Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Th17 cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Tyk2, a member of the Janus Kinase (JAK) family of signaling molecules, was the first JAK to be associated with AS in genome-wide association studies. Tyk2 plays a crucial role in Th17 cell function through mediating IL-23 intracellular signaling, making Tyk2 an attractive target for the treatment of AS. Here we examine the expression of Tyk2 at the cellular level in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) for evidence of SNP-mediated changes in expression. We further tested a novel, potent and selective Tyk2 inhibitor, NDI-031407, for therapeutic effect in the SKG mouse model of AS.
Methods:
Flow cytometry on PBMC was carried out on 76 AS patients, 47 healthy controls and 21 RA patients. Tyk2 mRNA was assessed in unstimulated cells using PrimeFlow and cytokines were assessed in PMA/ionomycin-stimulated cells. SKG mice were gavaged twice daily with NDI-031407 or methylcellulose vehicle from weeks 1 to 8 post-disease induction. Mice were scored weekly for clinical presence of peripheral and axial arthritis, dermatitis and blepharitis. Sacroiliitis was assessed by T1- and T2-weighted MRI. Histology was assessed by H&E staining. Th17 frequency and phenotype were assessed by flow cytometry in popliteal, mesenteric and sciatic lymph nodes.
Results:
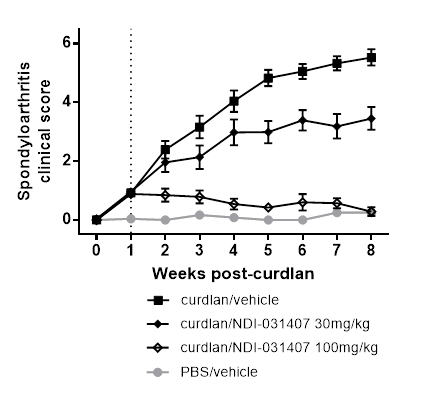
Tyk2 mRNA expression in PBMCs by flow cytometry did not demonstrate significant differences between AS and controls. Tyk2 expression levels did not stratify by candidate SNPs (rs12720356, rs35164067) and did not correlate with Th17 frequency. NDI-031407 is a small molecule Tyk2 inhibitor that inhibits Tyk2 with a Ki of 0.2 nM, and is 218-, 148-, and 20-fold selective against JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3, respectively. In SKG mice, therapeutic dosing with NDI-031407 significantly reduced the clinical scores of joint and skin inflammation to normal levels (see figure). MRI of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ) showed joint space narrowing and edema with disease progression and NDI-031407 protected against these SIJ changes. Enthesitis and bone erosion in the ankle and tail were prevented by Tyk2 inhibition. FACS showed that NDI-031407 suppressed the expansion of IL-17A+ Th17 cells (vehicle vs NDI-031407; 6.04% vs 2.73% of CD4+ T cells, p=<0.001) in addition to reducing IL-17F, IL-22, ICOS and Ki67 expression.
Conclusion:
AS-associated Tyk2 SNPs do not impart a difference in Tyk2 expression and likely contribute to AS through promoting Th17 cell function. Our findings indicate that Tyk2 inhibition can prevent disease progression in SKG mice by reducing Th17 cells and associated inflammatory cytokines. Future studies aim to unravel the role of Tyk2 in Th17 cell development to better understand the mechanism behind Tyk2 inhibition. This work provides the first evidence that Tyk2 inhibition presents as a viable therapeutic target in AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gracey E, Lim M, Qaiyum Z, Baglaenko Y, Miao W, Masse C, Westlin W, Inman RD. An Oral Tyk2 Inhibitor Effectively Suppresses the Development of Murine Th17 Cells In Vivo and Prevents Joint Damage in Experimental Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-oral-tyk2-inhibitor-effectively-suppresses-the-development-of-murine-th17-cells-in-vivo-and-prevents-joint-damage-in-experimental-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-oral-tyk2-inhibitor-effectively-suppresses-the-development-of-murine-th17-cells-in-vivo-and-prevents-joint-damage-in-experimental-ankylosing-spondylitis/