Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: B cell Biology and Targets in Rheumatolid Arthritis and other Autoimmune Disease Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Obinutuzumab (OBZ, a Type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody [mAb] with afucosylated Fc portion and enhanced affinity for Fcγ receptor III) is more efficient than Rituximab (RTX, a Type I mAb) at inducing malignant B cell cytotoxicity and is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Here we compared their effects against B cells from patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
Methods:
We used flow cytometry to perform: in vitro whole blood B cell depletion assays to compare the efficiency of OBZ and RTX in depleting target B cells; surface fluorescence-quenching assays to determine the extent of mAb internalization; complement dependent cellular cytotoxicity (CDC) assays to assess the ability to recruit complement and lyse target cells; NK cell degranulation assays to assess surface expression of CD107a as a measure of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC); and neutrophil activation assays assessing the surface expression of CD62L and CD11B. OBZ-gly (OBZ with Fc glycosylation similar to RTX) was used to assess the effects of afucosylation. All mAb were used at 1μg/mL except for the CDC assay (10μg/mL).
Results:
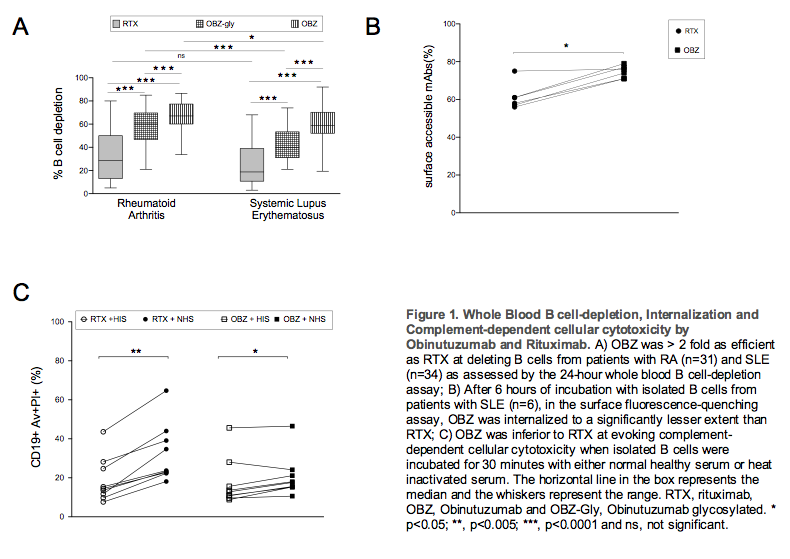
Obinutuzumab (OBZ) was > 2 fold more efficient than Rituximab (RTX) at inducing cytotoxicity in B cells from patients with RA (n=31) and SLE (n=34) in whole blood assays (Figure 1A). It was also internalized by isolated B cells from SLE patients (n=6) to a significantly lower extent than RTX with a median surface accessible mAb of 75% and 59%, respectively, after 6 hours of incubation (Figure 1B). OBZ was at least twice as efficient at inducing NK cell activation, Figure 2 in RA (n=13) and SLE (n=19); and also activated neutrophils more efficiently than RTX in SLE (n=15) (Figure 3). In contrast, RTX was significantly more efficient than OBZ at evoking CDC of isolated B cells (SLE, n=6) (Figure 1C).
Conclusion:
Obinutuzumab is more efficient than rituximab at inducing B cell cytotoxicity in vitro in both RA and SLE samples. Enhanced direct cell death, reduced CD20 internalization and superior FcR-mediated effector mechanisms are observed, while complement mediated cytotoxicity is reduced. These data provide a mechanistic basis for considering obinutuzumab as an alternative B cell depleting agent in RA and SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reddy V, Klein C, Isenberg DA, Cambridge G, Glennie M, Cragg M, Leandro MJ. Obinutuzumab Outperforms Rituximab at Inducing B-Cell Cytotoxicity in Vitro through Fc-Mediated Effector Mechanisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-outperforms-rituximab-at-inducing-b-cell-cytotoxicity-in-vitro-through-fc-mediated-effector-mechanisms-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-outperforms-rituximab-at-inducing-b-cell-cytotoxicity-in-vitro-through-fc-mediated-effector-mechanisms-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/