Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although skin lesion is the most typical findings in patients with psoriasis (PsO), nail psoriasis is also one of the important clinical manifestation. Moreover, nail disorders in PsO are known as a risk factor for psoriatic arthritis (PsA). However, pathological feature and the relationship with inflammation of the soft tissue around the nail is unknown. The aim of this study was to compare the soft tissue thickness around the nail in patients with PsO, PsA and healthy control or other rheumatic diseases by using ultrasonography. The relationship between nail disorders and peripheral arthritis or enthesitis in patients with psoriasis was also analyzed.
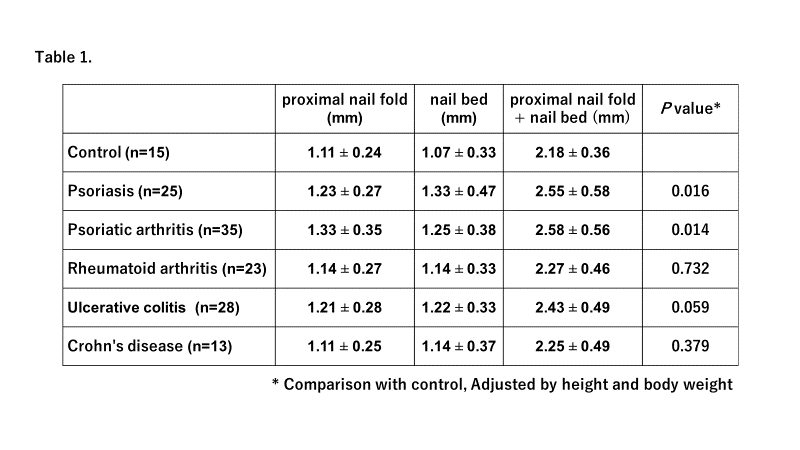
Methods: Ultrasonographic assessment was performed in 25 PsO · 35 PsA · 15 healthy control · 23 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) · 28 ulcerative colitis (UC) and 13 Crohn’s disease (CD) patients and included in this analysis. Ultrasonographic examination was performed by using HI VISION Ascendus (Hitachi Medical Corporation, Japan) with a multifrequency linear transducer (18-6 MHz) and the gray scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD) findings were assessed. The distance between the proximal nail fold on the dorsal side of the nail matrix and the nail bed on the volar side of the nail matrix was measured by electric caliper. The soft tissue thickness around nail was compared between groups and the the relationship between nail disorders and peripheral arthritis or enthesitis in patients with psoriasis was also analyzed.
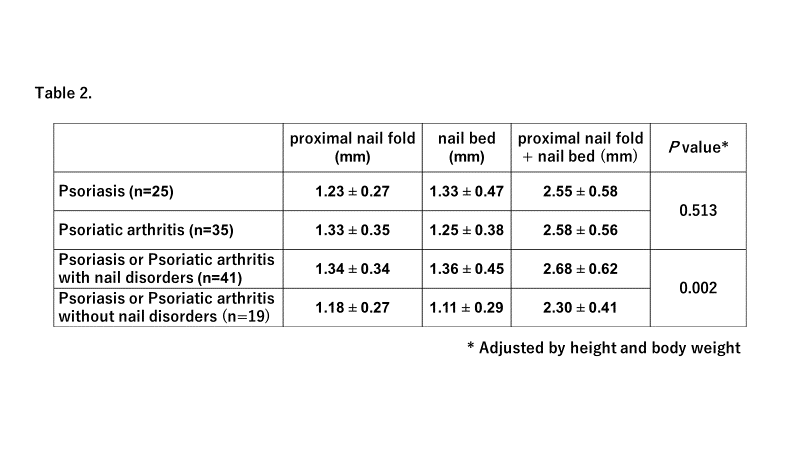
Results: The distance between the proximal nail fold and the nail bed was 2.58 } 0.56 mm in PsA and 2.55 } 0.58 mm in PsO patients (p=0.603). Among the 60 patients who combined PsO and PsA patients, 41 patients with nail psoriasis and 19 patients without nail psoriasis was compared. The distance was 2.68}0.62mm in patients with nail psoriasis and 2.30}0.41mm in without nail psoriasis (p<0.001), which was also swelling compared with control, RA, UC and CD group. The relationship between nail disorders and peripheral arthritis or enthesitis was not found in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Conclusion: Soft tissue thickness around the nail in patients with PsO and PsA was compared with other rheumatic diseases by ultrasonographic assessment. In patients with PsO and PsA with nail psoriasis, soft tissue swelling around nail was observed. However, the relationship between nail disorders and peripheral arthritis or enthesitis was not found in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Okano T, Inui K, Mandai K, Yamada Y, Koike T, Nakamura H. Ultrasonographic Research of the Relationship between Nail Disorders and Peripheral Arthritis or Enthesitis in Patients with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasonographic-research-of-the-relationship-between-nail-disorders-and-peripheral-arthritis-or-enthesitis-in-patients-with-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasonographic-research-of-the-relationship-between-nail-disorders-and-peripheral-arthritis-or-enthesitis-in-patients-with-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/