Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Women with SLE are at increased risk for cervical neoplasia likely because of infection with high risk (HR) HPV and thus should be considered for HPV vaccination. We previously showed quadrivalent human papillomavirus (qHPV) vaccine to be safe and immunogenic in women with SLE. We sought to determine the frequency of HRHPV infection and uptake of HPV vaccination in the female outpatient lupus population. The qHPV vaccine was approved for use in 2006 for women ages 9-26 years.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective chart review of women ages 16-70 years, with an ICD-10 diagnosis of SLE, seen in the Internal Medicine, Family Medicine, OB/Gyn and Rheumatology clinics associated with a large teaching hospital in Detroit, Michigan during the period 10/2015 to 2/2019. After obtaining IRB approval, data were collected on demographic and clinical characteristics. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test, analysis of variance followed by multiple pairwise comparisons using the Bonferroni correction of the p-value.
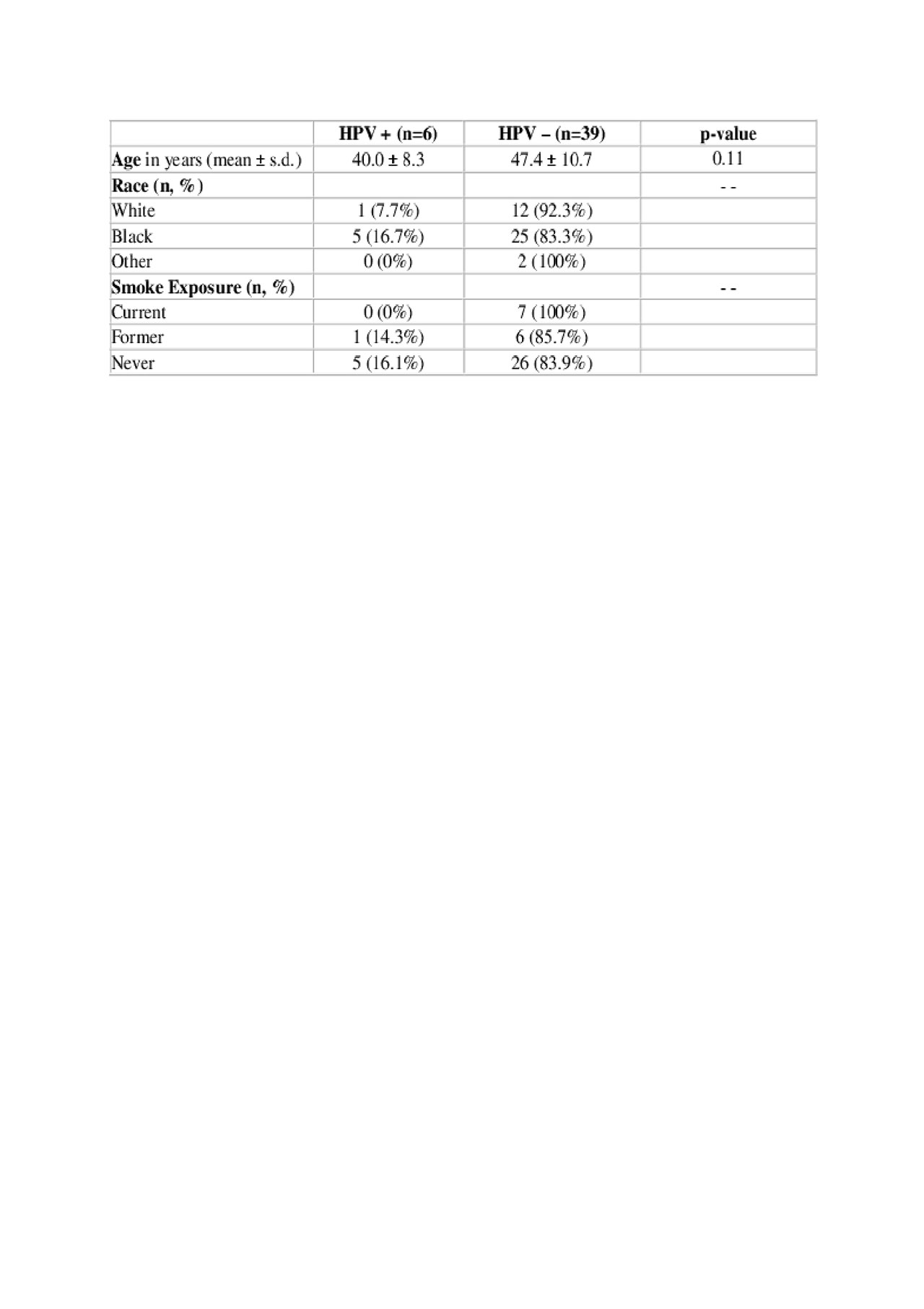
Results: We collected data on 118 women, mean age 44.5 ± 11.6 years, 40.7% Caucasian (48/119), 50% Black (59/118) and 9.3% other/unknown race (10/118). Current smoking was reported by 17.1% (20/117), with 26.5% being former smokers (31/117) and 56.4% never smokers (66/117). HRHPV testing was performed in 45 (38.1%) of these women; six were positive (13.3%). There were no significant differences in test results by age, race or smoking status (Table 1). Black women (50.8%) were more likely to be tested than Caucasians (27.1%) or other races (18.2%), p=0.02. Only 4.3% of the study group were vaccinated (5/117). Of the 112 women who were eligible to receive an HPV vaccine, 38.4% (43/112) were tested for HRHPV with 5 being positive. Of the 5 that were vaccinated, only one woman had testing for HRHPV and this female was positive for HRHPV.
Conclusion: Despite the fact that HPV related cervical disease and neoplasia are increased in women with SLE, the frequency of testing for HRHPV testing is low (38.4%) and vaccination rate even lower (4.3%) in our region. This highlights the importance of the need for monitoring for HRHPV and including HPV vaccination as part of general health care in this vulnerable population. Promoting awareness of this problem with primary care doctors and the lupus community would improve uptake of prophylactic HPV vaccination and be beneficial to gynecologic health in women with SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dhar J, Saravolatz L, Szpunar S. Lack of Uptake of Prophylactic Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Vaccination Among Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in the Detroit, MI Area, a High Risk Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lack-of-uptake-of-prophylactic-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-vaccination-among-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-in-the-detroit-mi-area-a-high-risk-population/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lack-of-uptake-of-prophylactic-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-vaccination-among-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-in-the-detroit-mi-area-a-high-risk-population/