Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) patients
with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) antibodies are at
increased risk of developing interstitial lung disease (ILD). The natural
history of ILD among this subset of DM patients is poorly characterized among
non-Asian populations. Skin disease studies in anti-MDA5 DM are largely
cross-sectional in nature. We sought to characterize the temporal trends in ILD
severity, cutaneous ulceration and calcinosis in anti-MDA5 DM patients.
Methods: We retrospectively
reviewed the charts of 25 anti-MDA5 DM patients seen between July 2004 and
September 2014.
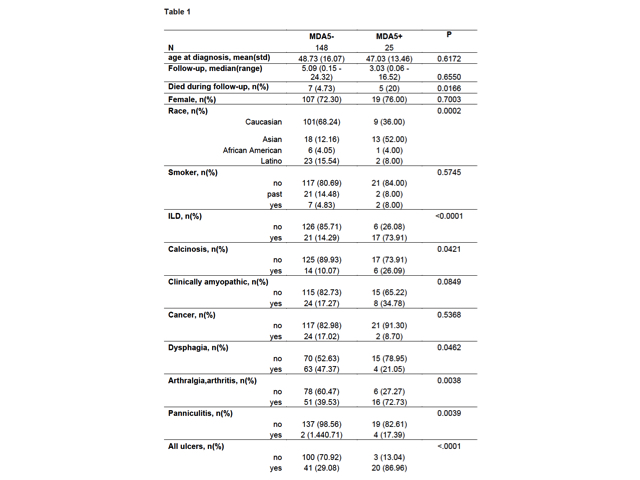
Results: Of the 25 anti-MDA5 DM
patients seen, 23 patients were assessed for evidence of ILD (Table 1). 17
patients (74%) had evidence of ILD corroborated by both pulmonary function
tests (diffusion capacity (DLCO) less than 75% predicted or forced vital
capacity (FVC) less than 80% predicted) and high-resolution chest computed
tomography scans. The median time to ILD development was 5 months, (range 0-71
months), with 89% of patients developing ILD within 9 months from symptom
onset.
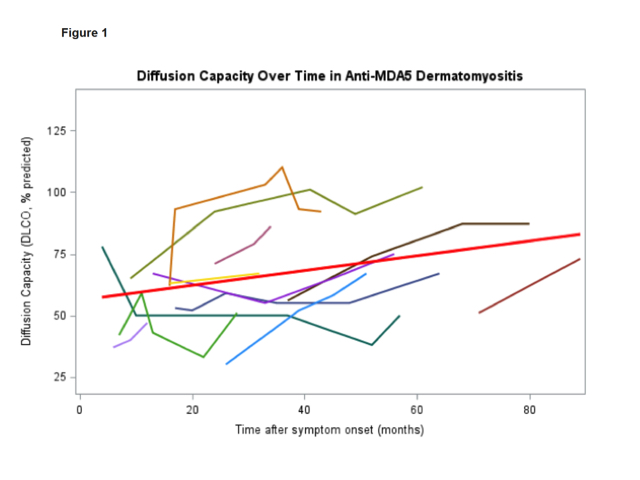
In the 12 patients with longitudinal data, we found a small, but
statistically significant increase in DLCO over time (Figure 1), 0.30% per
month (95% CI 0.02-0.58%, p=.036). All
12 patients with ILD received immunosuppressive therapy.
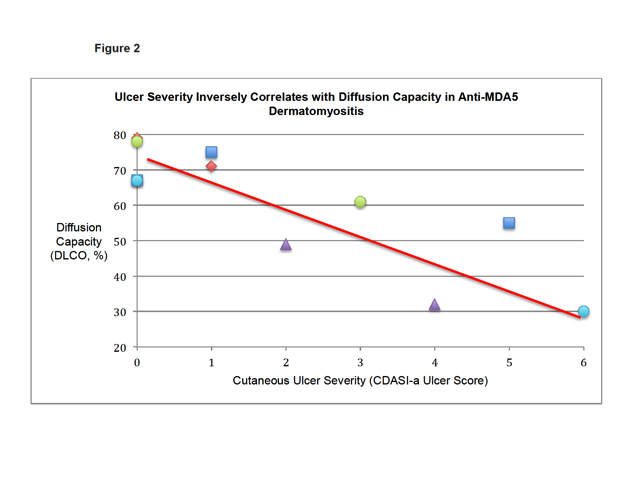
We found
a significant inverse relationship between DLCO and ulcer burden (p=0.006, Figure 2). The median times to onset of cutaneous
ulceration, ulcer healing and calcinosis were 6, 22 and 30 months,
respectively. Use of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil,
was associated with ulcer healing in 3 patients with recalcitrant cutaneous
ulceration.
The proportionate mortality was significantly greater in anti-MDA5
DM patients (5/25=20%) vs non-MDA5 DM patients (7/148=4.7%)
(p=.016).
Conclusion: In this cohort, 17 of 25
(74%) of anti-MDA5 DM patients developed ILD, most (89%) within 9 months of
symptom onset. The ILD severity as measured by DLCO may improve over time with
treatment. Among anti-MDA5 DM patients with ILD, the severity of their skin ulceration
appears to correlate with ILD severity. The classic mucocutaneous feature of
anti-MDA5 DM, cutaneous ulceration, appears during the onset of ILD but usually
resolves and is replaced by calcinosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lewis M, Li S, Chung L, Fiorentino D. Dermatomyositis Associated with Anti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene 5 Antibodies: A Longitudinal Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-associated-with-anti-melanoma-differentiation-associated-gene-5-antibodies-a-longitudinal-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-associated-with-anti-melanoma-differentiation-associated-gene-5-antibodies-a-longitudinal-analysis/