Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: B cell Biology and Targets in Rheumatolid Arthritis and other Autoimmune Disease Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : IgG4-associated cholangitis (IAC) and autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) are major manifestations of IgG4-related disease (IRD). Misdiagnosis and inadequate treatment are common since IAC and AIP mimic other inflammatory and malignant pancreatobiliary diseases and accurate diagnostic biomarkers are lacking. Moreover, relapse after tapering of immunosuppressive therapy is seen in 50% of patients, underscoring the need for biomarkers monitoring disease activity. Recently, using Next-Generation Sequencing, we found that dominant IgG4+ B-cell receptor clones in peripheral blood distinguish patients with active IAC/AIP from primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and pancreatobiliary malignancies (CA) [Hepatology 2013;57:2340]. Therefore, we aimed to develop a quantitative PCR (qPCR) protocol for diagnosing IAC/AIP and monitoring disease activity before and after treatment.
Methods : 15 patients with IAC and/or AIP according to HISORt criteria, 7 patients with PSC and 8 with CA formed the test cohort. Intra- and extramural replication cohorts consisted of 16 IAC/AIP, 5 PSC and 13 CA patients (Dutch cohort), and 8 IAC/AIP and 8 PSC patients (British cohort). From 20 Dutch IAC/AIP patients, follow-up samples after 4 and 8 weeks of corticosteroid therapy were available. RNA was isolated, and a forward primer amplifying all IgG subtypes, together with a generic reverse primer for all IgG subtypes and a specific reverse primer for IgG4 were used to amplify the constant region of the B-cell receptor. The ratio total IgG/IgG4 mRNA was calculated and expressed as ΔCT.
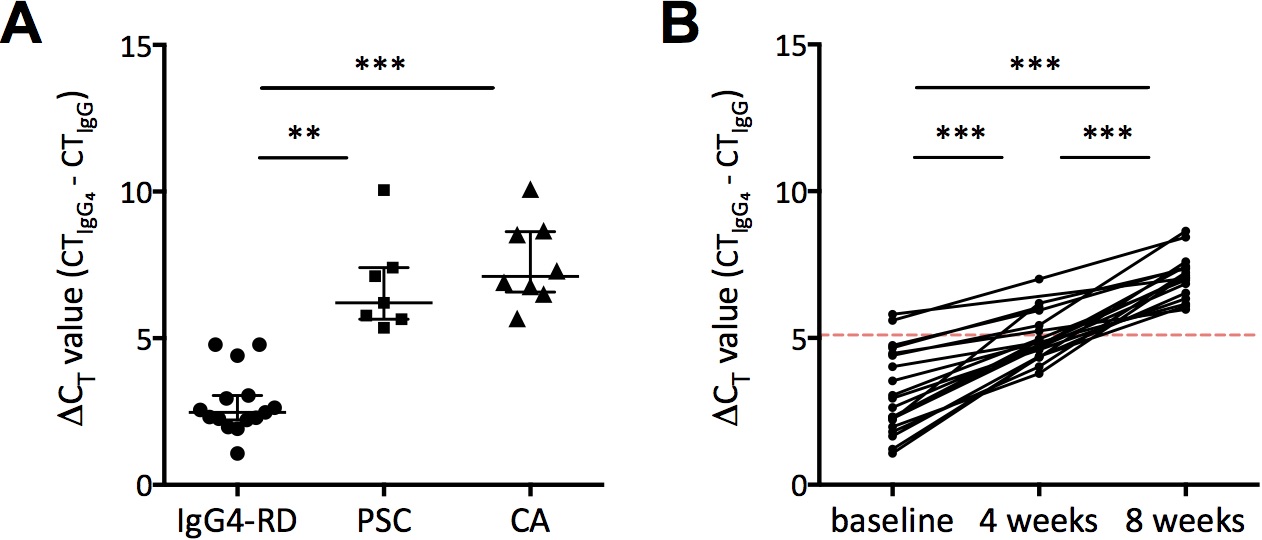
Results : ΔCT as measure of IgG/IgG4 mRNA expression in peripheral blood of the test cohort was 2.8±1.1 (mean+SD) in IAC/AIP patients, compared to 6.8±1.6 in PSC and 7.6±1.4 in CA (Figure 1A, p<0.0001). ROC analysis revealed a ΔCT cut-off value of 5.1 in the test cohort distinguishing all cases from controls. In the replication cohort sensitivity was 95% and specificity 100% (p=8.6*10-21). ΔCT increased after 4 weeks (5.1±0.8) and 8 weeks (7,1±0.7) of corticosteroid treatment, compared to pre-treatment (mean 3.1±1.4, p<0.0001, Figure 1B).
Conclusion : IgG4-related disease of the biliary tree and pancreas can accurately be distinguished from PSC or pancreatobiliary malignancies by ΔCT based on an affordable qPCR test. ΔCT can also be used as a marker for treatment response and disease activity in IgG4-related disease.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by grants from German and American PSC patient organizations (to UB).
Figure 1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hubers L, Doorenspleet M, Klarenbeek P, Culver E, Maillette de Buy Wenniger L, Chapman R, Van de Graaf S, Verheij J, Van Gulik T, Baas F, Barnes E, Beuers U, De Vries N. The IgG/IgG4 mRNA Ratio By Quantitative PCR Accurately Diagnoses IgG4-Related Disease and Predicts Treatment Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-iggigg4-mrna-ratio-by-quantitative-pcr-accurately-diagnoses-igg4-related-disease-and-predicts-treatment-response/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-iggigg4-mrna-ratio-by-quantitative-pcr-accurately-diagnoses-igg4-related-disease-and-predicts-treatment-response/