Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Diagnosis and Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Multiple cytokines are assumed to be involved in RA pathogenesis. It has been hypothesized that ACPA-negative RA with wrist affection constitutes a separate entity. Differences in cytokine profile between ACPA positive and negative RA are not known. A Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity (MBDA) assessment is commercially available. Intraarticular inflammatory activity can be measured using power-Doppler (PD) sonography. This study examines whether PD activity is correlated with different cytokines in ACPA positive (ACPA+) and ACPA negative (ACPA-) RA, and whether such differences are BMI dependent.
Methods:
120 visits by 89 patients from a single centre were evaluated retrospectively. All patients fulfilled the 2010 ACR criteria, and were treated with FDA-approved DMARDS. All ACPA- patients had PDS positive wrist arthritis. Patients were divided according to BMI: normal weight (NW, BMI 18.5-25) or overweight (OW, BMI>25), as well as ACPA status (+/-), yielding four groups. Bilateral sonography of MCP 2 and 3, ECU, wrist, and MTP 2 and 5 was performed by a single technician, activity was graded semiquantitatively (0-3), and a total PD score (PDT) was calculated. An MBDA was performed in all patients. Correlations between cytokines and BMI/PDT were calculated using Spearman’s r. The means between groups were compared using the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test. A multiple linear regression was performed for each group using a conditional inference trees approach.
