Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Serum anti-citrullinated protein autoantibodies (ACPA) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) display reactivity to a variety of cit-autoantigens. Studies of human ACPA mAbs have revealed that individual clones bind multiple cit-epitopes by recognition of consensus motifs. For certain ACPA, this cross-reactivity may extend also to other post-translational modifications (PTMs). Here we investigated anti-modified protein autoantibody (AMPA) reactivity to acetylated epitopes in RA.
Methods: Serum from 402 RA patients, 317 population controls and 160 SLE patients were screened by ELISA for IgG to an acetylated histone 2B peptide (His2B6-22(Ac-K12)). IgG values were normalized towards a reference and reactivities to the native lys-peptide were subtracted. Cutoff for positivity was set based on controls (Mean+3 SD Δac-lys: 4.25). ACPA fine-specificity in the RA cohort was assessed by the ISAC antigen microarray, CCP2 by CCPlus assay and RF IgM/G/A by ELiA. In addition, AMPA reactivity to Ac-His2B and His41-18(Ac-K5,8,12,16) peptides were investigated in 295 RA-derived single-cell cloned human mAbs (23 CCP2+ and 272 non-ACPA clones). A mAb-subset was further evaluated using the JPT Histone Code Array. Fisher’s exact test, Kruskal-Wallis analysis, and Spearman correlation were used for statistical analysis.
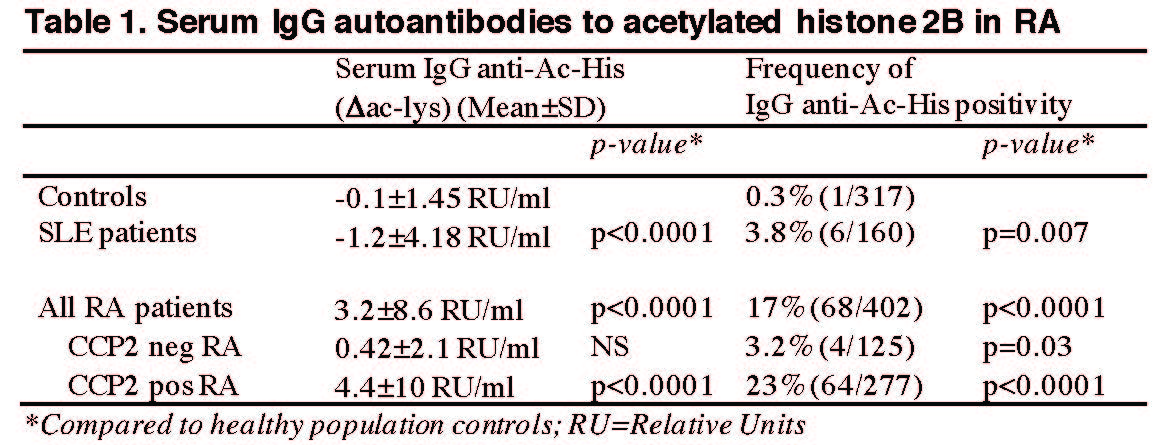
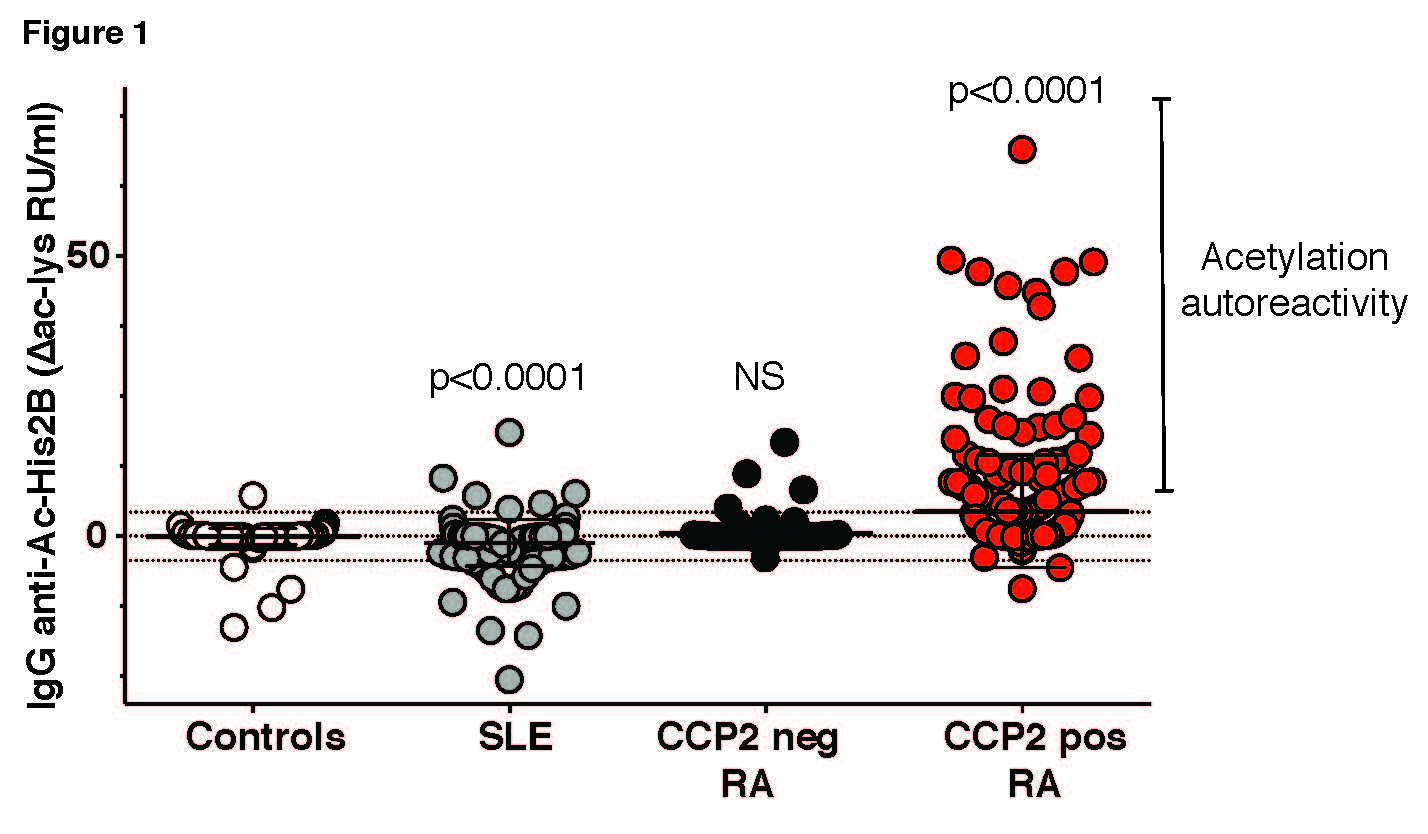
Results: RA patients displayed significant autoreactivity to acetylated histone compared to controls and SLE (Table 1, Fig. 1). Some SLE patients instead had increased reactivity to native His2B. 17% of all RA were positive for IgG anti-Ac-His2B distributing into 23% in the CCP2+ RA subset and 3.2% in CCP2 neg RA, while 0.3% in controls and 3.8% in SLE were positive. The CCP2 neg anti-Ac-His2B pos patients were RF positive and a majority had ACPA fine-specificities. At least one of the positive SLE patients was CCP2 positive. IgG anti-Ac-His2B correlated with IgG anti-CCP2 (R=0.41, p< 0.0001) as