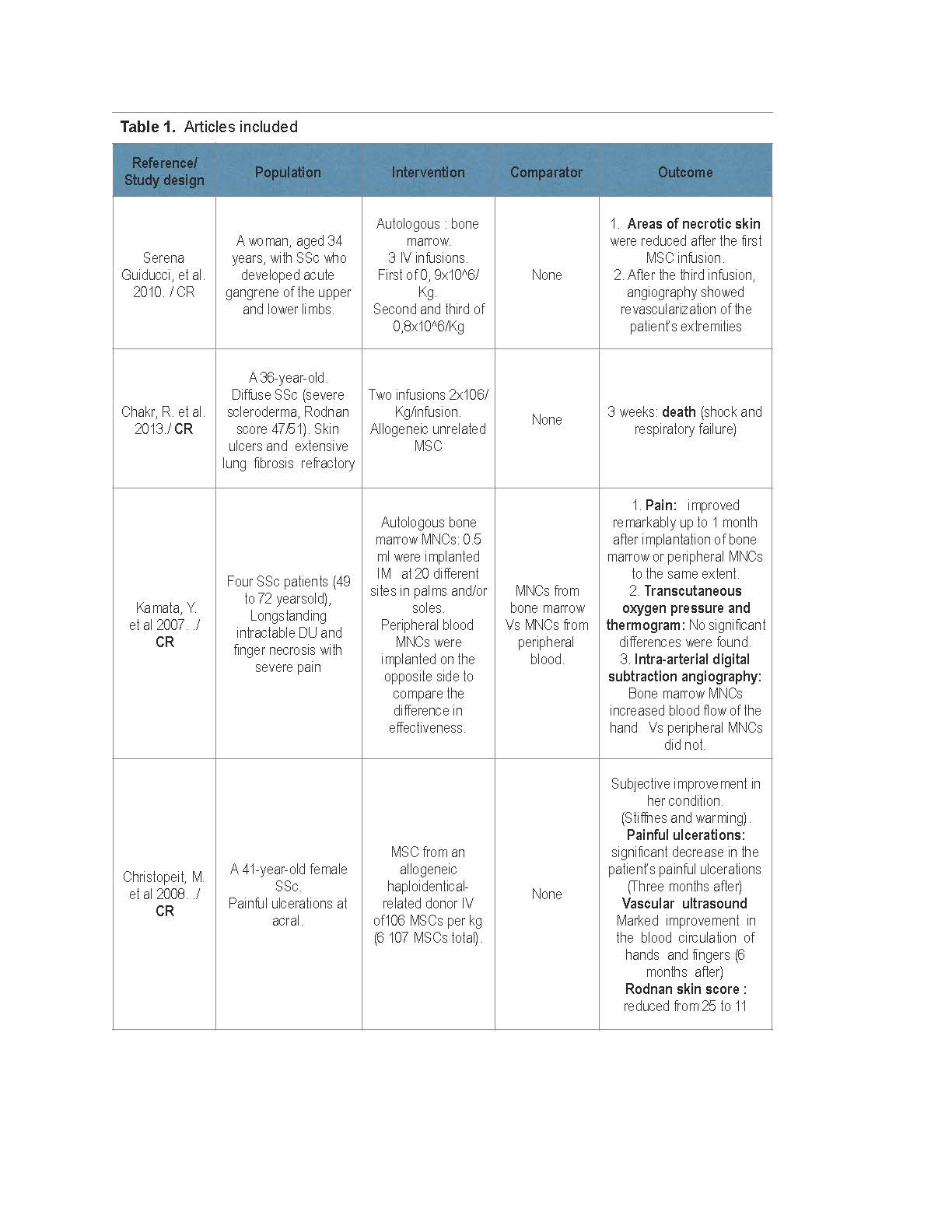
The total population corresponds to 62 patients (age range 18 – 75 years old), most of them refractory to conventional treatment. The different interventions and clinical outcomes are shown in Table 1. Overall appraisal through Joana Briggs checkout was inclusion decision. The level of evidence for the majority of studies was 4.
Conclusion: The reported data are too scarce to come to a clear assessment of the benefit/risk on the use of MSC in SSC. Further well-designed, standardized research studies are required assuming the potential challenges of SSc treatment and the great promise of MSC intervention based on its immunomodulatory functions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mejia-Romero R, Aguilera N, Alzate-Granados J, Escobar -Soto C, Mendoza-Pinto C, García-Carrasco M, Rojas-Villarraga A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Scleroderma: A Systematic Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mesenchymal-stem-cells-in-scleroderma-a-systematic-review/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mesenchymal-stem-cells-in-scleroderma-a-systematic-review/