Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Activated macrophages play a critical role in RA by perpetuating inflammation via TNFα release and participating in the destruction of bone and cartilage. Notably, macrophages are the dominant cell type in the synovial sublining of RA-affected joints. Thus, specific detection of activated macrophage infiltration in RA patients may provide valuable immunodiagnostic insight towards joint inflammation, destruction and overall disease progression.
Tc 99m Tilmanocept is a synthetic radiopharmaceutical imaging agent that binds to the activated macrophage mannose receptor (CD206) with high affinity. It is currently under investigation for intravenous (IV) administration in subjects with RA in a dose escalation study. The purpose of this report is to communicate safety and imaging findings from RA subjects who received the maximum study dose of 400 µg tilmanocept/10 mCi Tc 99m.
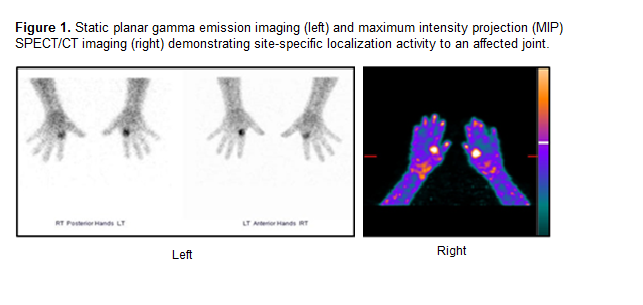
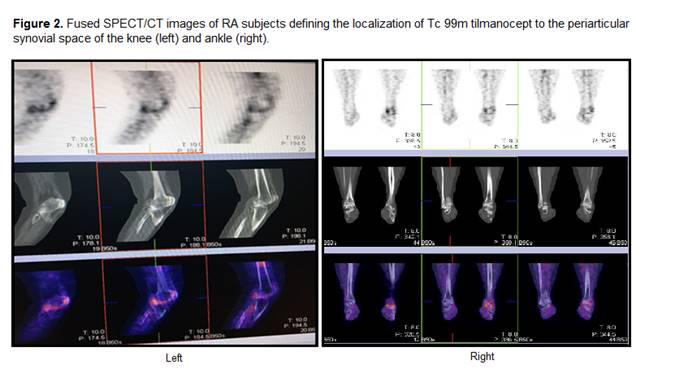
Methods: Nine subjects with clinically diagnosed RA were enrolled in the trial. All subjects received IV administration of 400 µg of tilmanocept radiolabeled with either 10 mCi (n=3), 5mCi (n=3), or 1 mCi (n=3) Tc 99m. Static planar gamma emission images of the whole body and affected joints were acquired at 60 and 180 min post injection with additional SPECT/CT imaging of affected joints.
Results: No adverse events were observed after IV administration of 400 µg Tc 99m tilmanocept radiolabeled with 1, 5, or 10 mCi of Tc 99m. There was strong correlation of radiotracer localization to affected joints observed in gamma emission imaging. SPECT/CT imaging further demonstrated that Tc 99m tilmanocept localization is specific to the PIP, MCP, knees, ankle, shoulder, elbow, and periarticular synovial spaces and not in cortical bone or osseous marrow spaces.
Conclusion: Overt joint-specific localization of Tc 99m tilmanocept activity was visualized in affected joints of all subjects who had undergone multiple RA flares despite previous successful treatments, which demonstrates macrophage infiltration of these joints as a key component of disease. IV injection of Tc 99m tilmanocept at the maximum study dose was well-tolerated with no adverse events. These findings, in addition to prior biopsy evaluations from other subjects, confirm activated CD206 macrophage infiltration to be a key component of RA pathology which can be safely and effectively visualized on gamma emission imaging with Tc 99m tilmanocept.
Disclosure: A. Kardan, None; B. Abbruzzese, None; J. Sanders, None; A. Kissling, None; D. Ralph, None; J. Shuping, None; M. Blue, None; C. Hartings, None; R. Hershey, None; A. Ismail, None; I. Gierach, None; H. Bailey, None; A. Spaulding, None; M. Haynam, None; G. Zubal, None; F. Cope, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kardan A, Abbruzzese B, Sanders J, Kissling A, Ralph D, Shuping J, Blue M, Hartings C, Hershey R, Ismail A, Gierach I, Bailey H, Spaulding A, Haynam M, Zubal G, Cope F. Evaluation of Intravenous Injection of Tc 99m Tilmanocept in Static Planar Gamma Emission Imaging and Fused SPECT/CT Imaging for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-intravenous-injection-of-tc-99m-tilmanocept-in-static-planar-gamma-emission-imaging-and-fused-spectct-imaging-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-intravenous-injection-of-tc-99m-tilmanocept-in-static-planar-gamma-emission-imaging-and-fused-spectct-imaging-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/