Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster I: Patient-Reported Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mood disorders, including depression, are amongst the most common manifestations of neuro-psychiatric SLE. Currently, the screening and diagnosis for depression in ambulatory settings are delayed and often missed due to the lack of standardized valid questionnaires for assessing depression in patients with SLE. This study aims to: 1) Determine the prevalence of depression in SLE patients using the Center for Epidemiological Studies-Depression Scale [CES-D] and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [HADS] questionnaires. 2) Study the criterion validity and interpretability of CES-D and HADS, and 3) evaluate their diagnostic accuracy when compared to the assessment of an independent psychiatric assessment using the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI), based on the DSMV, as the gold standard.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study of consecutive consenting SLE patients (n=227), aged 18-65 and attending the Toronto Lupus Clinic between June 2017–September 2017, was performed. Participants were screened for depression using the CES-D and HADS, and underwent the MINI on the same date of their clinic visit. Conventional cut-off scores were used to indicate the prevalence of depression: CES-D ≥ 16 and HADS-D ≥ 8. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were evaluated against the MINI. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves and the Youden Index were utilized to determine the optimal cut-off scores for CES-D and HADS-D.
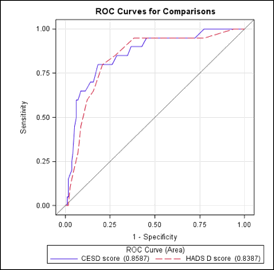
Results: Among 227 patients, the prevalence of depression ranged from 27.8% (HADS-D) to 46.3% (CES-D). ROC curves showed that the CES-D (AUC 0.86, 95% CI: 0.78-0.95) slightly outperformed HADS-D (AUC 0.84, 95% CI: 0.75-0.93) when compared to the MINI. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV for CES-D at the optimal cut-off of 26 was 80%, 82%, 43%, and 96%, respectively. The Youden index exhibited optimal cut-offs for CES-D at 26 and HADS-D at 8 that optimized their sensitivity and specificity as screening metrics for depression in SLE patients. The performance of the CES-D and HADS-D at various cut-offs are displayed in Table 1 below.
Conclusion: This study assessed the criterion validity and interpretability of patient-reported outcome tools HADS, and CES-D for depression screening in SLE patients. Compared to the gold standard, CES-D outperformed HADS-D. These results suggest that SLE-specific cut-offs may improve the diagnostic accuracy of current screening metrics in lupus.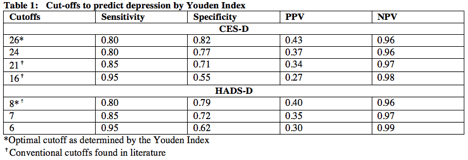
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kwan A, Marzouk S, Ghanean H, Vitti M, Ali K, Bonilla D, Anderson N, Su J, Touma Z. Assessment of the Psychometric Properties of Patient-Reported Outcomes of Depression in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-the-psychometric-properties-of-patient-reported-outcomes-of-depression-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-the-psychometric-properties-of-patient-reported-outcomes-of-depression-in-sle/
