Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Greater disease severity, older age, positive serum rheumatoid factor (RF), and long-standing glucocorticoid usage contribute to increased mortality of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. This study aimed to analyze all-cause mortality through 2015 as related to 1974 baseline cohort entry demographic factors, 1995 clinical assessment of therapy response (Rxresp) of incident RA, and RF status pre- and post-onset of RA vs non-RA matched cohort control (CN) subjects.
Methods: All incident RA cases identified in 1995 from the 1974 community-based cohort (n=21,061 adults) satisfied 1987 revised ACR criteria. Cases (n=54) were matched (1 RA: 4CN) with 216 cohort CN subjects on age, gender, and race (Caucasian). All subjects (N=270) were regularly followed for survival. Two investigators independently determined causes of death (CODs) from the completed death certificate codes without knowledge of RA vs CN status. Baseline (1974) serum isotype-specific IgM and IgA RF assays were performed (TheraTest Laboratories, Chicago, IL) with coefficients of variation (CVs ±SE) of 16.0 (±2.1) and 20.2 (± 1.6), respectively. In 1995, RF status was also extracted from RA patients’ clinical records. Therapy response (Rxresp) categories (1= good, 2=fair, 3=limited) were assessed by the sole community rheumatologist. Cox regression models estimated hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause mortality through 2015, including covariates of 1974 demographic and baseline serological variables, 1995 Rxresp, and RF categories by 1974 and 1995 results (0=both negative, 1=only 1995 positive, 2=both 1974 and 1995 positive).
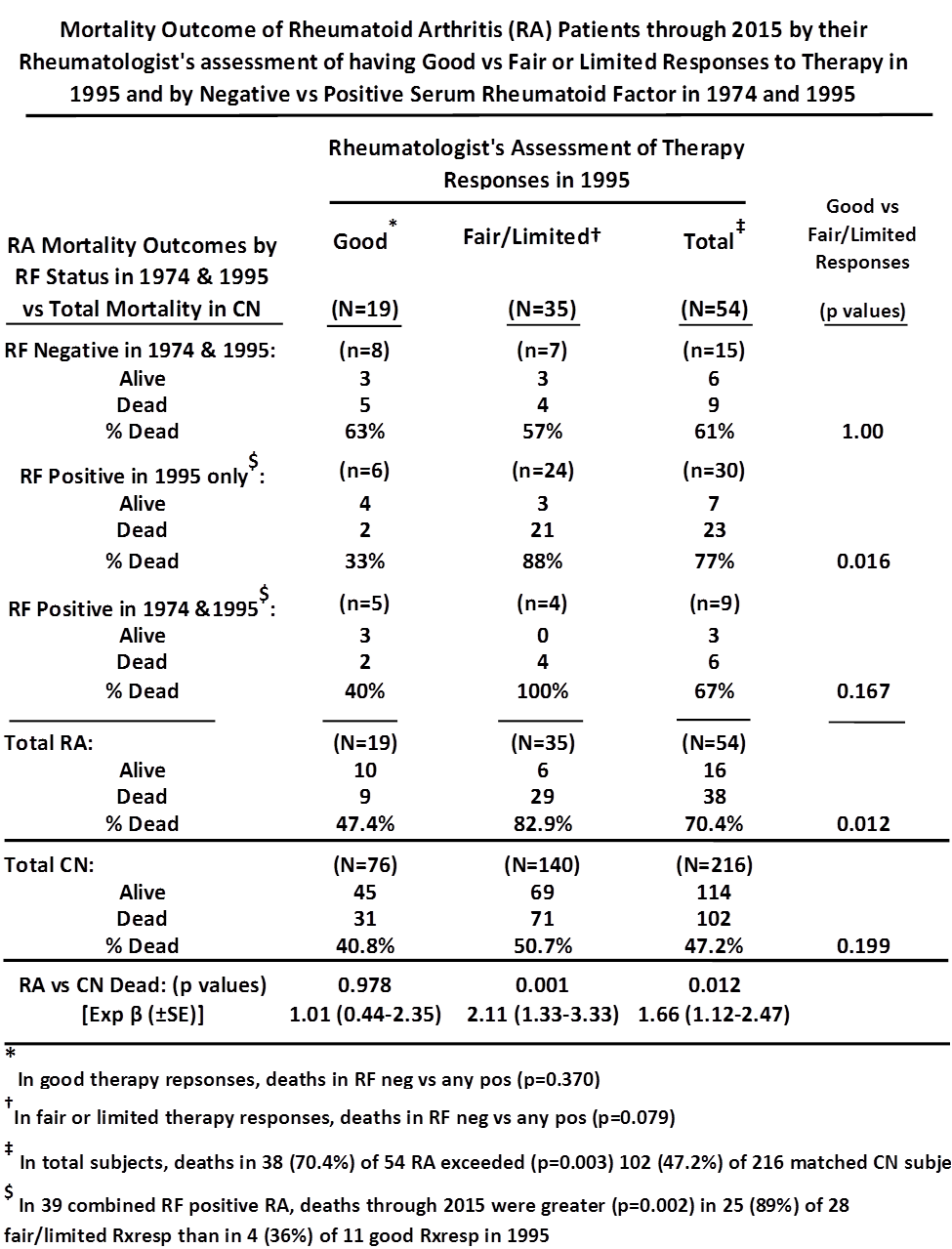
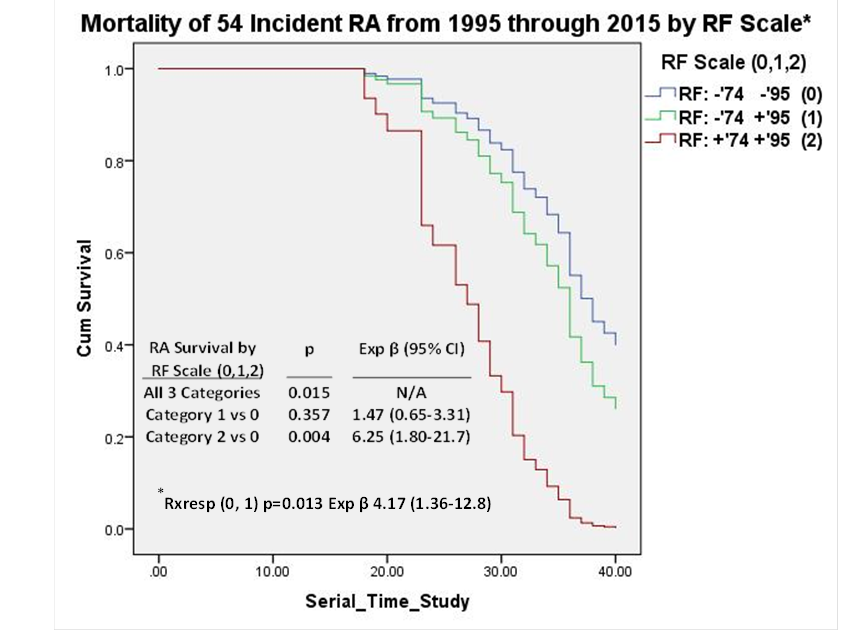
Results: The 38 (70.4%) deaths in 54 RA exceeded (p=0.003) the 102 (47.2%) in 216 matched CN (Table). The difference (p=0.012) persisted in Cox models (Exp β 1.66, 95% CIs 1.12-2.47), including covariates of cohort entry age deciles (p<0.001, Exp β 2.70, 95% CIs 2.19-3.33), years of completed education (p=0.010, Exp β 0.91, 95% CIs 0.85-0.98), and degree of cigarette smoking (p=0.048, Exp β 1.13, 