Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Abatacept is a new class of biologic agent for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that inhibits T cell activation by binding to CD80/86. Although some clinicians feel that the rapidity of treatment response of abatacept is slower than that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitors, some patients can respond to abatacept treatment quite rapidly. Recently, some reports have been published regarding the positive association between sero-positivity for anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) and clinical efficacy of abatacept in RA patients. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the effect of double-seropositivity for ACPA and rheumatoid factor (RF) on the rapidity of treatment response of abatacept using data from a Japanese multicenter registry system for RA patients treated with biologic agents.
Methods: Participants were selected from the consecutive 508 RA patients treated with abatacept who were registered in the Tsurumai Biologics Communication Registry (TBCR). We excluded the patients with previous biologic agent treatment history since it has been already reported as an independent factor affecting the clinical efficacy of abatacept. A total of 146 biologics-naïve and ACPA positive patients with baseline data of RF were included in this study. We compared the proportion of patients that achieved good EULAR response at 24 weeks between the RF negative and RF positive (>20 U/ml) group within the ACPA positive patients. We defined the ACPA positive as >13.5 U/ml of anti-CCP antibody (3 times cutoff value) to ensure that the positivity was reasonably sure.
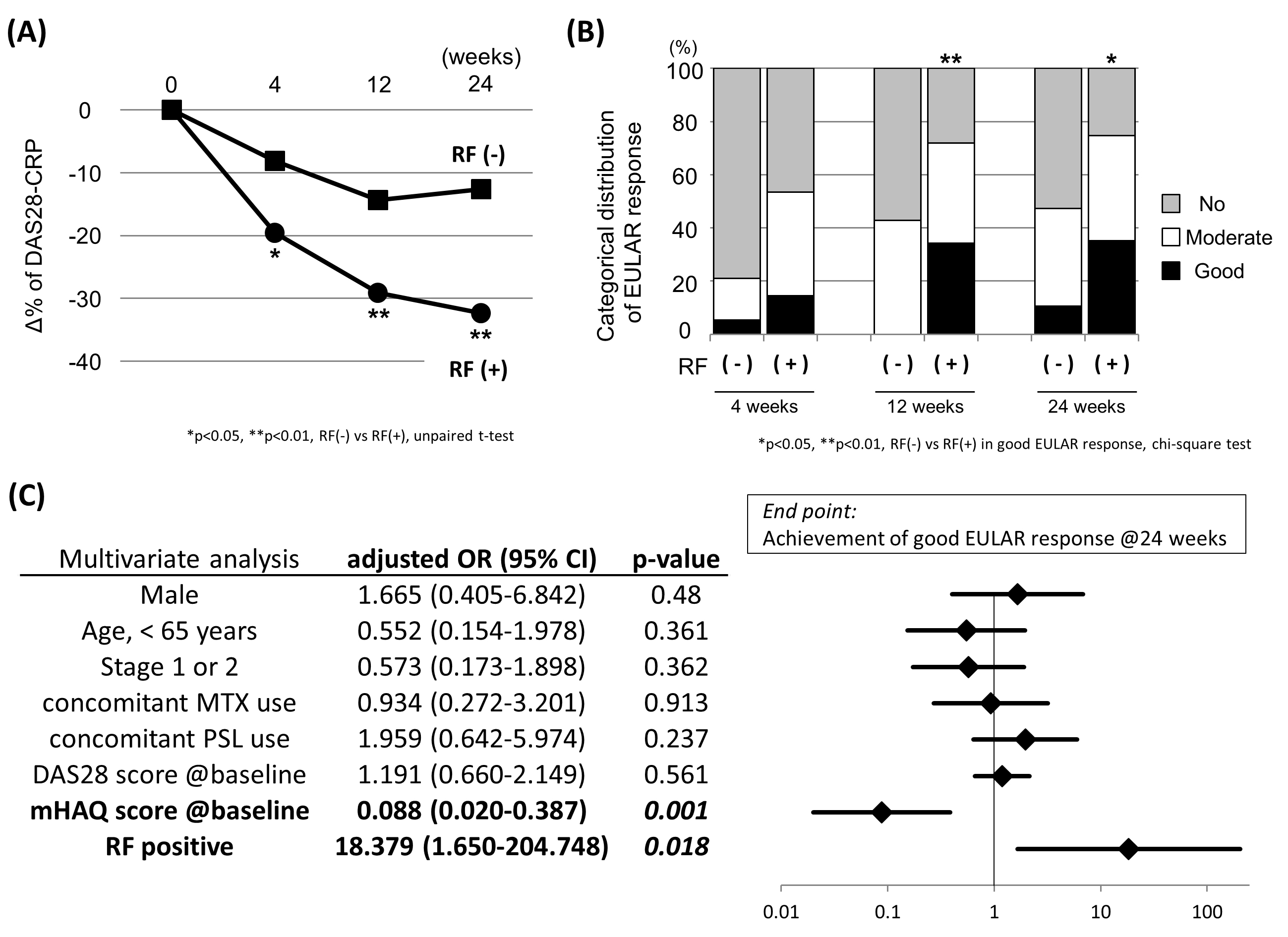
Results: In the ACPA positive patients, the percent decreasing of DAS28-CRP scores in the RF positive group were significantly greater than those in the RF negative group at all time points (Figure A, e.g. -32.3 vs -12.6% at 24 weeks, p < 0.01). The proportion of patients that achieved the good EULAR response was significantly higher in the RA positive group at 12 and 24 weeks (Figure B). Multivariate logistic regression analysis (adjusted with gender, age, Steinbrockerfs stage, concomitant MTX and oral steroid usage, and DAS28-CRP score at baseline) revealed that the RF positivity, along with the modified HAQ score at baseline, was the independent predictor for the achievement of good EULAR response at 24 weeks (Figure C).
Conclusion: We clearly demonstrated that the positive association of the double-seropositivity for ACPA and RF with the rapid and good clinical response for abatacept in the biologics-naïve RA patients. This new clinical evidence regarding the effect of double-seropositivity is the valuable real-world data for the prediction of clinical efficacy of abatacept in daily clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Takahashi N, Kojima T, Asai S, Ishiguro N. Sero-Positivity for Rheumatoid Factor Is an Independent Predictor for Achievement of Good EULAR Response at 24 Weeks in ACPA Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Abatacept: Results from Japanese Multicenter Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sero-positivity-for-rheumatoid-factor-is-an-independent-predictor-for-achievement-of-good-eular-response-at-24-weeks-in-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-abatacept-results-from/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sero-positivity-for-rheumatoid-factor-is-an-independent-predictor-for-achievement-of-good-eular-response-at-24-weeks-in-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-abatacept-results-from/