Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are immune-mediated chronic inflammatory diseases. Synovial membrane is the initial site of inflammation in PsA and RA joints. This tissue can be used for diagnostic purposes since pathophysiological events occurring in the synovial are more likely than dispersed serum factors to reflect the clinical status and outcome in patients. Even though both tissues are morphologically similar, we hypothesize that there are differences in the molecular signature of the PsA and RA synovial membranes that can be employed for an accurate diagnosis of both pathologies. The purpose of this study is to create a new method for arthritic patient classification based on the spatially resolved molecular profiles detected by mass spectrometry imaging (MSI).
Methods:
Synovial membrane slices obtained from 10 PsA and 10 RA patients were analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-FT-ICR-MSI) to characterize the specific profile and distribution of metabolites. Images of differentially expressed metabolites were generated with FlexImaging 4.1 software. Principal component analysis (PCA) and discriminant analysis (DA) were used to look for the metabolites with the highest differences between PsA and RA synovial membranes. Annotation of the detected metabolites was performed by matching accurate mass with METLIN and Human Metabolome Databases.
Results:
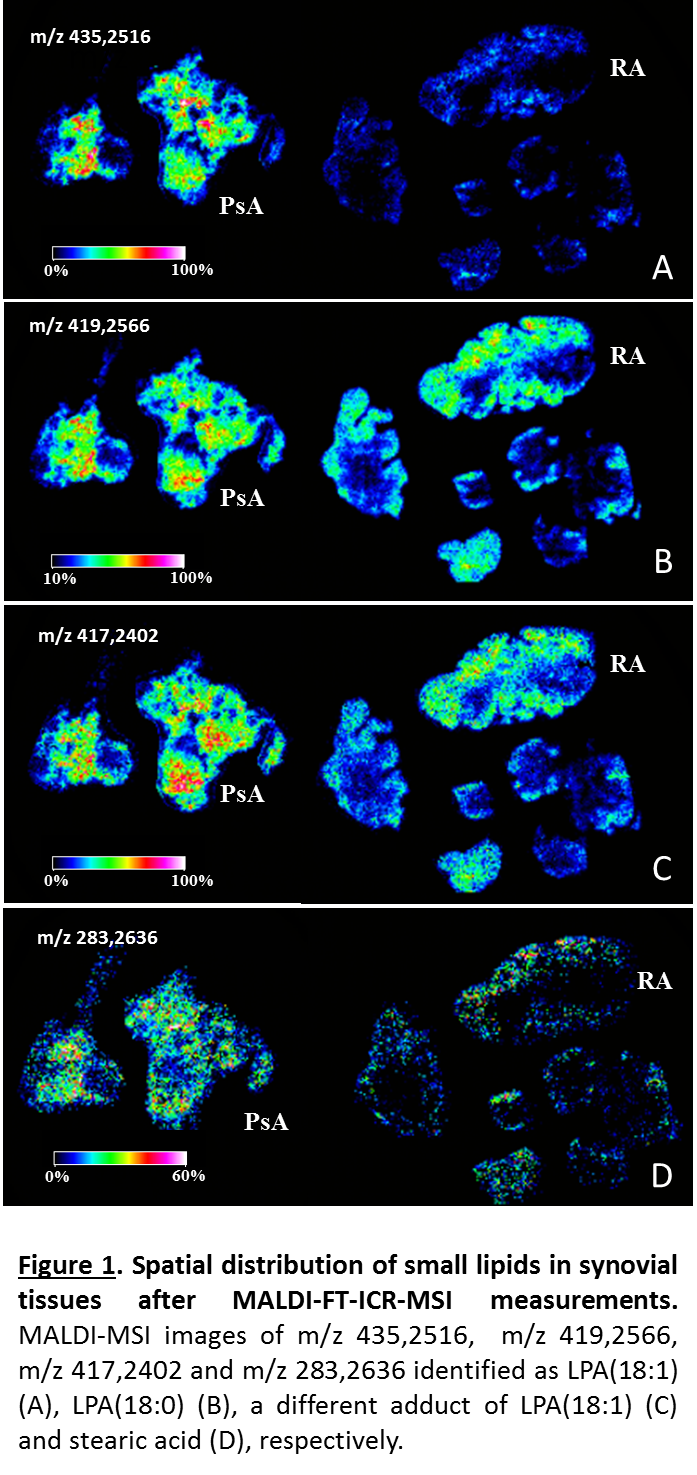
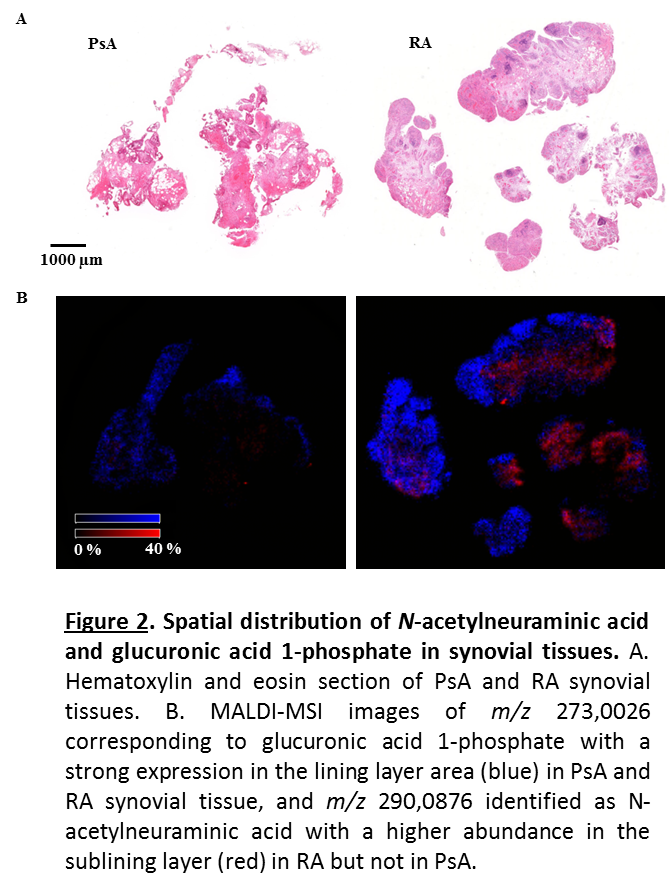
PsA and RA synovial membranes were discriminated based on their metabolic signature using discriminant analysis. Sugars including N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate (m/z 282,0276), glucuronic acid 1-phosphate (m/z 273,0026), N-acetylneuraminic acid (m/z 290,0876) and different small lipids were identified and localized. Fatty acids and lysophosphatidic acids (LPAs) showed a higher expression in PsA compared to RA (Figure 1). On the contrary, all sugars displayed a stronger intensity in RA synovial tissues when compared to PsA. N-acetylneuraminic acid showed a higher abundance in the synovial sublining layer whereas glucuronic acid 1-phosphate was specifically localized in the lining layer (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
We have localized and identified for the first time metabolites from human PSA and RA synovial membranes using MALDI-FT-ICR-MSI. Our results provide a fast and reliable classification of patients affected by PsA and RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rocha B, Cillero-Pastor B, Eijkel G, Huizing LR, Ruiz-Romero C, Cuervo A, Heeren RMA, Cañete JD, Blanco FJ. Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Synovium: A Novel Approach to Classify the Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mass-spectrometry-imaging-of-synovium-a-novel-approach-to-classify-the-rheumatoid-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mass-spectrometry-imaging-of-synovium-a-novel-approach-to-classify-the-rheumatoid-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/