Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T108 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes V: Outcomes Measures (2868–2873)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Tender joints may be caused by non-inflammatory pathologies but are still included in composite scores like CDAI. The present objective was to explore the impact of tender joints by use of Tender-Swollen Joint Difference (TSJD) assessing patients with predominantly tender (TSJD>0) in comparison to predominantly swollen (TSJD≤0) joints.
Methods:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients assessed by US in a Nordic study of tocilizumab sc to csDMARDs non-responders (1) were included. Clinical (28 tender/swollen joint count (TJC/SJC)), patient reported outcomes, laboratory tests and US examination (36 joints and 4 tendons, scored according to the Norwegian US atlas (2)) were performed at baseline (BL), 4, 12 and 24 weeks. CDAI and EULAR/ACR Boolean remission and sum score grey scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD) were calculated, with PD sum score=0 as US remission. Associations were explored by Spearman’s rank correlation and differences between TSJD>0 vs ≤0 by Mann-Whitney test.
Results:
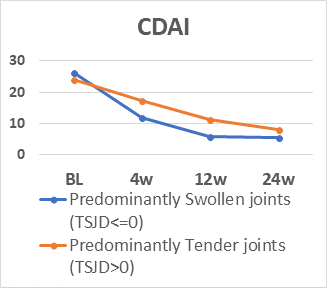
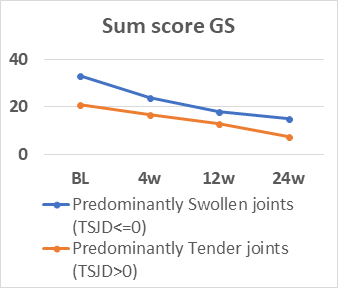
110 patients (83% female, mean (SD) age 55.6 (12.1) years and RA duration 8.7 (9.5) years, 81% anti-CCP positive) were assessed. All variables decreased significantly (p<0.001) (table). Number of patients with TSJD>0 decreased during follow-up (64% to 39%). During the study, TJC had low correlation coefficients (range) with SJC (0.24-0.47), examiner’s assessment (0.19-0.48) and sum score GS (0.13-0.25)/PD (0.00-0.22). There were no differences in CDAI for patients with TSJD>0 vs ≤0 at BL, but at 4, 12 and 24 weeks patients with TSJD>0 had higher CDAI levels (p≤0.002), but lower GS sum scores at BL, 4 and 26 weeks(p=0.026-0.002) and lower PD scores at BL and 24 weeks (p≤0.009). The figure illustrates mean levels of CDAI and GS levels during follow-up dependent on TSJD group. CDAI/Boolean remission in patients with TSJD>0 vs ≤0 was 0%/0% vs 45.2%/33.3% at 12 weeks and 8.1%/5.4% vs 50.8%/40.7% at 24 weeks, while PD remission at 12 and 24 weeks was found in 41.8-70.7% independent of TSJD.
Conclusion:
In patients with established RA, TJC had low association with objective signs of inflammation, and patients with predominantly tender joints seldom reached composite score remission despite PD remission. These findings question the dominant role of tender joints in assessment of inflammatory activity.
References:
1. EULAR 2017 Abstract SAT0199. 2. Hammer HB et al, ARD, 2011
|
|
Baseline Median (IQR) n=110 |
4 weeks Median (IQR) n=102 |
12 weeks Median (IQR) n=95 |
24 weeks Median (IQR) n=91 |
|
Sum score GS |
21 (13-36) |
16 (8-30) |
12 (5-21) |
9 (3-19) |
|
Sum score PD |
8 (2-20) |
4 (1-10) |
1 (0-4) |
0 (0-2) |
|
Tender joint count |
8 (5-12) |
4 (1-9) |
2 (0-5) |
1 (0-3) |
|
Swollen joint count |
6 (2-10) |
2 (0.5-6) |
1 (0-2.5) |
0 (0-2) |
|
Patient’s global VAS (0-100) |
55 (36-70) |
32 (18-49) |
16 (7-31) |
12 (4-28) |
|
Assessor’s global VAS (0-100) |
35 (25-49) |
17 (11-31) |
10 (5-18) |
5 (2-11) |
|
CRP (mg/L) |
5.5 (2.6-13.1) |
0.2 (0.2-0.4) |
0.2 (0.2-0.6) |
0.2 (0.2-0.4) |
|
ESR (mm/h) |
21 (12-34) |
4 (2-7) |
3 (2-5) |
3 (2-5) |
|
CDAI |
23.8 (17.1-31.2) |
12.9 (7.3-21.9) |
7.2 (3.6-11.4) |
4.3 (1.8-9.8) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hammer HB, Hansen IMJ, Järvinen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, Ziegelasch M, Agular B, Terslev L. Tender Joint Count May Not Reflect Inflammatory Activity in Established Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients; Results from a Longitudinal Study of Tocilizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tender-joint-count-may-not-reflect-inflammatory-activity-in-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-from-a-longitudinal-study-of-tocilizumab/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tender-joint-count-may-not-reflect-inflammatory-activity-in-established-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-from-a-longitudinal-study-of-tocilizumab/