Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M105 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Diagnosis & Prognosis II (1929–1934)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Small RNAs (sRNAs) are important regulators of biological processes and are potential biomarkers of disease and drug response. We previously found that microbial sRNAs are abundant in human plasma, altered in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared to control subjects, and inversely associated with disease activity in RA. The aim of this study was to determine if pre-treatment plasma levels of microbial sRNAs: 1. Predict clinical response to initiation of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD); or 2. change 6 months after DMARD initiation.
Methods: Plasma samples and clinical data were provided from a longitudinal multi-center study (Treatment Efficacy and Toxicity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Database and Repository). RNA was extracted from plasma of 70 patients with RA before and 6 months after first-time starts of: methotrexate (n=24), adalimumab (n=23), or tocilizumab (n=23). Sequencing was performed using Illumina NextSeq500. Using TIGER, an in-house sRNA analysis pipeline, high quality reads were first aligned to the human genome allowing for 1 mismatch. Remaining reads were aligned to 57 genomes of bacteria previously found to be altered in RA, representative genomes of 207 human microbiome bacteria, 8 fungi, and 167 environmental bacteria. Differential expression of sRNAs and microbial genome counts were performed using DESeq2 with 5% false discovery rate. Benjamini and Hochberg method was used for multiple test correction. Clinical improvement was defined as a decrease in DAS28 score from pre-treatment to 6 months after starting DMARD treatment. Spearman correlation was used to correlate continuous variables.
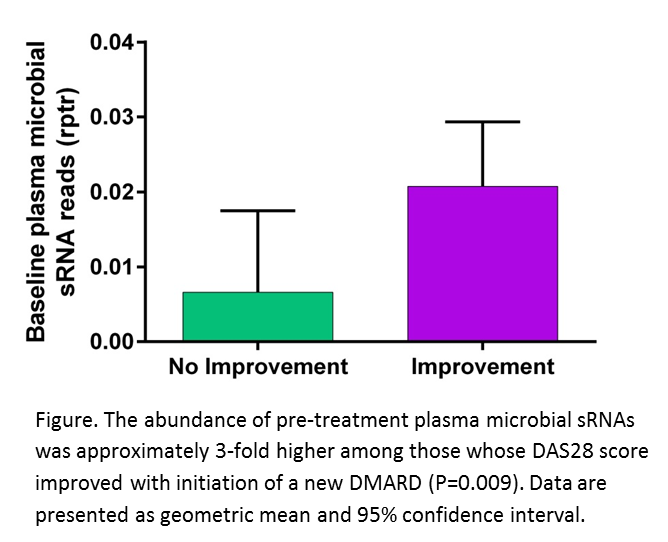
Results: Baseline total microbial sRNAs were ~3-fold higher (P=0.009) (Figure) among patients whose DAS28 improved after starting a DMARD. Moreover, baseline total microbial sRNA read counts had an AUC=0.75 (P=0.009) for predicting improvement with therapy. Microbial sRNAs (total abundance, genome counts and individual sRNAs) did not significantly change after DMARD initiation. On a cross-sectional basis a greater abundance of total microbial sRNA reads were associated with lower tender joint count (P<0.05), which validated prior observations.
Conclusion: The abundance of plasma microbial sRNAs was predictive of improvement in DAS28 after first-time initiation of a DMARD. Initiation of these drugs did not significantly change the abundance of plasma microbial sRNA. Future studies will determine if microbial sRNAs modify host immune responses in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ormseth MJ, Sheng Q, Zhao S, Solus JF, Wu Q, Allen R, Guo Y, Ye F, Ramirez M, Vickers K, Bridges SL Jr., Curtis JR, Stein CM. Abundance of Plasma Microbial Small RNAs Are Predictive of Improvement in Disease Activity after DMARD Initiation for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abundance-of-plasma-microbial-small-rnas-are-predictive-of-improvement-in-disease-activity-after-dmard-initiation-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abundance-of-plasma-microbial-small-rnas-are-predictive-of-improvement-in-disease-activity-after-dmard-initiation-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/