Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) occasionally overlaps Sjogren’s syndrome (SS), and RA patients with secondary SS have a higher disease activity of RA and worse joint damage compared with RA patients without SS.
A previous report indicated that the positivity of anti-Ro/SSA antibody (Ab), which is diagnostic maker for SS, was an independent factor associated with poor response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in RA patients. While, abatacept have showed the efficacy of both synovitis and glandular symptoms in RA patients with secondary SS. However, few reports show comparable efficacy of abatacept therapy between anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative and -positive patients with RA.
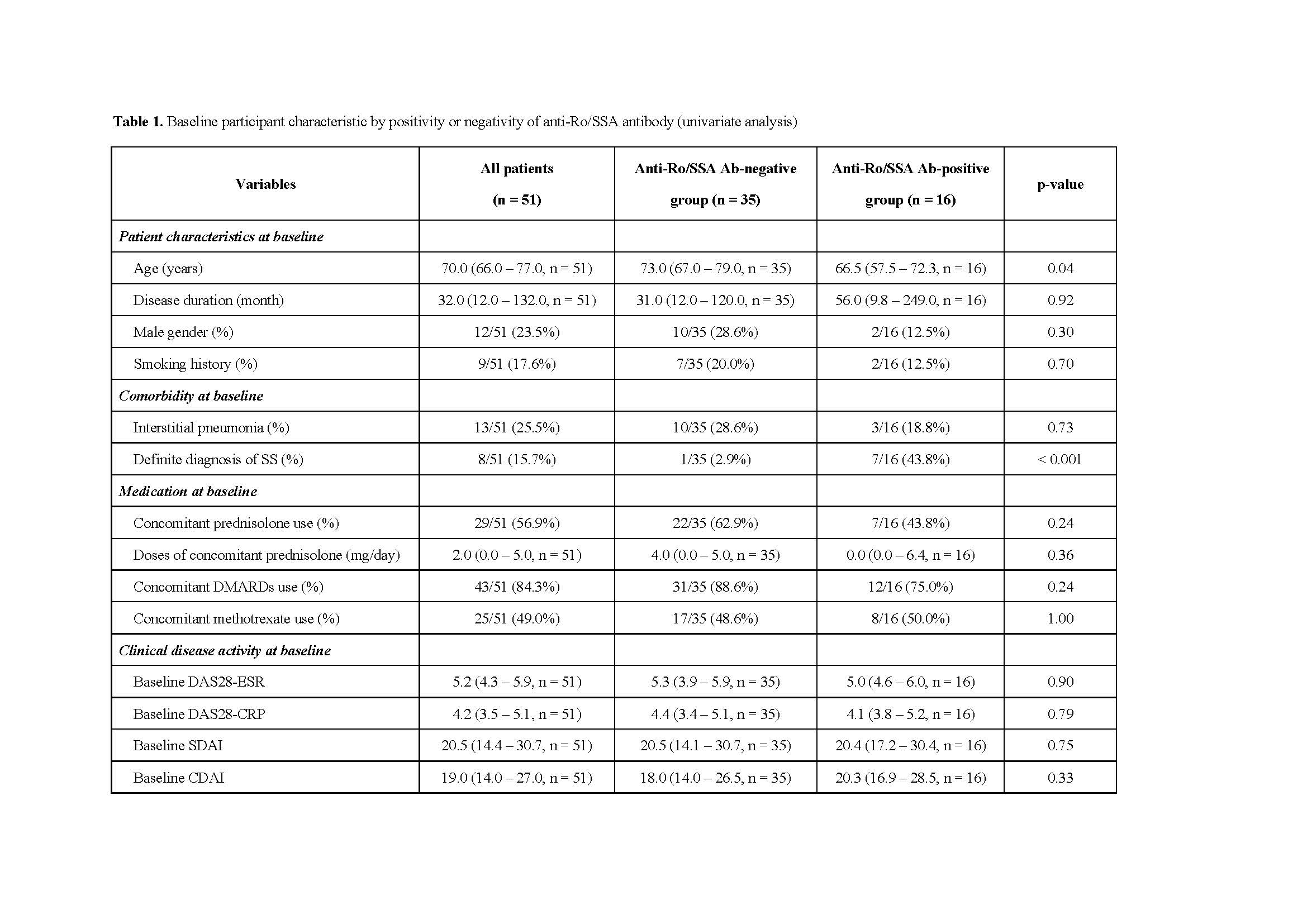
To clarify whether the positivity of baseline anti-Ro/SSA Ab influence response to abatacept therapy, we compared clinical profiles between anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative and -positive patients with RA using a multicenter RA ultrasonography prospective cohort.
Methods: We initially reviewed Japanese RA patients who newly started abatacept therapy as a first biological DMARDs between June 2013 and April 2018. Subsequently, we excluded patients whose baseline anti-Ro/SSA Ab status were uncleared and patients with baseline low disease activity at the initiation of abatacept therapy. Overall, enrolled total 51 patients were divided into anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative and -positive groups of 35 and 16, respectively, according to the result of anti-Ro/SSA Ab assay. The Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Score (GLOESS), which is composite PDUS scores of the greyscale (GS) and power Doppler (PD), was calculated at above examined 22 joints as an indicator of comprehensive ultrasonography activity.
Results: The median age at baseline was significantly higher in anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative group (p = 0.04). Anti-Ro/SSA Ab-positive group had significantly higher frequencies of definite SS diagnosis and baseline antinuclear antibody > 80 times (p < 0.001, p = 0.02, respectively). The persistence ratio and the percentage of EULAR good responders at 12 months were significantly higher in anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative group (p = 0.008, p = 0.02, respectively). Although there was no significant difference in changes in both SDAI and CDAI scores between anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative and -positive groups, both DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP scores decreased significantly at 12 months in anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative group (p = 0.02, p = 0.04, respectively). In addition, GLOESS scores also decreased significantly at 6 months in anti-Ro/SSA Ab-negative group (p = 0.03). Univariate and multivariate analyses showed that negativity of anti-Ro/SSA Ab was an independent factor associated with good responders to abatacept therapy.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the positivity of anti-Ro/SSA Ab confer poor response and persistence to abatacept therapy by comprehensive assessments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Endo Y, Koga T, Kawashiri S, Nishino A, Okamoto M, Morimoto S, Tsuji S, Takatani A, Shimizu T, Sumiyoshi R, Igawa T, Iwamoto N, Ichinose K, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Ueki Y, Yoshitama T, Eiraku N, Matsuoka N, Okada A, Fujikawa K, Hamada H, Tsuru T, Nagano S, Arinobu Y, Hidaka T, Tada Y, Kawakami A. Positivity of Anti-Ro/SSA Antibody Confer Poor Response and Persistence with Abatacept Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/positivity-of-anti-ro-ssa-antibody-confer-poor-response-and-persistence-with-abatacept-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/positivity-of-anti-ro-ssa-antibody-confer-poor-response-and-persistence-with-abatacept-therapy/