Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Follicular helper T (Tfh) cell is a novel T cell subset which promotes follicular B cell activation, differentiation to plasma cell and antibody production. Recently, circulating Tfh has been reported to be increased in RA and other autoimmune diseases. Some reports have showed the existence of Tfh subsets which share same characteristics as conventional Th subsets, but their function in RA has been still unclear. The aim of this study was to explore the role of Tfh subsets in glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI) induced arthritis (GIA), which mouse model was dependent on CD4+ T cells, B cells and IL-17.
Methods:
1) The fluctuation in numbers of Tfh, the subsets and germinal center (GC) B cell in draining lymph nodes from GIA were analyzed by FACS during the course of arthritis.
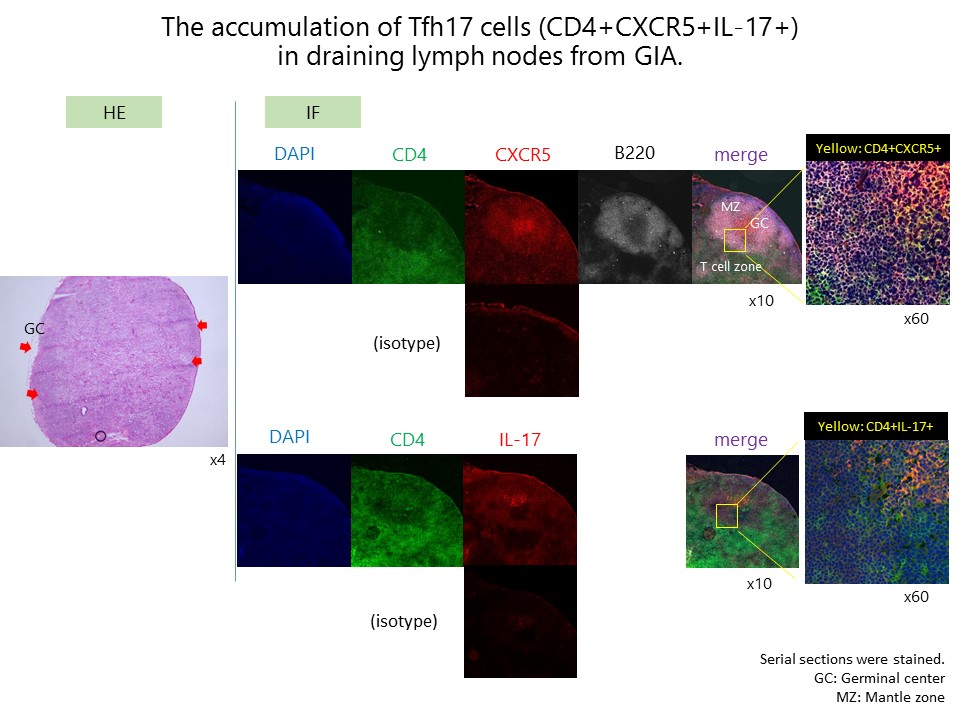
2) The localization of Tfh and the subsets were analyzed by IF staining of the draining lymph nodes.
3) Anti-GPI antibody titers of sera from GIA were measured by ELISA. To assess Tfh function, Tfh and plasmablasts from GIA were co-cultured and the antibody titers of the culture supernatant were also measured.
Results:
1) Tfh cell population was increased after the immunization of GPI. The increase was peaked on day 7, just at the onset of the arthritis, then gradually subsided. The subset analysis revealed the specific increase of IL-17 producing Tfh (Tfh17) at the same phase. The increased population of GC B cells was also observed through the course of arthritis. Its increase started on day 7 in response to Tfh, and peaked on day 14.
2) The IF staining showed that Tfh17 cells were accumulated in the T cell zone of GC and physically contacted with GC B cells in the draining lymph nodes of GIA (Figure).
3) Anti-GPI antibody was detected from day 7 in the sera from GIA, and the titers were gradually elevated over time. The titers of anti-GPI antibody in the culture supernatant were significantly increased compared with those from non-Tfh CD4+ cells and plasmablasts co-culture.
Conclusion:
Tfh, particularly Tfh17, might have a crucial role in the development of arthritis via B cell activation and anti-GPI antibody production in GIA. We are now elucidating the function of Tfh17 in the generation of GIA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kurata I, Matsumoto I, Osada A, Ebe H, Kawaguchi H, Kondo Y, Tsuboi H, Sumida T. The Role of Follicular Helper 17 T Cells in Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase Induced Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-follicular-helper-17-t-cells-in-glucose-6-phosphate-isomerase-induced-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-follicular-helper-17-t-cells-in-glucose-6-phosphate-isomerase-induced-arthritis/