Results:
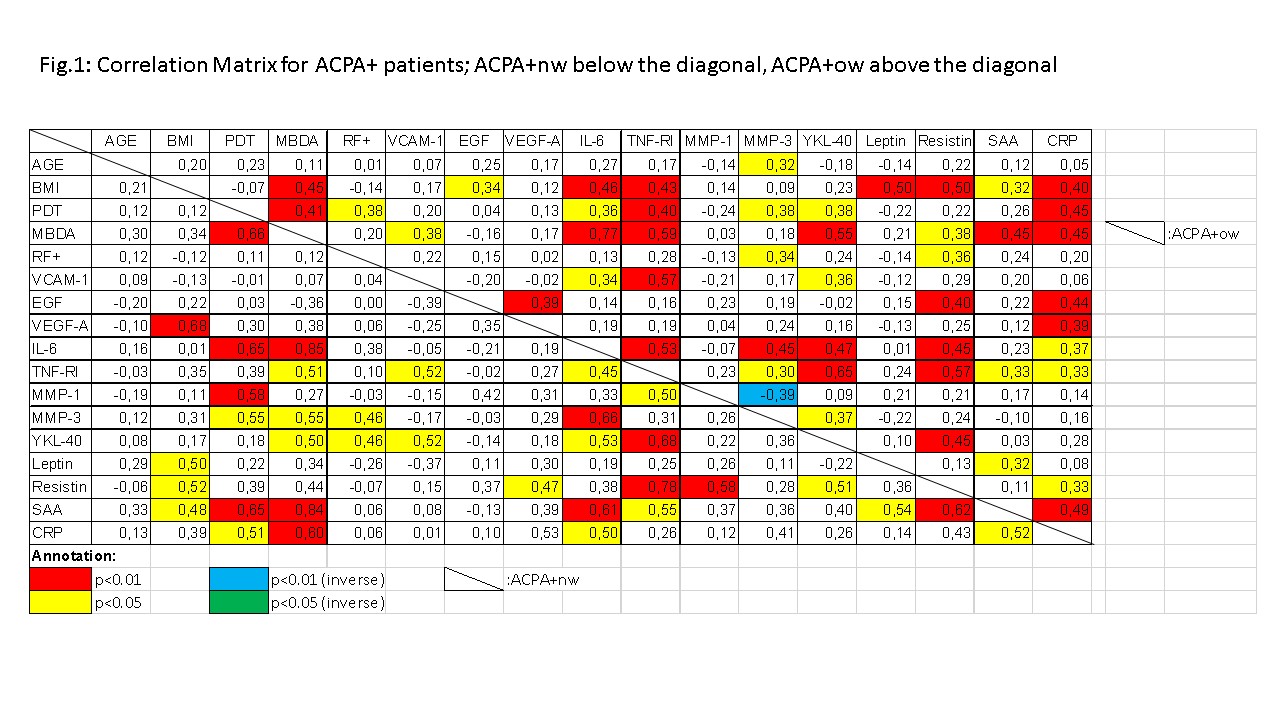
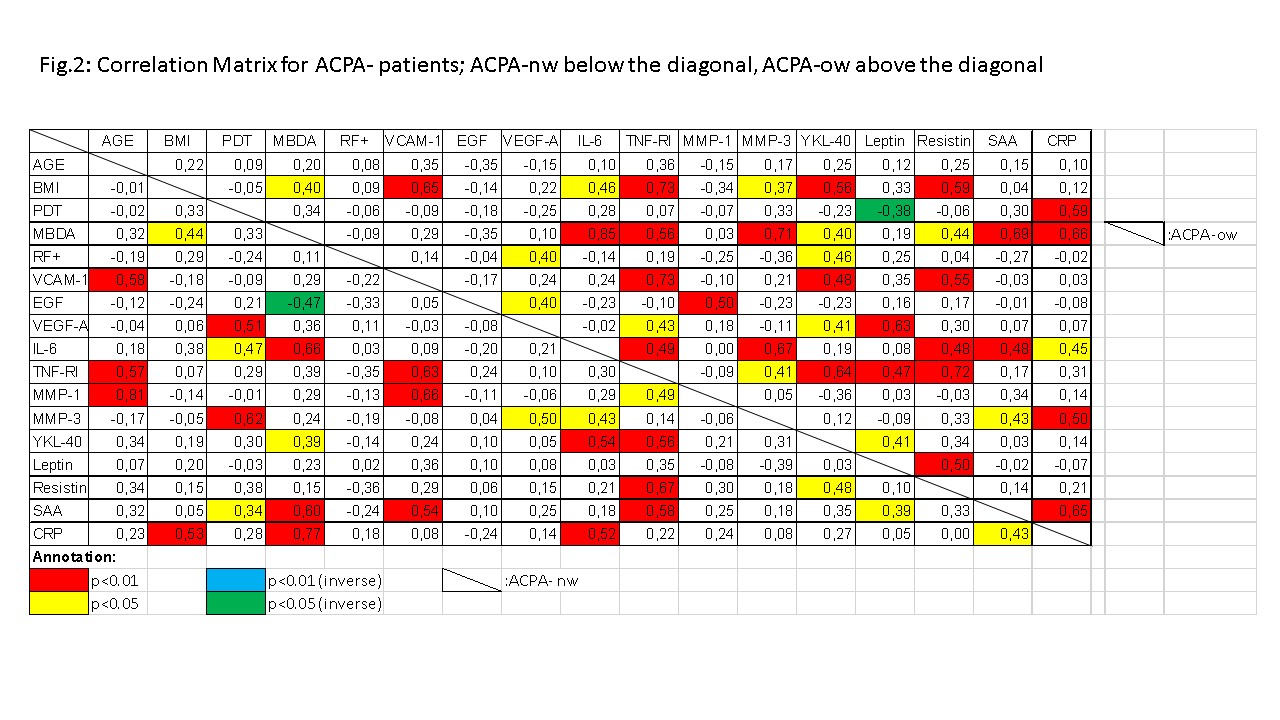
Overall treatment did not differ between the groups. PDT and MBDA total scores did not differ significantly between groups. Leptin correlated significantly with BMI in ACPA+ both normal and overweight, but neither in ACPA- normal nor overweight. In the linear regression, the following variables best predicted PDT: ACPA+nw: log(IL-6) (p=0.1, n.s); ACPA-nw: Log(IL-6) (p=0.04); ACPA+ow: Log(CRP)(p=0.03); ACPA-ow: Log(MMP-3)(p=0.01). Further cytokine associations were also different in different groups (Fig. 1 and 2).
Conclusion:
Different cytokines are associated with PD activity in ACPA+ and ACPA- RA. This finding supports the theory that the etiology of the two forms is different. The differences appear to be BMI dependent. Further research into cytokines in RA should take BMI into account.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gadeholt O, Arnold E, Gorman C, Mueller T, Arnold W. Correlation between Cytokine Levels and Power-Doppler Ultrasound Activity Is BMI Dependent, and Different in ACPA Positive and ACPA Negative RA with Wrist Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-cytokine-levels-and-power-doppler-ultrasound-activity-is-bmi-dependent-and-different-in-acpa-positive-and-acpa-negative-ra-with-wrist-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-cytokine-levels-and-power-doppler-ultrasound-activity-is-bmi-dependent-and-different-in-acpa-positive-and-acpa-negative-ra-with-wrist-arthritis/