well as a range of cit-peptide reactivities (e.g. cit-Vim, cit-Fib, CEP-1). No significant association with DAS28, CRP or shared epitope HLA-DRB1 could be shown. However, levels were increased in smokers (p=0.04; Δac-lys: 3.8±9.6 RU/ml vs 1.9±6.7 RU/ml) and correlated with the number of positive ACPA fine-specificities (R=0.44 p< 0.0001). Among ACPA mAbs, 30% had ac-his reactivity (7/23, derived from 4 different patients and either lung/BAL, synovial plasma cells, or blood memory). None of the non-ACPA mAbs showed any binding. PTM cross-reactivity of these AMPA, and acetyl-lysine consensus motifs, were confirmed by the histone code array. Of note, some ACPA displayed restricted cit-reactivity.
Conclusion: A subset of ACPA can bind to acetyl-lysine peptides and elevated serum IgG anti-acetylated histone was confirmed in RA patients. We hypothesize that acetyl-autoreactivity in RA is associated with increased levels of cross-reactive AMPA. Notably, while AMPA activity is not restricted to histone motifs, anti-Ac-His may have functional properties by PAD-independent NET-interactions. These novel findings substantially extend our understanding of autoreactivity in RA and provide insight in RA pathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sahlström P, Liljefors L, Joshua V, Sherina N, Thyagarajan R, Israelsson L, Stålesen R, Hansson M, Amara K, Reimer U, Padyukov L, Svenungsson E, Lundberg K, Catrina A, Klareskog L, Malmström V, Grönwall C. Autoreactivity to Acetylated Histones Defines a Subset of RA Patients and Is Associated with Acetyl – Citrulline Anti-Modified Protein Autoantibody (AMPA) Cross-Reactivity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoreactivity-to-acetylated-histones-defines-a-subset-of-ra-patients-and-is-associated-with-acetyl-citrulline-anti-modified-protein-autoantibody-ampa-cross-reactivity/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoreactivity-to-acetylated-histones-defines-a-subset-of-ra-patients-and-is-associated-with-acetyl-citrulline-anti-modified-protein-autoantibody-ampa-cross-reactivity/