95% CIs 1.00-1.28). In Cox models, 19 good Rxresp RA had similar (p=0.978) mortality to their 76 matched CN (Table). Mortality was strongly (p=0.001) increased in 35 fair/limited Rxresp RA vs 140 CN (Exp β 2.11, 95% CIs 1.33-3.33) (Table). The 35 fair/limited Rxresp RA had significantly (p=0.012) greater mortality (29, 82.9%) than the 19 good Rxresp RA (9, 47.4%) (Table). In 15 RF-negative RA cases in 1974 and 1995, the 8 good Rxresp had similar mortality (63%) to the 7 fair/limited Rxresp cases (57%) (p=1.00). In the 39 RF-positive cases, fair/limited Rxresp was a strong (p=0.002) predictor of mortality (Table, footnote). Mortality of RA cases was also predicted (p=0.015) by a scale of 1974 and 1995 RF status, particularly for 1974 and 1995 RF-positive cases (p=0.004, Exp β 6.25, 95% CI 1.80-21.7) (Figure). Fair/limited vs good Rxresp independently predicted (p=0.013) RA mortality in Cox model, including the RF scale (0,1,2) and demographic covariates (Fig).
Conclusion: Assessment in 1995 of fair/limited vs good Rxresp in RA patients predicted (p=0.012) greater mortality through 2015, particularly in RF-positive cases (p=0.002). Mortality was significantly (p=0.004) greater in 9 consistently RF-positive RA vs 15 consistently RF-negative cases. Interaction of Rxresp categories and RF status on RA mortality outcome deserves further research.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Masi AT, Rehman AA, Jorgenson L, Aldag JC. A Rheumatologist’s Assessment of Therapy Responses (Rxresp) and Rheumatoid Factor Status (neg/pos) in 1995 Predicted Mortality through 2015 in a Community-Based Cohort of Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis Cases and Matched Control Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-rheumatologists-assessment-of-therapy-responses-rxresp-and-rheumatoid-factor-status-negpos-in-1995-predicted-mortality-through-2015-in-a-community-based-cohort-of-incident-rheumatoid-a/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-rheumatologists-assessment-of-therapy-responses-rxresp-and-rheumatoid-factor-status-negpos-in-1995-predicted-mortality-through-2015-in-a-community-based-cohort-of-incident-rheumatoid-a/